Detention is a disciplinary measure used in schools to address rule violations and encourage better behavior. It can involve staying after school or during breaks, providing time for reflection and accountability. Learn more about how detention impacts student discipline and ways to handle it effectively in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
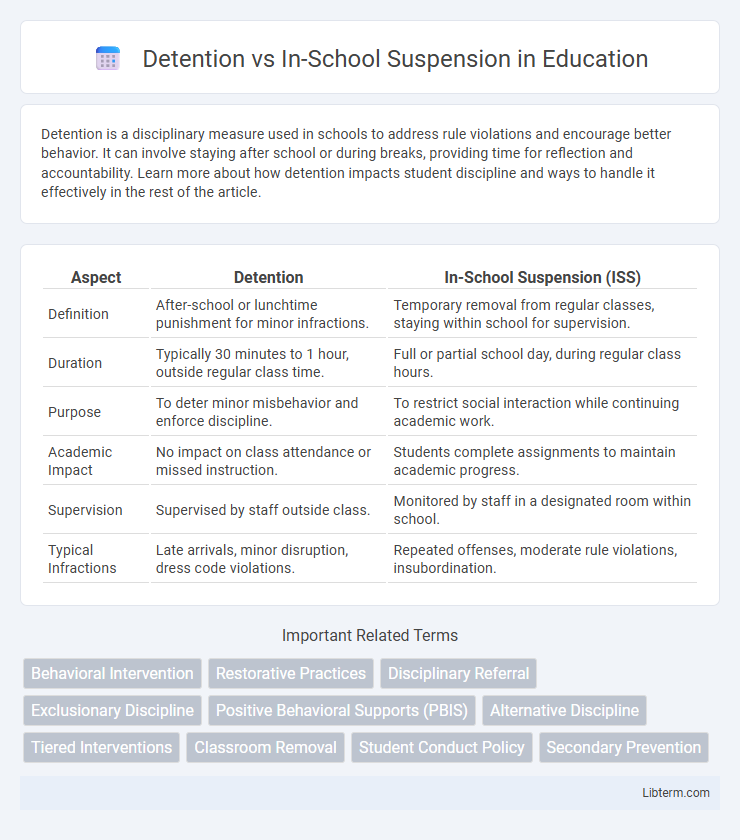
| Aspect | Detention | In-School Suspension (ISS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | After-school or lunchtime punishment for minor infractions. | Temporary removal from regular classes, staying within school for supervision. |
| Duration | Typically 30 minutes to 1 hour, outside regular class time. | Full or partial school day, during regular class hours. |
| Purpose | To deter minor misbehavior and enforce discipline. | To restrict social interaction while continuing academic work. |
| Academic Impact | No impact on class attendance or missed instruction. | Students complete assignments to maintain academic progress. |
| Supervision | Supervised by staff outside class. | Monitored by staff in a designated room within school. |
| Typical Infractions | Late arrivals, minor disruption, dress code violations. | Repeated offenses, moderate rule violations, insubordination. |
Understanding Detention and In-School Suspension
Detention involves students staying after school or during lunch to complete assignments or reflect on behavior, often serving as a mild disciplinary action. In-School Suspension (ISS) requires students to attend a separate, supervised classroom within the school, allowing them to continue their studies while being removed from the regular classroom environment. Both methods aim to address behavioral issues while minimizing academic disruption, but ISS typically involves more structured supervision and time away from peers.
Key Differences Between Detention and In-School Suspension
Detention typically requires students to remain after school or during free periods as a disciplinary consequence, whereas in-school suspension involves isolating students within the school environment for a designated time while they continue academic work. Detention usually lasts for a shorter duration, often an hour or less, while in-school suspension can span one or more full school days. Both serve to address behavioral issues, but in-school suspension removes students from the classroom environment more extensively, impacting their daily academic routine more significantly than detention.
Objectives of Detention in School Discipline
Detention serves as a disciplinary measure aimed at promoting student accountability and reinforcing school rules through supervised confinement, typically outside regular school hours. It targets behavior modification by providing a structured environment where students reflect on their actions and understand the consequences of rule violations. This approach helps maintain orderly conduct and deters future infractions by emphasizing responsibility and adherence to school policies.
Purpose and Goals of In-School Suspension
In-School Suspension (ISS) serves as a corrective measure designed to address student behavior while maintaining their engagement with academic instruction, contrasting with traditional detention that often excludes educational activities. The primary purpose of ISS is to provide structured consequences that promote reflection on misconduct and encourage behavioral improvement without disrupting the student's learning process. Goals of ISS include fostering accountability, minimizing academic loss, and facilitating behavioral interventions to support long-term positive outcomes for students.
Impact on Student Behavior and Academic Performance
Detention often results in temporary behavior correction but may not address underlying issues, leading to recurring infractions and minimal academic improvement. In-School Suspension removes students from regular classes while providing structured academic support, which can reduce negative behavior patterns and sustain academic engagement. Studies reveal that students in In-School Suspension maintain higher grades and demonstrate better long-term behavioral outcomes compared to those assigned to detention.
Procedural Process: Detention vs In-School Suspension
Detention typically requires students to remain after school hours under supervision, with minimal interaction and tasks focused on reflection or completing assignments. In-School Suspension involves isolating students within the school environment, often in a designated room, where they complete regular academic work under stricter supervision throughout the school day. Both processes mandate clear communication of rules, parental notification, and adherence to school district policies to ensure consistency and fairness.
Teacher and Administrator Roles in Enforcement
Teachers primarily monitor student behavior during detention, implementing corrective strategies to address infractions while providing immediate feedback. Administrators coordinate the scheduling and enforcement of both detention and in-school suspension (ISS), ensuring policies align with school discipline codes and effectively communicate consequences to students and parents. Collaboration between teachers and administrators is crucial to maintain consistency, uphold authority, and support a conducive learning environment during disciplinary measures.
Student Perspectives and Experiences
Students often perceive detention as more punitive due to its requirement to stay after school, limiting social and extracurricular activities, while in-school suspension (ISS) allows them to remain on campus and continue academic work. Many students report feeling isolated and stigmatized during ISS, describing it as a space where they are removed from peers but still responsible for completing assignments. Both disciplinary methods impact student motivation and engagement differently, with detention perceived as a temporary penalty and ISS offering a structured yet restrictive environment for reflection and learning.
Parental Involvement and Communication
Effective parental involvement in detention requires timely notifications and clear communication regarding the infraction and consequences to foster accountability and support behavior improvement. In-school suspension demands proactive engagement through regular updates and constructive dialogue between school staff and parents, ensuring consistent monitoring and encouragement for academic progress and social skills development. Both disciplinary approaches benefit from transparent communication channels that empower parents to collaborate in reinforcing positive student behavior.
Effectiveness and Long-Term Outcomes
Detention primarily serves as a short-term disciplinary measure with limited impact on behavioral improvement, while in-school suspension (ISS) allows students to remain in an educational setting, mitigating learning loss and promoting accountability. Research indicates that ISS is more effective than detention in reducing repeat offenses and improving student engagement by combining consequences with continued instruction. Long-term outcomes reveal that ISS contributes to better academic performance and lower dropout rates compared to detention, which often fails to address underlying behavioral issues.
Detention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com