Student motivation drives engagement and enhances learning outcomes by fostering a sense of purpose and personal achievement. Effective strategies include setting clear goals, providing meaningful feedback, and creating an inspiring learning environment. Discover how to boost your classroom's motivation and unlock students' full potential in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
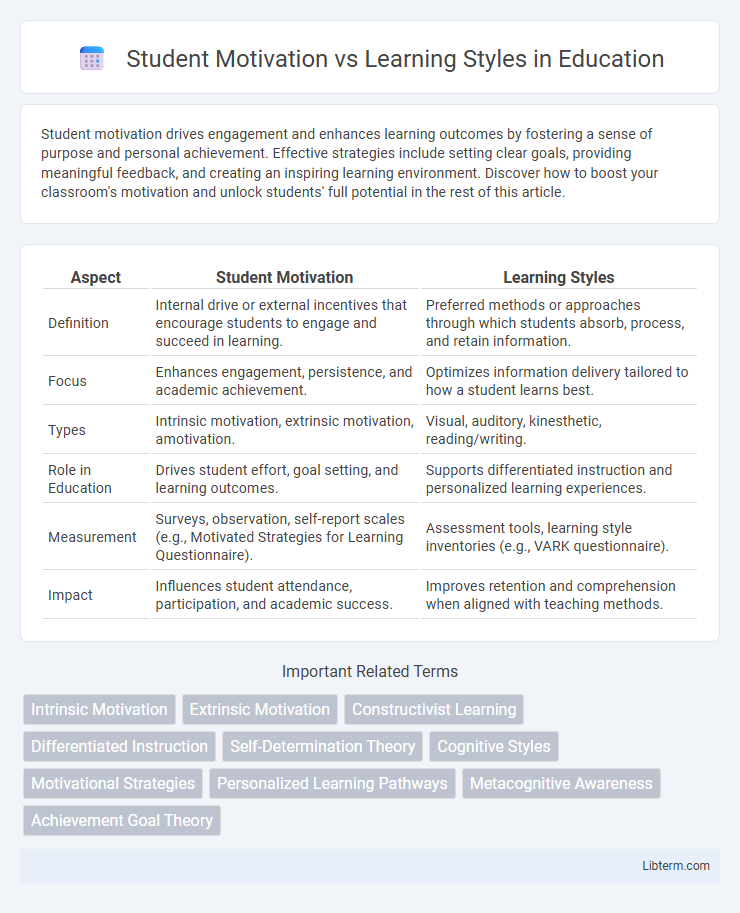
| Aspect | Student Motivation | Learning Styles |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal drive or external incentives that encourage students to engage and succeed in learning. | Preferred methods or approaches through which students absorb, process, and retain information. |
| Focus | Enhances engagement, persistence, and academic achievement. | Optimizes information delivery tailored to how a student learns best. |
| Types | Intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, amotivation. | Visual, auditory, kinesthetic, reading/writing. |
| Role in Education | Drives student effort, goal setting, and learning outcomes. | Supports differentiated instruction and personalized learning experiences. |
| Measurement | Surveys, observation, self-report scales (e.g., Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire). | Assessment tools, learning style inventories (e.g., VARK questionnaire). |
| Impact | Influences student attendance, participation, and academic success. | Improves retention and comprehension when aligned with teaching methods. |
Understanding Student Motivation in Education
Understanding student motivation in education involves recognizing intrinsic and extrinsic factors that drive engagement and achievement. Research highlights the impact of goal orientation, self-efficacy, and interest on learner persistence and academic performance. Tailoring teaching strategies to match motivational profiles enhances student participation and knowledge retention.
Defining Learning Styles: Myths and Realities
Defining learning styles often involves misconceptions that students learn best through a singular mode such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic, yet research shows this categorization lacks strong empirical support. True learning is influenced by a complex interplay of cognitive, emotional, and environmental factors rather than fixed stylistic preferences. Understanding these myths helps educators focus on varied teaching strategies that enhance motivation and accommodate diverse learning needs effectively.
The Relationship Between Motivation and Learning Styles
Motivation significantly influences how students engage with different learning styles, enhancing their ability to absorb and retain information. For instance, intrinsically motivated students often prefer active learning styles such as kinesthetic or collaborative methods, which foster deeper understanding and personal investment. Understanding the relationship between motivation and learning styles allows educators to tailor instructional strategies, maximizing student engagement and academic performance.
Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Motivation in the Classroom
Intrinsic motivation in the classroom drives students to engage deeply with material out of personal interest and curiosity, enhancing long-term retention and critical thinking skills. Extrinsic motivation, such as grades, rewards, or praise, can boost short-term performance but may undermine intrinsic interest if overemphasized. Balancing intrinsic and extrinsic motivators optimizes student engagement and adapts to diverse learning styles, fostering a more effective and personalized educational experience.
Assessing Diverse Learning Preferences
Assessing diverse learning preferences involves identifying how student motivation interacts with learning styles to enhance educational outcomes. Tailoring instructional strategies to match visual, auditory, and kinesthetic preferences boosts engagement and knowledge retention. Data-driven assessments enable educators to create personalized learning environments that foster intrinsic motivation and optimize academic performance.
Impact of Motivation on Academic Achievement
Student motivation significantly enhances academic achievement by fostering persistence, engagement, and deeper cognitive processing in learning activities. Intrinsic motivation, driven by personal interest and self-efficacy, correlates with higher grades and improved retention of information compared to extrinsic motivation alone. Understanding the impact of motivation surpasses the traditional emphasis on learning styles, highlighting that motivated students are more likely to adapt strategies and overcome challenges effectively.
Adapting Teaching Strategies for Varied Learners
Adapting teaching strategies to align with student motivation and learning styles enhances engagement and knowledge retention, catering to visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners. Incorporating diverse instructional methods such as multimedia presentations, interactive discussions, and hands-on activities addresses individual preferences and emotional drivers, fostering a more inclusive learning environment. Utilizing feedback and ongoing assessment helps educators tailor approaches dynamically, improving academic outcomes and student satisfaction.
Motivational Techniques for Different Learning Styles
Motivational techniques tailored to different learning styles enhance student engagement by aligning instructional methods with their preferred modes of information processing. Visual learners benefit from graphic organizers and colorful presentations, kinaesthetic learners thrive with hands-on activities and movement-based tasks, while auditory learners are motivated through discussions, storytelling, and verbal explanations. Incorporating these targeted strategies boosts intrinsic motivation and improves overall academic performance by addressing the unique needs of each learner type.
Challenges in Balancing Motivation and Learning Styles
Balancing student motivation with diverse learning styles presents challenges in maintaining engagement and effective knowledge retention across varied educational preferences. Educators must tailor instructional methods to accommodate visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners while sustaining intrinsic and extrinsic motivation to prevent disengagement. Misalignment between motivational strategies and learning styles often results in reduced academic performance and decreased student enthusiasm.
Best Practices for Enhancing Student Engagement
Implementing differentiated instruction tailored to diverse learning styles--visual, auditory, kinesthetic--boosts student motivation by aligning content delivery with individual preferences. Employing active learning techniques such as collaborative projects and interactive technology fosters higher engagement and deeper comprehension. Regular formative feedback and goal-setting encourage self-regulation and sustained motivation, enhancing overall academic achievement.
Student Motivation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com