Lecture-based teaching delivers structured information directly from the educator to students, enabling efficient coverage of extensive material. This approach emphasizes clarity and organization, often supporting your learning with visual aids and focused explanations. Explore the rest of the article to discover how lecture-based methods can enhance your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
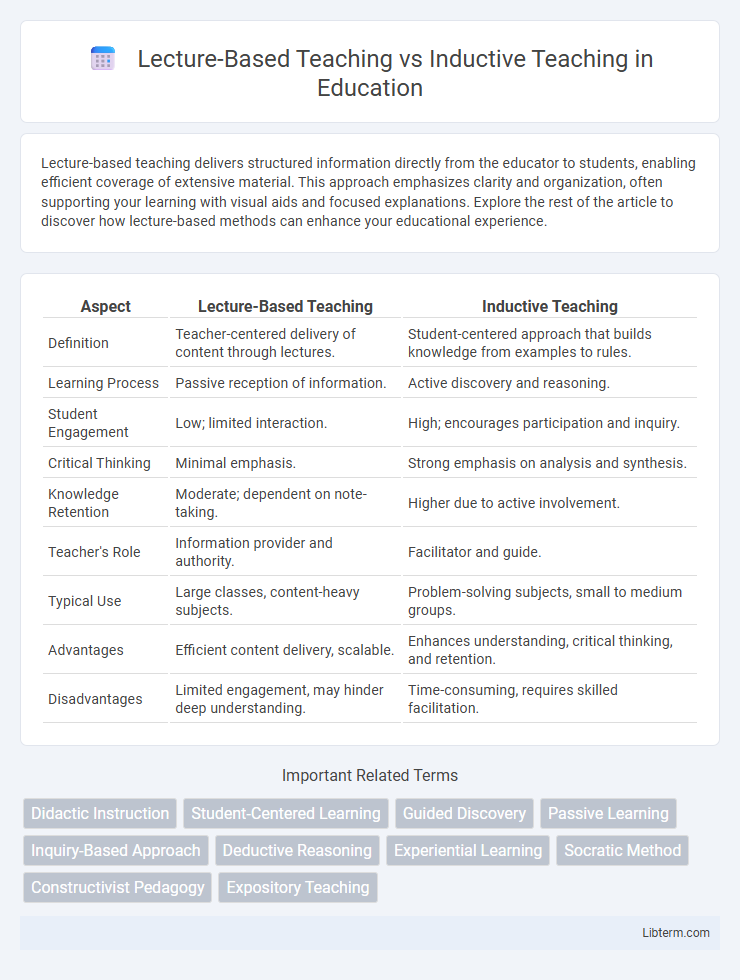
| Aspect | Lecture-Based Teaching | Inductive Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-centered delivery of content through lectures. | Student-centered approach that builds knowledge from examples to rules. |
| Learning Process | Passive reception of information. | Active discovery and reasoning. |
| Student Engagement | Low; limited interaction. | High; encourages participation and inquiry. |
| Critical Thinking | Minimal emphasis. | Strong emphasis on analysis and synthesis. |
| Knowledge Retention | Moderate; dependent on note-taking. | Higher due to active involvement. |
| Teacher's Role | Information provider and authority. | Facilitator and guide. |
| Typical Use | Large classes, content-heavy subjects. | Problem-solving subjects, small to medium groups. |
| Advantages | Efficient content delivery, scalable. | Enhances understanding, critical thinking, and retention. |
| Disadvantages | Limited engagement, may hinder deep understanding. | Time-consuming, requires skilled facilitation. |
Introduction to Teaching Methodologies
Lecture-based teaching emphasizes the direct transmission of knowledge from instructor to students, typically using structured presentations and systematic explanations. Inductive teaching, in contrast, encourages students to observe, analyze, and derive principles through active exploration and problem-solving, fostering deeper conceptual understanding. Both methodologies form foundational approaches in teaching, with lecture-based methods prioritizing content delivery and inductive methods emphasizing student-centered inquiry and critical thinking.
