Citation analysis examines the frequency and patterns of citations in academic publications to evaluate the impact and relevance of research. Understanding citation metrics helps you identify influential works, track emerging trends, and assess scholarly communication within specific fields. Explore the full article to learn how citation analysis can enhance your research strategy and academic performance.
Table of Comparison
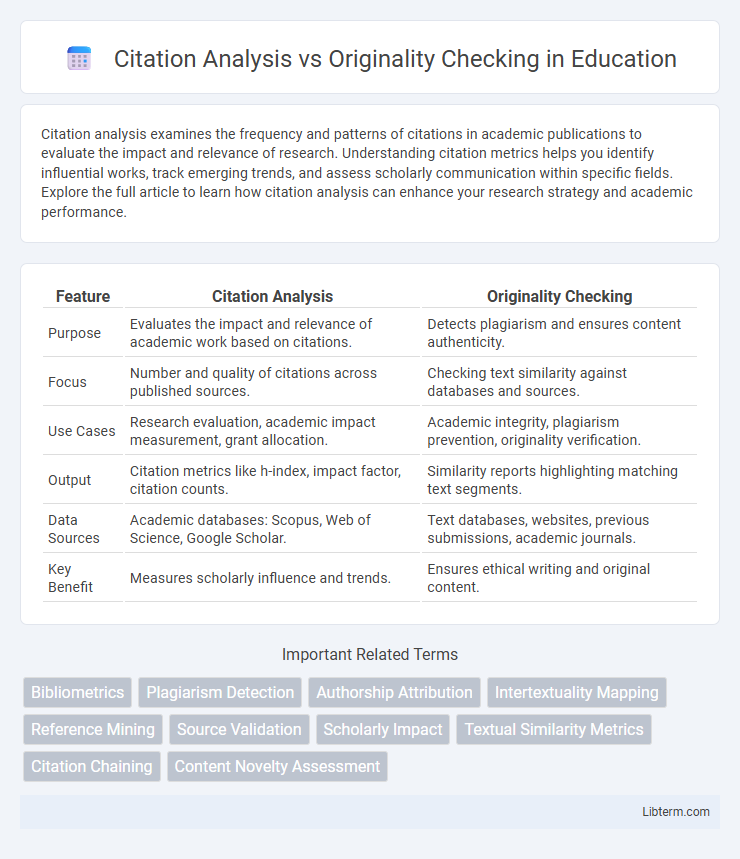
| Feature | Citation Analysis | Originality Checking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluates the impact and relevance of academic work based on citations. | Detects plagiarism and ensures content authenticity. |
| Focus | Number and quality of citations across published sources. | Checking text similarity against databases and sources. |
| Use Cases | Research evaluation, academic impact measurement, grant allocation. | Academic integrity, plagiarism prevention, originality verification. |
| Output | Citation metrics like h-index, impact factor, citation counts. | Similarity reports highlighting matching text segments. |
| Data Sources | Academic databases: Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar. | Text databases, websites, previous submissions, academic journals. |
| Key Benefit | Measures scholarly influence and trends. | Ensures ethical writing and original content. |
Introduction to Citation Analysis and Originality Checking
Citation analysis evaluates the impact and relevance of academic works by examining citation counts and patterns, helping to identify influential research and trends within specific fields. Originality checking uses advanced software to detect potential plagiarism by comparing submitted texts against extensive databases, ensuring the authenticity and uniqueness of scholarly content. Both tools are essential in academic publishing for maintaining research quality and intellectual integrity.
Defining Citation Analysis
Citation analysis is a method used to evaluate the impact and relevance of academic works by examining how frequently and where they have been cited in other scholarly publications. This technique helps identify key research contributions, emerging trends, and influential authors within a specific field. By mapping citation networks, citation analysis provides valuable insights into the dissemination and development of scientific knowledge.
Understanding Originality Checking
Originality checking involves comparing a document against extensive databases, including academic papers, web pages, and publications, to detect copied or closely paraphrased content. It focuses on identifying unoriginal text passages rather than assessing the influence or impact of the work, which is the primary goal of citation analysis. Effective originality checking helps uphold academic integrity by preventing plagiarism and ensuring that submitted work is authentically produced.
Key Objectives of Citation Analysis
Citation analysis primarily aims to evaluate the impact and relevance of scholarly work by quantifying how often and where a publication is cited within the academic community. It helps identify influential authors, key research trends, and the interconnectedness of scientific literature through metrics such as citation counts, h-index, and impact factors. Unlike originality checking, which detects plagiarism and assesses content uniqueness, citation analysis focuses on measuring research visibility and contribution to knowledge advancement.
Main Functions of Originality Checking Tools
Originality checking tools primarily function to detect instances of plagiarism by comparing submitted text against extensive databases of academic papers, web content, and other sources to identify unoriginal content. They generate similarity reports highlighting matched phrases and sentences, enabling users to review and ensure the integrity of their work. These tools support academic honesty by verifying the uniqueness of manuscripts and helping authors correct improper citations before publication.
Differences Between Citation Analysis and Originality Checking
Citation analysis evaluates the frequency and patterns of citations in academic works to assess impact, influence, and scholarly connections. Originality checking detects duplicated or plagiarized content by comparing submitted text against databases and published materials to ensure authenticity. While citation analysis focuses on the relationships and influence of research, originality checking centers on verifying the uniqueness and integrity of the content.
Advantages of Citation Analysis in Academic Research
Citation analysis enhances academic research by identifying influential studies and key trends within a discipline, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of scholarly impact. It quantifies the frequency and patterns of citations, enabling researchers to evaluate the credibility and relevance of sources more effectively. This method supports systematic literature reviews and helps in mapping the development of ideas over time, which originality checking lacks as it primarily detects textual similarity without assessing scholarly influence.
Benefits of Originality Checking for Authors and Institutions
Originality checking enhances the credibility of authors by ensuring their work is free from plagiarism and maintains academic integrity. Institutions benefit from originality checking through improved reputation and reduced risk of copyright infringement, promoting a culture of ethical research. This process supports authors in refining their work by identifying unintentional similarities and fostering genuine scholarship.
Limitations and Challenges of Both Methods
Citation analysis often struggles with citation bias and the inability to evaluate the context or quality of references, leading to potential misinterpretation of an article's impact. Originality checking tools face challenges such as detecting paraphrased plagiarism, differentiating common knowledge from plagiarism, and handling diverse source languages, which can result in false positives or negatives. Both methods require complementary use to overcome inherent limitations, improving the accuracy and reliability of academic integrity assessments.
Best Practices for Implementing Citation Analysis and Originality Checking
Effective implementation of citation analysis and originality checking requires integrating advanced algorithms and comprehensive databases to ensure accurate source identification and plagiarism detection. Leveraging tools such as Turnitin for originality checking and Scopus or Google Scholar for citation analysis enhances the reliability of academic integrity assessments. Regular updates, staff training, and clear institutional policies support consistent application and foster a culture of ethical research practices.
Citation Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com