Reforestation restores ecosystems by planting trees that absorb carbon dioxide and improve air quality, helping to combat climate change. It also enhances biodiversity and protects soil from erosion while providing habitats for wildlife. Discover how your involvement in reforestation efforts can make a lasting impact by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
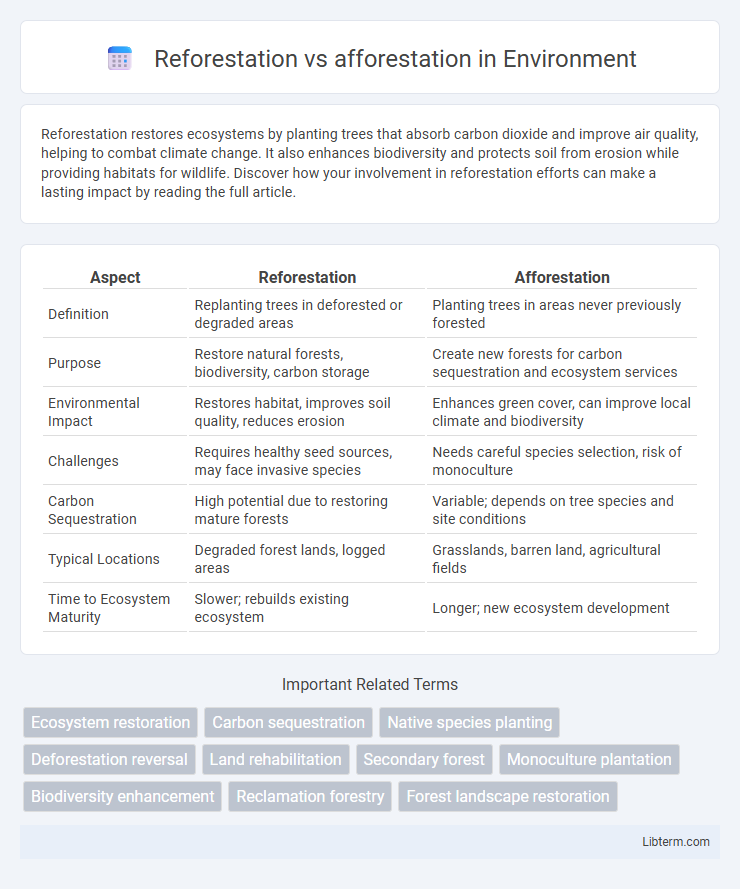
| Aspect | Reforestation | Afforestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replanting trees in deforested or degraded areas | Planting trees in areas never previously forested |
| Purpose | Restore natural forests, biodiversity, carbon storage | Create new forests for carbon sequestration and ecosystem services |
| Environmental Impact | Restores habitat, improves soil quality, reduces erosion | Enhances green cover, can improve local climate and biodiversity |
| Challenges | Requires healthy seed sources, may face invasive species | Needs careful species selection, risk of monoculture |
| Carbon Sequestration | High potential due to restoring mature forests | Variable; depends on tree species and site conditions |
| Typical Locations | Degraded forest lands, logged areas | Grasslands, barren land, agricultural fields |
| Time to Ecosystem Maturity | Slower; rebuilds existing ecosystem | Longer; new ecosystem development |
Introduction to Reforestation and Afforestation
Reforestation involves replanting trees in deforested or degraded areas to restore ecosystems and enhance biodiversity, while afforestation refers to the process of establishing forests on lands that have not been previously forested. Both techniques play crucial roles in carbon sequestration, climate change mitigation, and soil conservation. Effective implementation of reforestation and afforestation projects supports habitat restoration and promotes sustainable land management.
Defining Reforestation
Reforestation refers to the process of replanting trees in areas where forests have been recently depleted or destroyed due to natural disasters, logging, or other human activities. This practice helps restore biodiversity, improve air quality, and sequester carbon dioxide, making it a crucial tool in combating climate change. Unlike afforestation, which involves planting trees in previously unforested areas, reforestation focuses on rehabilitating existing forest ecosystems.
Understanding Afforestation
Afforestation involves planting trees in areas that have never been forested, aiming to create new forest ecosystems and enhance biodiversity. This process plays a critical role in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change by absorbing atmospheric CO2. Understanding afforestation helps optimize land use for environmental restoration and sustainable development initiatives.
Key Differences Between Reforestation and Afforestation
Reforestation involves replanting trees in deforested or degraded areas to restore original forest ecosystems, primarily aimed at repairing environmental damage and enhancing biodiversity. Afforestation refers to planting trees in regions that have not previously been forested, often targeting land reclamation, carbon sequestration, and combating desertification. The key difference lies in reforestation restoring prior forest cover, while afforestation creates new forested areas on previously non-forested land.
Ecological Benefits of Reforestation
Reforestation enhances biodiversity by restoring native habitats and supporting wildlife populations, which maintains ecosystem stability and resilience. It improves carbon sequestration significantly by revitalizing existing soil quality and accelerating carbon absorption rates compared to afforestation on new land. Reforestation also regulates water cycles effectively, reducing soil erosion and improving watershed health through reestablished forest cover.
Environmental Advantages of Afforestation
Afforestation significantly enhances carbon sequestration by establishing new forests on previously non-forested land, contributing to climate change mitigation. It promotes biodiversity by creating new habitats for various species, aiding in the restoration of ecological balance. Afforestation also improves soil quality and water retention, reducing erosion and enhancing local water cycles.
Challenges and Limitations of Reforestation
Reforestation faces challenges such as limited availability of native seed sources, soil degradation, and climate change impacts that hinder tree growth and survival rates. Restoration efforts often struggle with fragmented habitats and invasive species competition, reducing biodiversity benefits. Financial constraints and land-use conflicts further limit the scale and effectiveness of reforestation projects compared to afforestation initiatives.
Potential Drawbacks of Afforestation
Afforestation, the process of planting trees in areas without previous forest cover, can lead to soil nutrient depletion and disrupt local water cycles, potentially causing water scarcity. Introducing non-native species through afforestation may reduce biodiversity and alter existing ecosystems. Large-scale afforestation projects sometimes compete with agricultural land, impacting food production and local livelihoods.
Case Studies: Global Examples and Success Stories
Reforestation projects in the Amazon Basin have restored over 1 million hectares of degraded forest, enhancing biodiversity and carbon sequestration. In Kenya, afforestation initiatives such as the Green Belt Movement have planted over 51 million trees, improving soil quality and providing community livelihoods. China's Grain for Green Program has successfully converted 9.2 million hectares of cropland to forest, significantly reducing soil erosion and boosting ecosystem resilience.
Which Strategy is Best for Sustainable Forest Management?
Reforestation involves replanting trees in deforested areas, restoring ecosystems and enhancing biodiversity, while afforestation creates new forested areas on non-forested land, increasing carbon sequestration and preventing soil erosion. Sustainable forest management benefits from reforestation by rehabilitating degraded lands and supporting native species, whereas afforestation helps expand forest cover and mitigate climate change effects on a broader scale. The best strategy depends on regional ecological conditions and land availability, with a combination of both approaches often yielding optimal environmental and socio-economic outcomes.
Reforestation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com