Defining Lecture-Based Teaching
Lecture-based teaching is a traditional instructional method where the educator delivers content through verbal presentations, focusing on direct transmission of knowledge to students with limited interaction. It emphasizes structured delivery of facts, principles, and concepts, often relying on note-taking and passive learning. This approach prioritizes efficient coverage of material but may reduce opportunities for student engagement and critical thinking development.
Understanding Inductive Teaching
Inductive teaching emphasizes student-centered discovery by presenting specific examples before guiding learners to infer general principles, enhancing deeper comprehension and critical thinking skills. This method promotes active engagement through exploration, questioning, and problem-solving, contrasting with the more passive reception typical in lecture-based teaching. Research indicates inductive approaches improve long-term retention and application of knowledge across diverse educational contexts.
Historical Context and Evolution
Lecture-based teaching originated in ancient Greece and Rome, dominating education for centuries by emphasizing authoritative knowledge transfer from teacher to student. Inductive teaching evolved during the Enlightenment with thinkers like Locke and Rousseau advocating experiential learning and critical thinking, challenging rote memorization. Modern education increasingly blends these methods, reflecting a historical shift toward student-centered, inquiry-based learning models.
Core Principles and Techniques
Lecture-Based Teaching centers on direct instruction where the teacher delivers structured information, emphasizing clarity and efficient knowledge transfer through presentations or demonstrations. Inductive Teaching employs discovery learning, encouraging students to engage actively by observing examples and deriving rules or principles, fostering critical thinking and retention. Core techniques in lecture-based methods include outlining key concepts and summarizing content, while inductive approaches utilize guided questioning and exploratory activities to promote deeper understanding.
Student Engagement and Participation
Lecture-based teaching often results in lower student engagement as learners adopt a passive role, limiting opportunities for active participation and critical thinking. Inductive teaching methods, such as inquiry-based or problem-solving approaches, foster higher engagement by encouraging students to explore concepts, ask questions, and collaborate actively. Research shows that inductive teaching increases motivation, deepens understanding, and enhances retention compared to traditional lecture formats.
Learning Outcomes and Assessment
Lecture-based teaching often leads to the effective transfer of factual knowledge and structured content comprehension, making it suitable for assessments like multiple-choice and short-answer exams that measure retention and recall. Inductive teaching enhances critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper conceptual understanding by encouraging learners to discover principles through exploration, which aligns with performance-based assessments such as projects, presentations, and open-ended questions. Research indicates that inductive methods generally yield higher-order cognitive skills and improved long-term retention, whereas lecture-based approaches excel in foundational knowledge acquisition evaluated through standardized testing.
Pros and Cons of Lecture-Based Teaching
Lecture-based teaching efficiently delivers structured content to large groups, maximizing information coverage in limited time. This method supports expert-driven explanations but may limit student engagement and critical thinking opportunities. Its passive learning nature can lead to lower retention compared to more interactive approaches like inductive teaching.
Advantages and Limitations of Inductive Teaching
Inductive teaching fosters active learning by encouraging students to explore concepts through observation and pattern recognition, which enhances critical thinking and long-term retention. This approach allows learners to construct knowledge independently, promoting deeper understanding and adaptability in diverse learning contexts. However, inductive teaching can be time-consuming, may overwhelm students lacking foundational knowledge, and requires skilled instructors to guide discovery without causing confusion.
Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Learning
Lecture-based teaching efficiently delivers structured content and is ideal for covering extensive material quickly, promoting clear understanding of core concepts through expert explanation. Inductive teaching fosters active learner engagement by encouraging exploration and discovery, enhancing critical thinking and retention through hands-on problem-solving and real-world examples. Selecting the right approach depends on the learning objectives, student needs, and subject complexity, balancing direct instruction with opportunities for inquiry-based learning to optimize educational outcomes.
Lecture-Based Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com