Inquiry-Based Learning enhances critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics deeply. This method fosters curiosity and promotes active engagement, helping learners develop problem-solving skills essential for real-world challenges. Discover how Inquiry-Based Learning can transform Your educational experience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
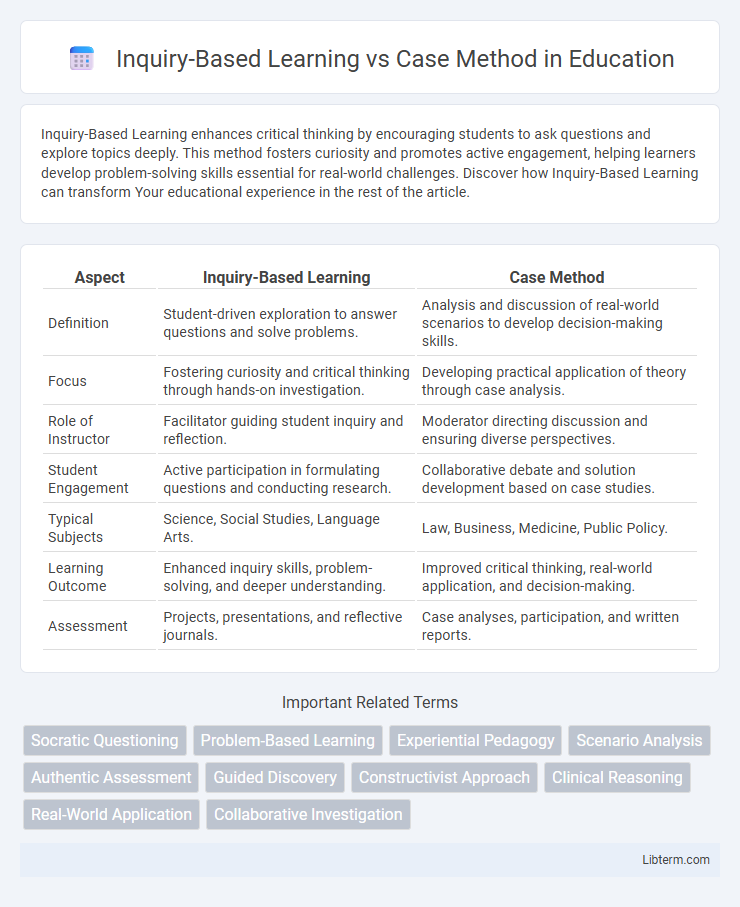
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Case Method |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven exploration to answer questions and solve problems. | Analysis and discussion of real-world scenarios to develop decision-making skills. |
| Focus | Fostering curiosity and critical thinking through hands-on investigation. | Developing practical application of theory through case analysis. |
| Role of Instructor | Facilitator guiding student inquiry and reflection. | Moderator directing discussion and ensuring diverse perspectives. |
| Student Engagement | Active participation in formulating questions and conducting research. | Collaborative debate and solution development based on case studies. |
| Typical Subjects | Science, Social Studies, Language Arts. | Law, Business, Medicine, Public Policy. |
| Learning Outcome | Enhanced inquiry skills, problem-solving, and deeper understanding. | Improved critical thinking, real-world application, and decision-making. |
| Assessment | Projects, presentations, and reflective journals. | Case analyses, participation, and written reports. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning and Case Method
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking, fostering deep understanding through questioning and investigation of real-world problems. The Case Method engages learners by analyzing complex, context-rich scenarios, encouraging application of theory to practical decision-making processes. Both methods enhance active learning but cater to different cognitive and pedagogical approaches, enriching educational experiences across disciplines.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven questioning, exploration, and discovery, fostering critical thinking and deep understanding through active investigation. It emphasizes the development of skills in formulating hypotheses, conducting research, and reflecting on findings, promoting ownership of learning. Unlike the Case Method, which analyzes predefined scenarios, Inquiry-Based Learning encourages learners to generate original inquiries and seek evidence-based solutions.
Fundamentals of the Case Method Approach
The Fundamentals of the Case Method Approach emphasize real-world problem-solving by presenting students with detailed scenarios requiring critical analysis and decision-making. This method fosters active learning through discussion, enabling learners to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. By simulating business or professional environments, it develops strategic thinking and communication skills essential for effective leadership.
Key Differences Between Inquiry-Based Learning and Case Method
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-led exploration and questioning to construct knowledge through active investigation. Case Method involves analyzing real-world scenarios to apply theoretical concepts and develop decision-making skills. The key difference lies in Inquiry-Based Learning fostering open-ended discovery, while Case Method emphasizes structured problem-solving based on provided cases.
Advantages of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to actively explore questions and problems. This method promotes student engagement and autonomy, enhancing knowledge retention through hands-on investigation and collaboration. Evidence shows that inquiry-based approaches improve problem-solving skills and adaptability in real-world scenarios compared to more structured case method learning.
Benefits of the Case Method
The Case Method enhances critical thinking by immersing students in real-world scenarios, promoting active problem-solving and decision-making skills. It provides practical insights by exposing learners to diverse business challenges, fostering deeper understanding of complex concepts. This approach also encourages collaborative learning, improving communication and teamwork essential for professional success.
Challenges of Implementing Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning faces challenges such as requiring significant instructor facilitation skills and extensive preparation time to design open-ended questions that promote critical thinking. Students often struggle with self-directed learning, leading to uneven participation and potential gaps in foundational knowledge. Unlike the structured Case Method, Inquiry-Based Learning demands continuous assessment and adaptation to maintain engagement and ensure learning objectives are met effectively.
Obstacles in Applying the Case Method
The primary obstacles in applying the Case Method include students' lack of prior knowledge and critical thinking skills, which hinder active participation and analysis. Instructors face challenges in selecting relevant, up-to-date cases that resonate with diverse learners and maintaining student engagement throughout discussions. Time constraints during class and the need for extensive preparation limit the method's adaptability in various educational settings.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and student-driven exploration by encouraging learners to ask questions and seek answers through investigation, ideal for developing research skills. The Case Method emphasizes practical application and analytical reasoning by examining real-world scenarios, making it effective for fields like business and law. Selecting the right approach depends on curriculum goals, student readiness, and desired skill development, ensuring alignment with educational objectives and classroom dynamics.
Future Trends in Experiential Learning Models
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking, fostering deep understanding through questioning and investigation. Case Method engages learners with real-world scenarios, enhancing decision-making and practical application skills essential for dynamic industries. Future trends in experiential learning models highlight hybrid approaches integrating AI-driven simulations and adaptive learning platforms to personalize inquiry and case analysis, accelerating skill development and knowledge retention.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com