Project-based learning enhances critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in hands-on projects that connect theory to practice. This approach promotes collaboration, creativity, and deeper understanding of subject matter through active participation. Explore the full article to discover how project-based learning can transform your educational experience and boost engagement.
Table of Comparison
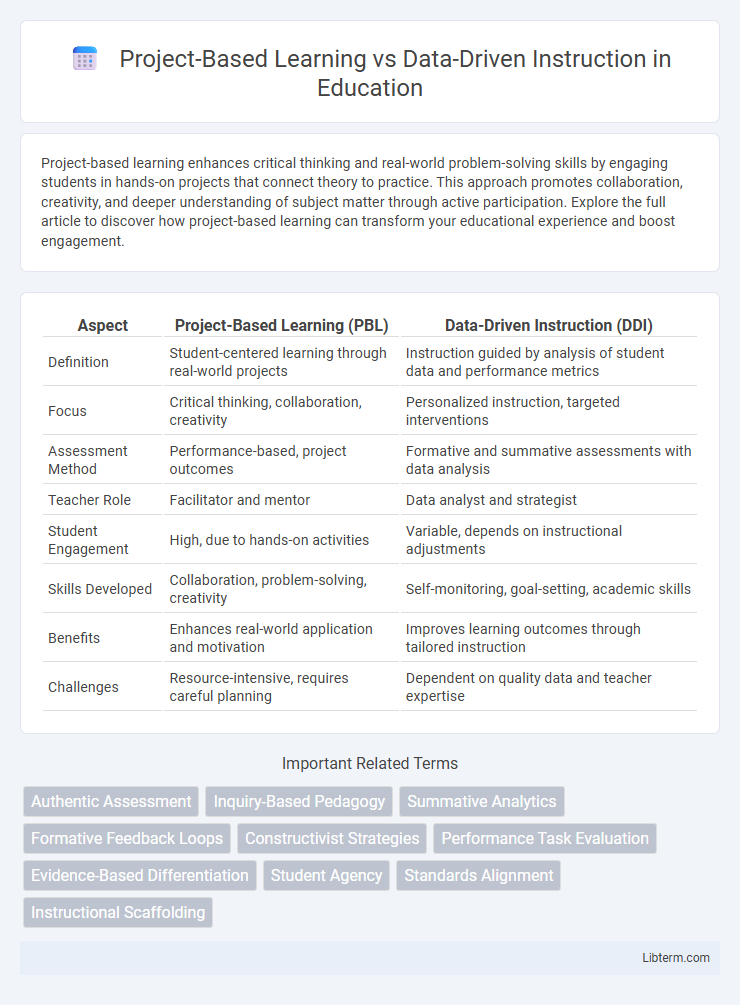
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Data-Driven Instruction (DDI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered learning through real-world projects | Instruction guided by analysis of student data and performance metrics |
| Focus | Critical thinking, collaboration, creativity | Personalized instruction, targeted interventions |
| Assessment Method | Performance-based, project outcomes | Formative and summative assessments with data analysis |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and mentor | Data analyst and strategist |
| Student Engagement | High, due to hands-on activities | Variable, depends on instructional adjustments |
| Skills Developed | Collaboration, problem-solving, creativity | Self-monitoring, goal-setting, academic skills |
| Benefits | Enhances real-world application and motivation | Improves learning outcomes through tailored instruction |
| Challenges | Resource-intensive, requires careful planning | Dependent on quality data and teacher expertise |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning (PBL)
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional approach emphasizing student engagement through real-world problems, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity. In PBL, learners actively explore complex questions or challenges over extended periods, resulting in tangible outcomes or presentations. This method contrasts with traditional instruction by centering learning experiences on hands-on projects that integrate interdisciplinary knowledge and skills.
Defining Data-Driven Instruction (DDI)
Data-Driven Instruction (DDI) involves using empirical data from student assessments, attendance, and behavior to tailor teaching strategies and enhance learning outcomes. This approach leverages quantitative analysis to identify student strengths and weaknesses, informing targeted interventions and continuous improvement in instructional practices. Unlike Project-Based Learning (PBL), which emphasizes hands-on exploration and real-world problem-solving, DDI prioritizes evidence-based decision-making to optimize educational effectiveness.
Core Principles of PBL and DDI
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes student-centered inquiry, real-world problem solving, and collaborative exploration to foster deep understanding and critical thinking skills. Data-Driven Instruction (DDI) relies on continuous assessment and analysis of student performance data to tailor teaching strategies and improve academic outcomes effectively. The core principles of PBL involve authentic projects and active student engagement, while DDI focuses on evidence-based decision making and targeted intervention.
Benefits of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning enhances critical thinking and collaboration skills by engaging students in real-world problem-solving tasks that promote deeper understanding. It fosters creativity and motivation through hands-on projects that connect academic content to practical applications. This approach also improves retention and helps develop communication and teamwork abilities essential for future careers.
Advantages of Data-Driven Instruction
Data-driven instruction leverages real-time student data to tailor teaching strategies, enhancing personalized learning and improving academic outcomes. This approach enables educators to identify learning gaps promptly, facilitating targeted interventions that boost student performance. By continuously analyzing assessment results, data-driven instruction promotes accountability and informed decision-making in educational settings.
Challenges Faced in PBL and DDI
Project-Based Learning (PBL) faces challenges such as ensuring consistent assessment metrics, managing diverse student collaboration dynamics, and aligning projects with standardized curriculum requirements. Data-Driven Instruction (DDI) struggles with data accuracy, timely analysis, and effectively translating data insights into personalized teaching strategies. Both approaches demand significant professional development and resource allocation to overcome implementation barriers and maximize educational outcomes.
Comparing Student Engagement in PBL vs DDI
Project-Based Learning (PBL) significantly boosts student engagement by immersing learners in hands-on, real-world problems that foster collaboration, creativity, and critical thinking. In contrast, Data-Driven Instruction (DDI) uses assessment data to tailor teaching strategies, which improves engagement by addressing individual learning gaps but may lack the sustained immersive experience of PBL. Studies indicate that PBL promotes deeper intrinsic motivation and sustained engagement, while DDI provides timely, targeted support that enhances engagement through personalized feedback and goal setting.
Impact on Academic Achievement
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances academic achievement by promoting critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills, resulting in deeper understanding and retention of subject matter. Data-Driven Instruction (DDI) uses assessment data to tailor teaching strategies, allowing for targeted interventions that address individual student needs and improve learning outcomes. Combining PBL with DDI can maximize academic growth by aligning engaging projects with personalized, data-informed instruction.
Integrating PBL and DDI in the Classroom
Integrating Project-Based Learning (PBL) and Data-Driven Instruction (DDI) in the classroom enhances student engagement and academic achievement by aligning hands-on projects with targeted learning goals informed by real-time data analysis. Educators use assessment metrics and formative data to tailor project scopes, ensuring that student-driven inquiry addresses specific skill gaps and learning standards. This synergy promotes personalized learning paths and fosters critical thinking while continuously monitoring progress to adapt instructional strategies effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your School
Selecting the ideal instructional approach requires evaluating your school's goals, resources, and student needs. Project-Based Learning (PBL) fosters critical thinking and collaboration through hands-on experiences, ideal for schools emphasizing creativity and real-world skills. Data-Driven Instruction leverages analytics to personalize learning and improve academic performance, making it suitable for institutions prioritizing measurable outcomes and continuous assessment.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com