Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods to address the diverse learning styles, abilities, and interests of students, ensuring all learners can access the curriculum effectively. By incorporating varied instructional strategies, educators foster a more inclusive and engaging classroom environment. Discover how differentiated instruction can transform your approach to teaching in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
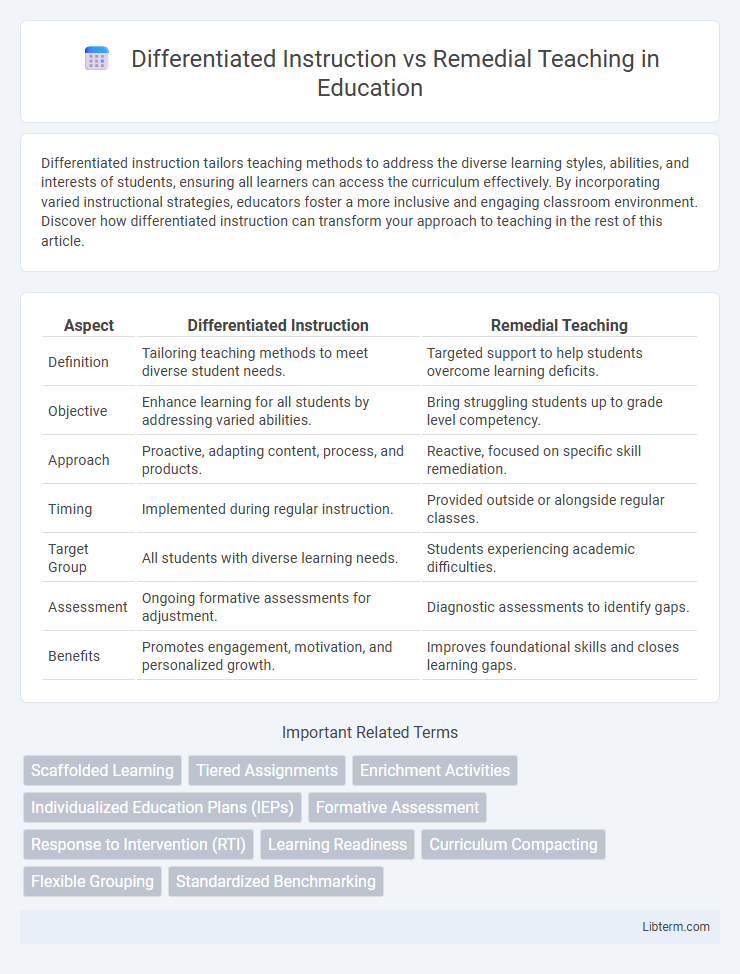
| Aspect | Differentiated Instruction | Remedial Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tailoring teaching methods to meet diverse student needs. | Targeted support to help students overcome learning deficits. |
| Objective | Enhance learning for all students by addressing varied abilities. | Bring struggling students up to grade level competency. |
| Approach | Proactive, adapting content, process, and products. | Reactive, focused on specific skill remediation. |
| Timing | Implemented during regular instruction. | Provided outside or alongside regular classes. |
| Target Group | All students with diverse learning needs. | Students experiencing academic difficulties. |
| Assessment | Ongoing formative assessments for adjustment. | Diagnostic assessments to identify gaps. |
| Benefits | Promotes engagement, motivation, and personalized growth. | Improves foundational skills and closes learning gaps. |
Introduction to Differentiated Instruction and Remedial Teaching
Differentiated Instruction tailors teaching methods and content to accommodate diverse student learning styles, abilities, and interests within the same classroom, enhancing engagement and comprehension for all learners. Remedial Teaching specifically targets students struggling with foundational skills, providing focused support to bridge learning gaps and bring them up to grade level. Both approaches aim to improve student outcomes but differ in scope, with Differentiated Instruction addressing varied learner needs proactively, while Remedial Teaching intervenes reactively after learning difficulties arise.
