Student-centered learning prioritizes the needs, interests, and abilities of each learner, fostering active engagement and personalized education pathways. This approach encourages critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem solving, making education more relevant and motivating for students. Discover how implementing student-centered strategies can transform your classroom experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
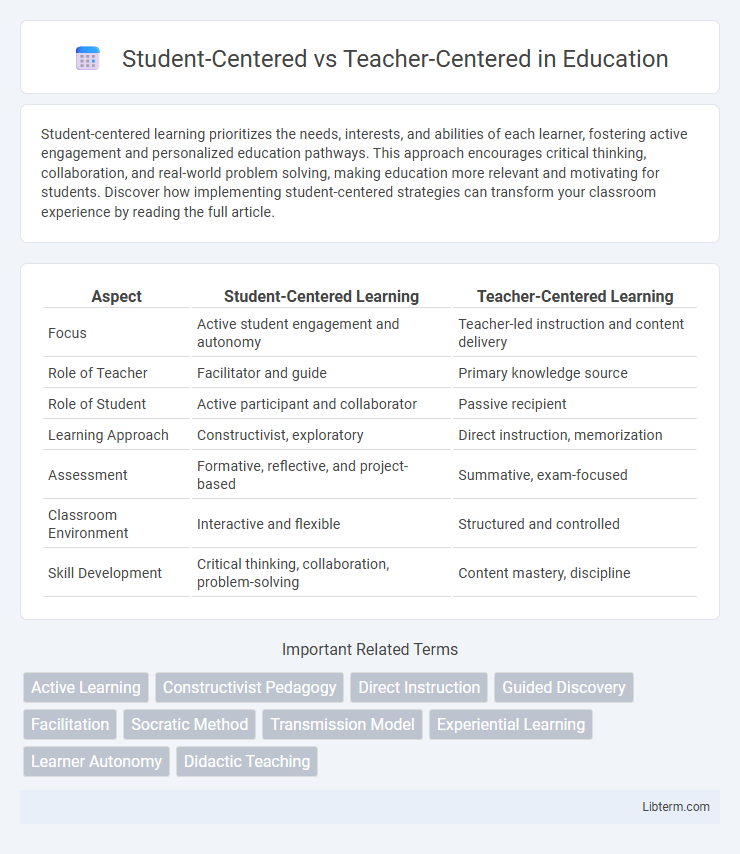
| Aspect | Student-Centered Learning | Teacher-Centered Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Active student engagement and autonomy | Teacher-led instruction and content delivery |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide | Primary knowledge source |
| Role of Student | Active participant and collaborator | Passive recipient |
| Learning Approach | Constructivist, exploratory | Direct instruction, memorization |
| Assessment | Formative, reflective, and project-based | Summative, exam-focused |
| Classroom Environment | Interactive and flexible | Structured and controlled |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, collaboration, problem-solving | Content mastery, discipline |
Understanding Student-Centered and Teacher-Centered Approaches
Student-centered approaches emphasize active learning, where students engage in problem-solving, critical thinking, and collaboration, fostering deeper understanding and autonomy. Teacher-centered approaches focus on direct instruction, with the teacher controlling content delivery and pacing to ensure foundational knowledge acquisition. Understanding these approaches helps educators balance guidance and independence, tailoring strategies to enhance student motivation and learning outcomes.
Key Characteristics of Student-Centered Learning
Student-centered learning emphasizes active student engagement, personalized learning paths, and collaborative knowledge construction, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It prioritizes student autonomy, allowing learners to take ownership of their education through inquiry-based activities and real-world applications. Assessment methods focus on formative feedback and self-reflection rather than solely on standardized testing, promoting deeper understanding and continuous improvement.
Key Features of Teacher-Centered Instruction
Teacher-centered instruction emphasizes structured lessons with the teacher as the primary authority, delivering content through lectures and direct instruction. It prioritizes rote memorization, standardized testing, and a clear curriculum progression, with students often playing a passive role as knowledge recipients. Classroom management relies on teacher control to maintain order and ensure adherence to academic standards.
Benefits of Student-Centered Education
Student-centered education fosters active engagement, critical thinking, and personalized learning, enhancing student motivation and retention. This approach promotes collaboration and communication skills by encouraging students to participate in discussions and group work. Research indicates improved academic achievement and deeper understanding when students take responsibility for their learning.
Advantages of Teacher-Centered Teaching
Teacher-centered teaching offers structured learning environments that promote efficient content delivery and consistent curriculum coverage. It allows educators to maintain control over classroom dynamics, ensuring discipline and minimizing distractions. This approach benefits students who thrive under clear guidance and prefer a consistent, organized framework for absorbing information.
Challenges of Student-Centered Classrooms
Student-centered classrooms often face challenges such as managing diverse learning paces, maintaining student motivation, and ensuring equitable participation. Teachers must skillfully balance facilitation with guidance while adapting to individual student needs and fostering collaborative learning environments. Overcoming these obstacles requires ongoing professional development and effective classroom management strategies to maximize student engagement and learning outcomes.
Limitations of Teacher-Centered Methods
Teacher-centered methods often limit student engagement by emphasizing passive learning and rote memorization, reducing opportunities for critical thinking and problem-solving development. This approach can stifle creativity and fails to accommodate diverse learning styles, resulting in lower retention and motivation. Constraints on individualized instruction hinder the ability to address students' unique needs and promote active participation.
Comparing Student Outcomes: Student-Centered vs Teacher-Centered
Student-centered learning fosters higher engagement and critical thinking, resulting in improved problem-solving skills and long-term retention compared to teacher-centered methods. Students in student-centered environments demonstrate greater autonomy and collaboration, which enhances creativity and adaptability in real-world situations. In contrast, teacher-centered approaches often lead to passive learning and lower motivation, affecting overall academic achievement and the development of higher-order cognitive skills.
Integrating Both Approaches for Effective Learning
Integrating student-centered and teacher-centered approaches fosters an adaptive learning environment that balances active student engagement with structured guidance, enhancing comprehension and retention. Employing technology and collaborative activities within teacher-directed lessons promotes personalized learning pathways while maintaining curriculum standards. This hybrid model leverages the strengths of both methods to optimize educational outcomes and accommodate diverse learning styles.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Selecting the appropriate approach--student-centered or teacher-centered--depends on your classroom goals, students' learning styles, and subject matter. Student-centered learning fosters critical thinking and collaboration through active participation, while teacher-centered instruction emphasizes structured guidance and content delivery for foundational knowledge. Balancing these methods by incorporating interactive activities and direct teaching ensures effective learning outcomes tailored to diverse student needs.
Student-Centered Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com