Original credit practices play a crucial role in establishing trust between lenders and borrowers while ensuring transparent financial transactions. Understanding how original credit impacts your financial reputation and borrowing power can help you make informed decisions. Explore this article to discover the importance of original credit and how it affects your financial future.
Table of Comparison
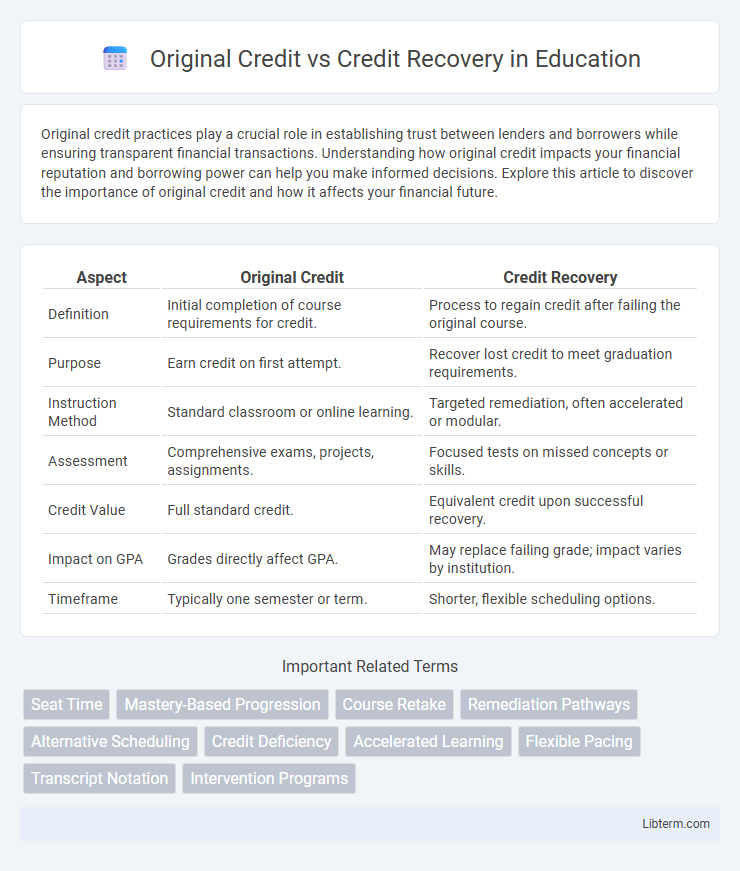
| Aspect | Original Credit | Credit Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initial completion of course requirements for credit. | Process to regain credit after failing the original course. |
| Purpose | Earn credit on first attempt. | Recover lost credit to meet graduation requirements. |
| Instruction Method | Standard classroom or online learning. | Targeted remediation, often accelerated or modular. |
| Assessment | Comprehensive exams, projects, assignments. | Focused tests on missed concepts or skills. |
| Credit Value | Full standard credit. | Equivalent credit upon successful recovery. |
| Impact on GPA | Grades directly affect GPA. | May replace failing grade; impact varies by institution. |
| Timeframe | Typically one semester or term. | Shorter, flexible scheduling options. |
Understanding Original Credit
Original credit refers to the initial score assigned to a financial transaction or loan based on its inherent creditworthiness, reflecting the borrower's credit risk at the time of issuance. It serves as the baseline metric for assessing future credit performance, unaffected by any subsequent modifications or recoveries. Understanding original credit is crucial for lenders to evaluate risk accurately and establish appropriate terms before credit recovery or adjustments occur.
Defining Credit Recovery
Credit Recovery is an educational process that allows students to retake courses or earn credits for previously failed classes, enabling them to stay on track for graduation without repeating entire semesters. Original Credit refers to the initial credit earned when a student successfully completes a course for the first time. Credit Recovery programs utilize targeted instruction and assessments to help students demonstrate mastery of course content efficiently, differentiating them from Original Credit pathways which involve traditional course progression.
Key Differences Between Original Credit and Credit Recovery
Original credit refers to the initial earning of academic credit through first-time course completion, reflecting a student's mastery of new material. Credit recovery allows students to retake courses or complete assignments to earn credit for previously failed classes, enabling them to stay on track for graduation. The key differences lie in the timing and purpose: original credit emphasizes new learning achievements, while credit recovery focuses on remediation and credit restoration.
Purpose and Objectives of Original Credit
Original Credit is designed to provide new learning opportunities, aiming to assess a student's mastery of course content for the first time and award academic credit upon successful completion. The purpose centers on ensuring students gain foundational knowledge and skills aligned with curriculum standards, fostering genuine comprehension and competency. Objectives include promoting academic integrity by evaluating initial understanding and supporting progression within a structured educational pathway.
Goals and Benefits of Credit Recovery
Credit Recovery aims to help students regain academic credit for courses they previously failed, enabling them to stay on track for graduation without repeating entire semesters. This process offers personalized, flexible learning opportunities that address individual student needs, improving engagement and retention rates. The main benefit lies in accelerating student progress and reducing dropout rates by providing targeted support tailored to each learner's pace and style.
Eligibility Criteria for Each Program
Original Credit programs require students to be enrolled in a course for the first time, meeting age and grade-level requirements set by the school district or state education department, often designed for regular progression towards graduation. Credit Recovery programs target students who have previously failed or earned incomplete credits, with eligibility typically limited to those needing to improve their grades or complete missing coursework to meet minimum graduation requirements. Both programs prioritize student enrollment status and academic history, ensuring targeted support aligns with individual credit attainment goals.
Instructional Methods: Original Credit vs Credit Recovery
Original Credit instructional methods emphasize in-depth, comprehensive learning experiences tailored to new content acquisition, incorporating interactive lectures, hands-on activities, and formative assessments to build foundational knowledge. Credit Recovery, in contrast, employs targeted, streamlined instructional strategies designed to address specific learning gaps quickly, often utilizing adaptive technology, focused remediation, and modular lessons to efficiently restore academic credit. Both approaches prioritize student engagement but differ significantly in pacing, content depth, and method complexity to meet distinct educational goals.
Impact on Student Academic Records
Original credit earned through initial course completion typically carries a stronger impact on student academic records, signaling proficiency and timely mastery of subject matter. Credit recovery allows students to retake failed courses, providing an opportunity to improve grades and maintain progression but may be flagged differently on transcripts, potentially affecting GPA calculations and college admissions evaluations. Understanding distinctions in how schools report original credit versus credit recovery is crucial for students aiming to optimize academic standing and future educational opportunities.
Effectiveness in Supporting Student Success
Original credit courses provide foundational learning by introducing new content, crucial for building essential skills and knowledge that support long-term academic success. Credit recovery programs focus on helping students regain lost credits efficiently, addressing credit deficiencies to keep students on track for graduation. Research shows a combined approach enhances student outcomes by ensuring mastery of material while facilitating timely progression through academic requirements.
Choosing the Right Option for Student Needs
Selecting between Original Credit and Credit Recovery depends on the student's academic goals and learning pace, with Original Credit designed for new content mastery and Credit Recovery focused on retaking failed courses. Analyze the student's understanding of foundational concepts and motivation to determine if a comprehensive curriculum or targeted remediation suits their needs. Schools should consider course rigor, credit requirements, and personalized support when choosing the right option to maximize student success and graduation outcomes.
Original Credit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com