A dissertation represents a comprehensive, research-driven document that showcases your expertise and contributes original knowledge to your academic field. Crafting a well-structured dissertation involves meticulous planning, critical analysis, and clear articulation of your findings. Discover valuable tips and strategies to guide you through the entire dissertation process in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
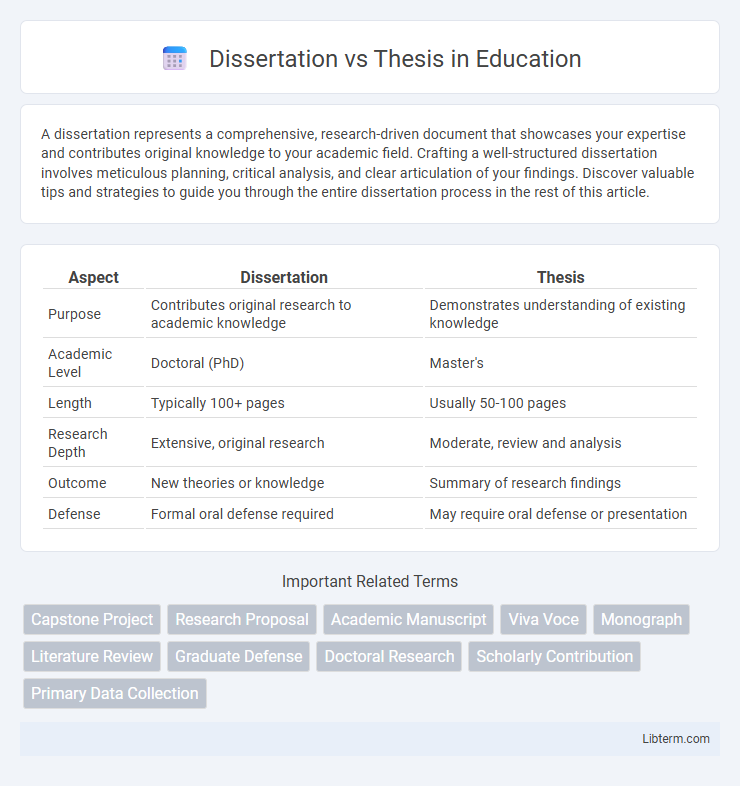
| Aspect | Dissertation | Thesis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Contributes original research to academic knowledge | Demonstrates understanding of existing knowledge |
| Academic Level | Doctoral (PhD) | Master's |
| Length | Typically 100+ pages | Usually 50-100 pages |
| Research Depth | Extensive, original research | Moderate, review and analysis |
| Outcome | New theories or knowledge | Summary of research findings |
| Defense | Formal oral defense required | May require oral defense or presentation |
Understanding Dissertation and Thesis: Key Definitions
A dissertation is an extensive research project required for a doctoral degree, showcasing original contributions to the field, while a thesis is typically a shorter research paper for a master's degree that demonstrates a student's understanding of a specific topic. Both involve systematic investigation and critical analysis, but dissertations demand deeper, more comprehensive research and critical thinking skills. Key definitions highlight that dissertations aim to generate new knowledge, whereas theses primarily synthesize existing research to support a particular argument or hypothesis.
Historical Background of Dissertation and Thesis
The historical background of dissertations and theses traces back to medieval European universities, where the terms originated from Latin, with "dissertatio" meaning debate or argument and "thesis" referring to a proposition or claim to be defended. The dissertation historically evolved as a formal document submitted for a doctoral degree, focused on original research, while the thesis served as a requirement for master's degrees or bachelor's honors, emphasizing comprehensive knowledge on a topic. Over centuries, these academic traditions solidified, reflecting the evolving standards of higher education and scholarly contribution across different cultures.
Main Differences Between Dissertation and Thesis
A dissertation typically involves original research and contributes new knowledge, whereas a thesis generally summarizes existing research to demonstrate understanding. Dissertations are usually required for doctoral degrees and are longer with more comprehensive analysis, while theses are often associated with master's programs and are shorter in scope. The evaluation criteria for dissertations emphasize innovation and critical thinking, while theses focus more on mastering subject content and research methodology.
Purpose and Objectives of Each Document
A dissertation aims to contribute original research to a specific academic field, demonstrating the candidate's ability to conduct independent, in-depth study and advance scholarly knowledge. A thesis focuses on proving the student's understanding of existing research and theories through systematic analysis, often serving as a requirement for completing a master's degree. The primary objective of a dissertation is to present new findings, while a thesis synthesizes and evaluates existing information to showcase mastery of the subject matter.
Structure and Components: Dissertation vs Thesis
A dissertation typically includes a comprehensive structure with chapters such as introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion, focusing on original research and contribution to knowledge. A thesis is generally shorter and structured around an introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, and conclusion, emphasizing mastery of a subject area. Both require an abstract, references, and appendices, but dissertations demand more extensive data analysis and in-depth theoretical framework.
Academic Requirements and Expectations
Dissertations require original research contributing new knowledge and are typically mandatory for doctoral degrees, demanding extensive literature review, methodology, and analysis. Theses generally involve comprehensive research demonstrating mastery of a subject, often required for master's degrees, with a focus on summarizing existing knowledge and applying it analytically. Academic expectations for dissertations emphasize rigor, originality, and publication potential, whereas theses prioritize synthesis, understanding, and critical evaluation.
Regional and Institutional Variations
Dissertation and thesis terminology varies significantly across regions and institutions, with the term "dissertation" often used in the United States to describe a doctoral research project, while in Europe, it may refer to a master's level paper. Institutional requirements also influence these distinctions, where some universities mandate a thesis for undergraduates or master's degrees, while dissertations are exclusive to doctoral work. Understanding these regional and institutional nuances is crucial for accurately navigating academic expectations and research documentation.
Research Depth and Originality
Dissertations demand a higher level of research depth and originality, typically requiring extensive original contributions to the academic field, often pursued at the doctoral level. Theses usually focus on demonstrating comprehensive understanding and analysis of existing research, with some original insight, commonly associated with master's degree programs. The dissertation's emphasis on new knowledge creation distinguishes it from a thesis's goal of synthesizing and critically evaluating established scholarship.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Dissertation and thesis processes often encounter common challenges such as time management, research scope clarity, and effective data analysis, which can impede progress and quality. Addressing these issues involves setting realistic deadlines, refining research questions with advisor guidance, and utilizing advanced software tools for data processing. Consistent feedback and peer support also play crucial roles in overcoming obstacles to successful completion.
Choosing Between a Dissertation and a Thesis
Choosing between a dissertation and a thesis depends on the academic level and research goals of the student. A thesis is typically required for a master's degree and involves synthesizing existing research to demonstrate knowledge and analytical skills, while a dissertation is required for a doctoral degree and entails original research that contributes new knowledge to the field. Evaluating program requirements, career objectives, and the scope of research helps determine whether a thesis or dissertation is the appropriate academic project.
Dissertation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com