Concept mapping visually organizes information, linking key ideas and concepts to enhance understanding and memory retention. This technique helps you structure knowledge clearly, making complex subjects easier to grasp and analyze. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for creating powerful concept maps.
Table of Comparison
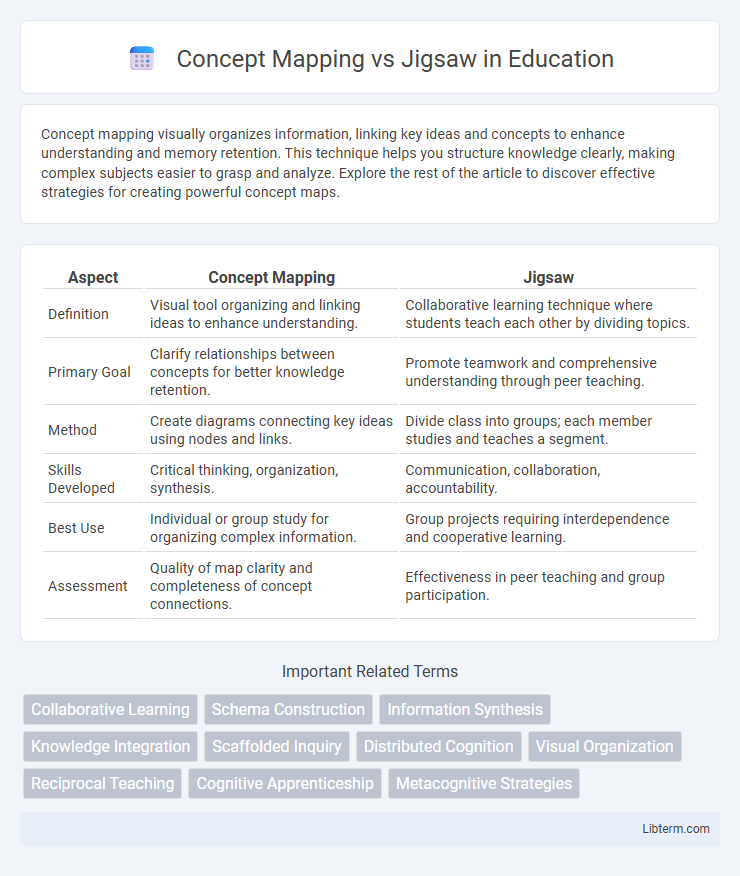
| Aspect | Concept Mapping | Jigsaw |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visual tool organizing and linking ideas to enhance understanding. | Collaborative learning technique where students teach each other by dividing topics. |
| Primary Goal | Clarify relationships between concepts for better knowledge retention. | Promote teamwork and comprehensive understanding through peer teaching. |
| Method | Create diagrams connecting key ideas using nodes and links. | Divide class into groups; each member studies and teaches a segment. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, organization, synthesis. | Communication, collaboration, accountability. |
| Best Use | Individual or group study for organizing complex information. | Group projects requiring interdependence and cooperative learning. |
| Assessment | Quality of map clarity and completeness of concept connections. | Effectiveness in peer teaching and group participation. |
Introduction to Concept Mapping and Jigsaw
Concept Mapping and Jigsaw are effective collaborative learning strategies designed to enhance comprehension and critical thinking. Concept Mapping visually organizes and represents relationships among ideas, facilitating deeper understanding through interconnected diagrams. The Jigsaw method divides topics into segments, assigning each group member to become an expert on a specific segment before teaching peers, promoting active participation and cooperative learning.
Defining Concept Mapping: Key Elements
Concept Mapping involves visually organizing information through nodes representing key concepts connected by labeled links that illustrate relationships. Key elements include hierarchical structure, linking phrases, and cross-links that highlight interconnections between different domains. This method enhances comprehension by clarifying how individual concepts integrate into broader knowledge frameworks.
Understanding the Jigsaw Technique
The Jigsaw technique is a cooperative learning strategy where students become experts on one segment of a topic and then teach it to peers, promoting deep comprehension and collaborative knowledge sharing. Unlike Concept Mapping, which visually organizes information, the Jigsaw method emphasizes interdependence and communication within diverse group settings. This approach enhances critical thinking and retention by requiring learners to engage actively with both content and group dynamics.
Cognitive Benefits of Concept Mapping
Concept mapping enhances cognitive benefits by promoting meaningful learning through visual organization of knowledge, which facilitates deeper understanding and retention of complex information. It supports the integration of new concepts with existing knowledge, improving critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Unlike the Jigsaw method, which primarily encourages collaborative learning and perspective sharing, concept mapping specifically strengthens cognitive processes by enabling learners to identify relationships and hierarchies among ideas.
Collaborative Learning with the Jigsaw Method
The Jigsaw Method enhances collaborative learning by dividing students into expert groups where each member masters a segment of the material, then teaches it to peers in mixed groups, fostering interdependence and active engagement. Concept Mapping supports collaborative learning by enabling students to visually organize and link key ideas collectively, promoting deeper understanding through shared knowledge construction. Both strategies improve critical thinking and knowledge retention but the Jigsaw Method uniquely emphasizes peer teaching and accountability within diverse group interactions.
Comparative Analysis: Structure and Process
Concept Mapping organizes knowledge visually by linking main ideas through nodes and labeled connections, promoting hierarchical understanding and integration of information. The Jigsaw method involves dividing content into segments assigned to individual group members who become experts and then collaboratively teach each other, fostering interdependence and peer learning. Concept Mapping emphasizes structural relationships and cognitive organization, whereas Jigsaw prioritizes collaborative process and social interaction in knowledge construction.
Learning Outcomes: Concept Mapping vs Jigsaw
Concept Mapping enhances learning outcomes by promoting deep understanding through visual organization of knowledge, allowing students to see relationships between concepts and improve critical thinking. Jigsaw learning outcomes emphasize cooperative skills and interdependence, as students become experts in different segments and teach peers, fostering communication and retention of diverse information. Both methods improve comprehension, but Concept Mapping strongly supports individual cognitive structuring, while Jigsaw excels in collaborative knowledge construction.
Classroom Applications and Examples
Concept mapping enhances students' understanding by visually organizing relationships between ideas, making it ideal for brainstorming during science lessons or planning essays in language arts. The jigsaw method promotes cooperative learning by assigning each student a segment of the material, which they become experts on before teaching their group, effective in history units or literature study circles. Both strategies improve critical thinking and retention through active engagement and peer collaboration in diverse classroom settings.
Challenges and Limitations
Concept Mapping often faces challenges related to cognitive overload as learners may struggle to organize complex information hierarchies effectively, limiting its usefulness in large-scale collaborative settings. Jigsaw methods encounter limitations in ensuring equal participation and accountability, as group interdependence can cause uneven engagement and learning disparities among members. Both techniques require careful facilitation to overcome barriers such as time constraints and varying student readiness levels, which impact their overall effectiveness in educational environments.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Key Considerations
When choosing between Concept Mapping and Jigsaw, consider the learning objectives and group dynamics; Concept Mapping excels in visualizing relationships and deepening understanding of complex topics, while Jigsaw promotes cooperative learning and accountability through divided content mastery. Evaluate student engagement and prior knowledge as Concept Mapping suits learners who benefit from structured visualization, whereas Jigsaw encourages peer teaching and active participation. Assess classroom size and available time, since Concept Mapping can be done individually or in small groups, and Jigsaw requires careful orchestration of teams to ensure balanced contribution and effective knowledge sharing.
Concept Mapping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com