Core Principles of Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction centers on tailoring teaching methods, content, and assessment strategies to meet the diverse learning needs, interests, and readiness levels of all students within a classroom. Core principles include flexible grouping, ongoing assessment to inform instruction, and providing multiple pathways for students to access content and demonstrate understanding. Unlike remedial teaching, which targets students struggling to meet grade-level standards, differentiated instruction proactively adapts the learning environment to support each learner's growth and engagement.
Core Principles of Remedial Teaching
Remedial teaching centers on diagnosing specific learning deficiencies and designing targeted interventions to address individual students' gaps in knowledge and skills. Its core principles include personalized pacing, focused skill reinforcement, and continuous progress monitoring to ensure mastery of foundational concepts. Unlike differentiated instruction, which adapts teaching for diverse learners within the general classroom, remedial teaching intensively supports students requiring extra help to meet standard benchmarks.
Key Differences Between Differentiated Instruction and Remedial Teaching
Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and learning activities to accommodate diverse student needs, readiness levels, and interests within the same classroom, promoting inclusive education. Remedial teaching specifically targets students who are struggling or below grade level, providing focused support to help them reach standard proficiency. Key differences include differentiated instruction's proactive, broad approach to varied learners versus remedial teaching's reactive, individualized intervention for academic gaps.
Goals and Objectives: Differentiation vs Remediation
Differentiated instruction aims to address diverse student needs by providing varied learning paths, materials, and assessments to promote growth for all learners, focusing on enhancing strengths and interests. Remedial teaching targets specific skill deficits, aiming to bring students up to standard proficiency levels through focused intervention and repetition. The objective of differentiation is to foster inclusive learning environments that support continuous development, while remediation centers on closing gaps in foundational knowledge and skills.
Strategies Used in Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction employs strategies such as flexible grouping, tiered assignments, and choice boards to address diverse student needs and learning styles within the same classroom. Unlike remedial teaching, which targets students who have fallen behind by reteaching specific skills, differentiated instruction proactively modifies content, process, and product to optimize engagement and mastery for all learners. Techniques like ongoing formative assessments and incorporating multiple modalities ensure personalized learning pathways that support cognitive development and motivation.
Strategies Used in Remedial Teaching
Remedial teaching strategies focus on targeted interventions such as one-on-one tutoring, scaffolding, and use of multisensory techniques to address specific learning gaps and reinforce foundational skills. Progress monitoring and formative assessments guide tailored lesson adjustments, ensuring students receive personalized support aligned with their individual needs. Emphasis on repetition, practice, and structured skill-building activities distinguishes remedial strategies from broader differentiated instruction approaches.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Approach
Differentiated instruction enhances student engagement and accommodates diverse learning styles by tailoring content, process, and assessments, but it demands significant teacher preparation and classroom management skills. Remedial teaching focuses on addressing specific learning gaps through targeted intervention, promoting mastery of foundational skills; however, it may stigmatize students and often requires additional resources and time outside regular class hours. Both approaches aim to improve academic outcomes but differ in scalability and impact on classroom dynamics.
When to Use Differentiated Instruction or Remedial Teaching
Differentiated instruction is best used proactively to address diverse learning needs within a heterogeneous classroom by tailoring content, process, and product to student readiness, interests, and learning profiles. Remedial teaching is applied reactively after identifying specific learning gaps or deficits, targeting students who struggle to meet grade-level standards through intensive, often one-on-one or small group interventions. Employing differentiated instruction maintains engagement and supports growth for all learners, whereas remedial teaching focuses on accelerating the catch-up process for those below proficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Student Success
Differentiated instruction tailors teaching strategies to meet diverse student needs within the general classroom, fostering engagement and growth for all learners. Remedial teaching targets specific skill deficits through focused intervention, aiming to bring struggling students up to grade level proficiency. Selecting the appropriate approach depends on individual learner profiles and instructional goals, ensuring optimized student success through personalized educational support.
Differentiated Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com