Mind mapping is a powerful technique for organizing ideas visually, enhancing creativity, and improving memory retention. By connecting related concepts through branches, you can see the big picture while breaking down complex information into manageable parts. Explore the full article to discover practical tips on creating effective mind maps for your projects and studies.
Table of Comparison
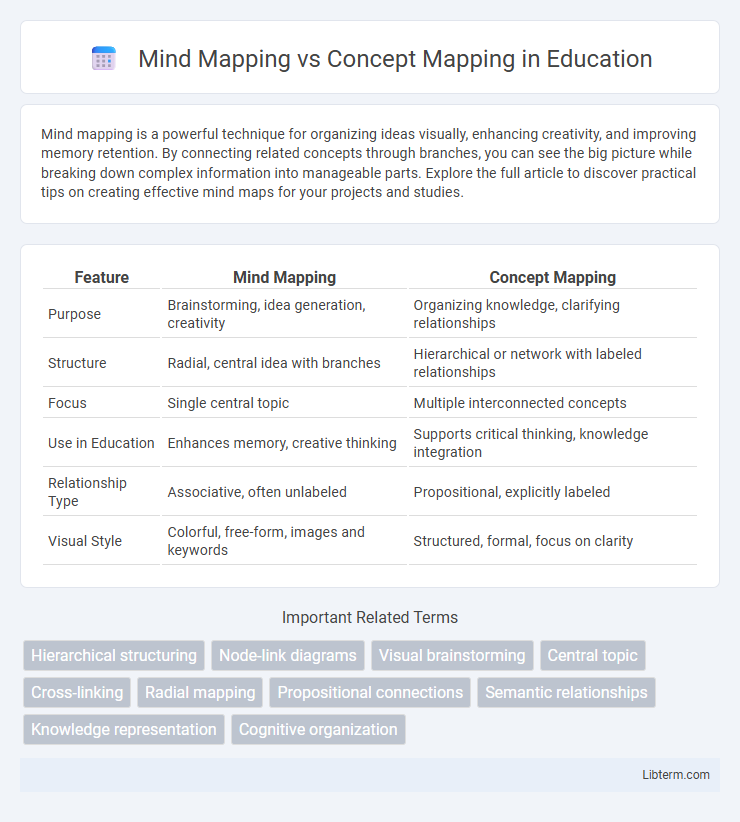
| Feature | Mind Mapping | Concept Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Brainstorming, idea generation, creativity | Organizing knowledge, clarifying relationships |
| Structure | Radial, central idea with branches | Hierarchical or network with labeled relationships |
| Focus | Single central topic | Multiple interconnected concepts |
| Use in Education | Enhances memory, creative thinking | Supports critical thinking, knowledge integration |
| Relationship Type | Associative, often unlabeled | Propositional, explicitly labeled |
| Visual Style | Colorful, free-form, images and keywords | Structured, formal, focus on clarity |
Introduction to Mind Mapping and Concept Mapping
Mind mapping organizes ideas around a central theme using branches that radiate outward, enabling intuitive visualization of relationships and hierarchical structure. Concept mapping connects concepts with labeled arrows to illustrate complex relationships and cross-links between multiple ideas, emphasizing precise semantic connections. Both techniques enhance learning and creativity but differ in their structural focus and application scope within cognitive frameworks.
Defining Mind Mapping: Key Features
Mind mapping is a visual tool that organizes information hierarchically around a central concept, using branches and keywords to represent relationships and ideas. Key features include a radial structure, use of colors and images to enhance memory and creativity, and emphasis on free association to foster brainstorming. This technique supports non-linear thinking, helping users capture complex ideas in an intuitive, easily navigable format.
Understanding Concept Mapping: Core Elements
Concept mapping centers on representing relationships between key concepts through nodes and labeled linking phrases, highlighting hierarchical and cross-linking structures that enhance knowledge integration. Core elements include concepts as labeled circles or boxes, propositional statements formed by connecting two concepts with a descriptive link, and an overall structure that reveals how ideas interrelate within a broader domain. This system emphasizes explicit connections and the organization of knowledge, supporting deep comprehension and critical thinking across various disciplines.
Visual Structure: Comparing Layouts
Mind mapping uses a radial layout where ideas branch out from a central concept, emphasizing the hierarchical relationship and facilitating quick brainstorming. Concept mapping employs a network or web-like structure connecting multiple concepts with labeled relationships, highlighting complex interconnections and fostering deeper understanding. The visual structure in mind mapping supports linear thinking, while concept mapping encourages multidimensional exploration of knowledge.
Purposes and Applications: When to Use Each
Mind mapping excels in brainstorming and organizing ideas visually, making it ideal for creative projects, note-taking, and problem-solving by emphasizing hierarchical relationships and free-form associations. Concept mapping is suited for illustrating complex relationships and knowledge structures, benefiting academic research, technical fields, and educational settings where clarity of connections between concepts is crucial. Use mind maps for idea generation and personal productivity, while concept maps enhance understanding, assessment, and communication of intricate subject matter.
Cognitive Benefits: Enhancing Learning and Creativity
Mind mapping enhances cognitive benefits by promoting hierarchical organization and visual clarity, which aids memory retention and idea generation. Concept mapping supports deeper understanding by illustrating relationships among complex concepts, encouraging critical thinking and knowledge integration. Both techniques stimulate creativity and learning efficiency through structured visualization of information.
Tools and Techniques: Digital vs Traditional Methods
Mind mapping tools like MindMeister and XMind offer intuitive, visually engaging interfaces for organizing ideas digitally, while traditional methods rely on hand-drawn diagrams and paper-based sketches for organic creativity. Concept mapping software such as CmapTools provides structured collaboration features and the ability to link complex relationships explicitly, contrasting with manual concept maps that emphasize tactile learning and freeform connections. Both digital and traditional techniques have unique benefits, with digital tools enhancing accessibility and sharing, and traditional methods fostering deeper cognitive processing through physical interaction.
Strengths and Limitations of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping excels in enhancing creativity and visualizing ideas through a central theme with radiating branches, making it ideal for brainstorming and note-taking. Its limitations include potential oversimplification of complex topics and difficulty in representing hierarchical relationships clearly. Mind maps are less effective for analytical tasks that require detailed connections and structured organization compared to concept maps.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Concept Mapping
Concept mapping offers clear visualization of complex relationships through hierarchical structuring, enhancing knowledge integration and critical thinking skills. Its main drawbacks include potential cognitive overload due to intricate links and the time-intensive process required to construct detailed maps. Despite this, concept mapping effectively supports collaborative learning and problem-solving by revealing connections that traditional linear notes may overlook.
Choosing the Right Mapping Technique for Your Needs
Mind mapping excels at brainstorming and organizing ideas around a central concept using radial branches, making it ideal for creative projects and individual note-taking. Concept mapping emphasizes relationships between ideas through labeled connections, which suits complex problem-solving and collaborative learning environments. Selecting the right technique depends on whether you need a flexible, free-flowing structure or a detailed, interconnected representation of knowledge.
Mind Mapping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com