Standardization ensures consistency and quality across products and services by establishing clear guidelines and specifications. It streamlines processes, reduces costs, and enhances compatibility and safety in various industries. Explore the rest of the article to understand how standardization can benefit your business and daily life.
Table of Comparison
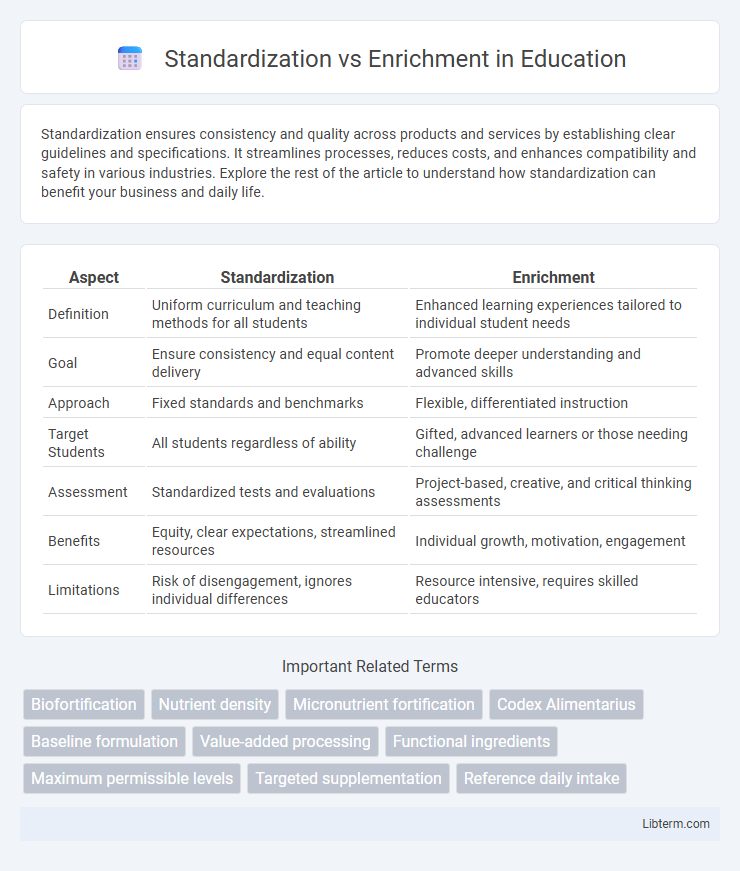
| Aspect | Standardization | Enrichment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniform curriculum and teaching methods for all students | Enhanced learning experiences tailored to individual student needs |
| Goal | Ensure consistency and equal content delivery | Promote deeper understanding and advanced skills |
| Approach | Fixed standards and benchmarks | Flexible, differentiated instruction |
| Target Students | All students regardless of ability | Gifted, advanced learners or those needing challenge |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and evaluations | Project-based, creative, and critical thinking assessments |
| Benefits | Equity, clear expectations, streamlined resources | Individual growth, motivation, engagement |
| Limitations | Risk of disengagement, ignores individual differences | Resource intensive, requires skilled educators |
Understanding Standardization and Enrichment
Standardization involves transforming diverse data formats into a consistent structure, enabling uniform interpretation and integration across systems. Enrichment enhances datasets by adding valuable information from external sources, improving data depth and usability. Both processes are crucial for effective data management, with standardization ensuring compatibility and enrichment providing contextual relevance.
Core Principles of Standardization
Core principles of standardization emphasize consistency, interoperability, and quality control across processes and data formats. Standardization aims to establish uniform protocols to reduce variability and enhance efficiency within industries, enabling seamless integration and communication. By creating clear guidelines and benchmarks, organizations ensure reliable outputs and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Key Concepts of Enrichment
Enrichment involves enhancing data quality by adding valuable information such as demographic details, geographic metadata, and behavioral insights to existing datasets. This process improves data usability and accuracy, facilitating better decision-making and personalized customer experiences. Unlike standardization, which focuses on uniform formatting, enrichment emphasizes augmenting data with context and relevance for deeper analysis.
Benefits of Standardization
Standardization improves data consistency by applying uniform formats, enhancing accuracy across datasets and reducing errors in data processing. It streamlines integration efforts, enabling seamless interoperability between diverse systems and facilitating efficient data exchange. Standardized data supports better decision-making by providing reliable, comparable information that drives analytics and reporting accuracy.
Advantages of Enrichment
Enrichment enhances data by adding valuable context and insights, enabling more accurate analysis and better decision-making. It improves data quality by integrating diverse sources, leading to richer profiles and deeper customer understanding. Enrichment also boosts personalization and targeting capabilities, increasing marketing effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations of Standardization
Standardization of data presents challenges such as limited flexibility in handling diverse formats, which can lead to loss of nuanced information essential for specific use cases. Strict adherence to standardized protocols often results in slow adaptation to emerging data types and evolving industry requirements. Furthermore, enforcing uniform standards across disparate systems poses integration difficulties, increasing the risk of inconsistent data interpretation.
Drawbacks and Risks of Enrichment
Enrichment can introduce data inaccuracies by integrating external sources with inconsistent or outdated information, leading to potential misinformation and decision errors. It also increases the risk of data privacy violations if sensitive information is improperly combined or exposed during the enrichment process. Furthermore, enrichment often demands significant computational resources, raising costs and complicating data management workflows compared to standardized, internally consistent datasets.
Applications Across Industries
Standardization streamlines data formats and processes to ensure consistency across platforms, essential for industries like finance and healthcare where regulatory compliance is critical. Enrichment enhances raw data by integrating additional context or insights, proving valuable in marketing and retail for personalized customer experiences. Combining standardization with enrichment drives operational efficiency and informed decision-making across manufacturing, logistics, and technology sectors.
Standardization vs Enrichment: A Comparative Analysis
Standardization ensures data uniformity by enforcing consistent formats and rules, which simplifies data integration and improves accuracy across systems. Enrichment enhances data value by appending additional information from external or internal sources, increasing context and insights for better decision-making. Comparing these processes reveals standardization as foundational for reliable data processing, while enrichment drives deeper analytics and comprehensive understanding.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Choosing the right approach between standardization and enrichment depends on the specific data quality goals and business requirements. Standardization enhances data consistency by formatting and aligning data to accepted norms, while enrichment adds valuable external information to improve data depth and context. Evaluating the balance between maintaining uniform data and amplifying its informational value helps organizations optimize decision-making and operational efficiency.
Standardization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com