Smart growth focuses on sustainable urban development by promoting efficient land use, reducing traffic congestion, and preserving natural resources. It encourages mixed-use neighborhoods, walkability, and public transportation to create livable, vibrant communities. Explore the rest of the article to discover how smart growth strategies can benefit your city and enhance your quality of life.
Table of Comparison
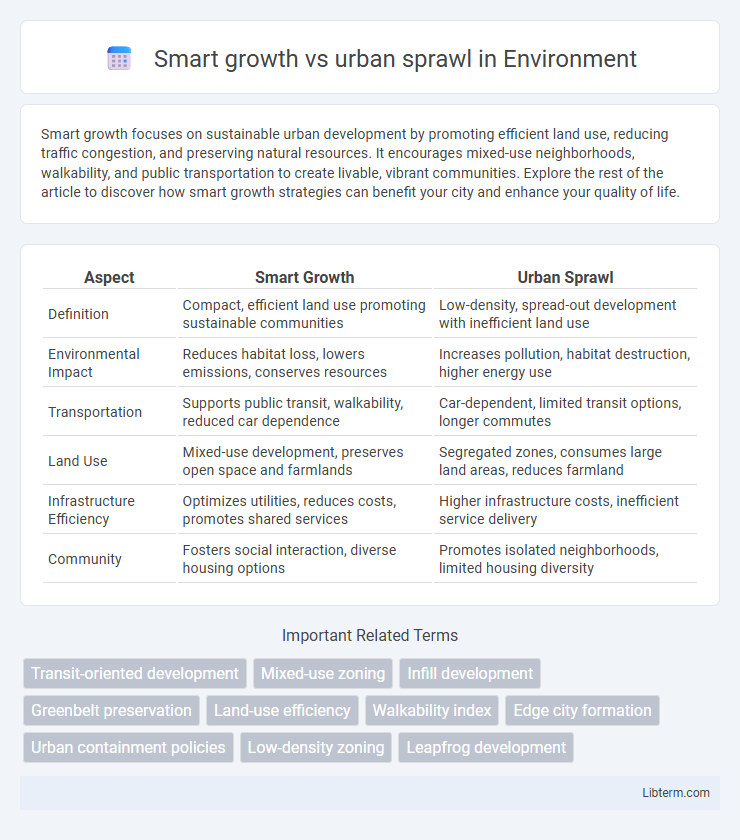
| Aspect | Smart Growth | Urban Sprawl |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compact, efficient land use promoting sustainable communities | Low-density, spread-out development with inefficient land use |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces habitat loss, lowers emissions, conserves resources | Increases pollution, habitat destruction, higher energy use |
| Transportation | Supports public transit, walkability, reduced car dependence | Car-dependent, limited transit options, longer commutes |
| Land Use | Mixed-use development, preserves open space and farmlands | Segregated zones, consumes large land areas, reduces farmland |
| Infrastructure Efficiency | Optimizes utilities, reduces costs, promotes shared services | Higher infrastructure costs, inefficient service delivery |
| Community | Fosters social interaction, diverse housing options | Promotes isolated neighborhoods, limited housing diversity |
Understanding Smart Growth: Principles and Goals
Smart Growth promotes compact, walkable communities with mixed-use development to reduce reliance on cars and preserve open space. Key principles include efficient land use, diverse housing options, and improved public transit access to enhance sustainability and quality of life. The main goal is to create environmentally responsible, economically viable, and socially equitable urban areas.
Defining Urban Sprawl: Causes and Characteristics
Urban sprawl refers to the uncontrolled and unplanned expansion of urban areas into peripheral rural land, driven by factors such as population growth, increased car dependency, and housing demand. Characterized by low-density development, extensive use of land, and segregation of residential, commercial, and industrial uses, it often leads to increased traffic congestion, environmental degradation, and loss of agricultural land. The lack of coordinated land use planning and reliance on automobile transportation are key contributors to the spread of urban sprawl.
Key Differences Between Smart Growth and Urban Sprawl
Smart growth emphasizes compact, walkable communities with mixed land uses that prioritize public transportation, energy efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Urban sprawl is characterized by low-density, car-dependent development that consumes large amounts of land and often leads to increased traffic congestion and habitat destruction. Key differences include smart growth's focus on preserving open space and reducing carbon footprints, while urban sprawl tends to expand infrastructure costs and fragment ecosystems.
Environmental Impacts: Smart Growth vs Urban Sprawl
Smart growth reduces environmental impacts by promoting compact, walkable communities that preserve green spaces and minimize habitat disruption. Urban sprawl increases carbon emissions through reliance on automobiles, causes habitat fragmentation, and leads to greater land consumption and resource depletion. Implementing smart growth strategies can significantly mitigate pollution, improve air quality, and support biodiversity conservation.
Transportation and Mobility: Contrasts and Consequences
Smart growth promotes efficient public transit systems and walkable neighborhoods that reduce reliance on cars, lowering traffic congestion and greenhouse gas emissions. Urban sprawl increases vehicle miles traveled due to dispersed development patterns, leading to higher fuel consumption and longer commute times. The contrast significantly impacts air quality, energy use, and overall mobility accessibility in metropolitan regions.
Economic Effects: Cost-Benefit Analysis
Smart growth promotes economic efficiency by concentrating development in existing urban areas, reducing infrastructure costs and increasing property values, while urban sprawl leads to higher public expenses due to extended roads, utilities, and services. Cost-benefit analysis of smart growth highlights long-term savings through improved transit accessibility, higher tax revenues, and reduced environmental remediation costs. Conversely, urban sprawl incurs greater fiscal burdens on municipalities and taxpayers by increasing commute times, vehicle emissions, and public health expenditures.
Community Health and Quality of Life
Smart growth promotes compact, walkable neighborhoods that improve air quality, reduce traffic accidents, and increase physical activity, enhancing community health. Urban sprawl leads to increased pollution, longer commutes, and limited access to healthcare and recreational spaces, negatively impacting quality of life. Concentrated development under smart growth supports social interaction and access to amenities, fostering stronger community cohesion and well-being.
Land Use Planning and Zoning Strategies
Smart growth prioritizes efficient land use planning and zoning strategies that promote higher-density development, mixed-use neighborhoods, and preservation of open spaces to reduce urban sprawl. Zoning regulations in smart growth frameworks often encourage infill development, transit-oriented design, and walkability to create sustainable, compact communities. In contrast, urban sprawl is characterized by low-density, single-use zoning that spreads development outward, leading to excessive land consumption, increased infrastructure costs, and environmental degradation.
Policy Approaches for Sustainable Urban Development
Policy approaches for sustainable urban development emphasize smart growth strategies that prioritize compact, mixed-use development, efficient public transit, and preservation of green spaces to counteract the negative impacts of urban sprawl. Zoning reforms encourage higher density and transit-oriented developments, reducing reliance on automobiles and limiting the spread of low-density, car-dependent suburban expansion. Incentives for infill development and brownfield redevelopment promote resource-efficient land use, minimizing environmental degradation and supporting resilient, inclusive urban communities.
Future Trends: Building Resilient Cities
Smart growth emphasizes compact, mixed-use development and efficient public transit to reduce environmental impact and enhance livability. Urban sprawl leads to increased infrastructure costs, traffic congestion, and degraded ecosystems, challenging long-term urban resilience. Future trends prioritize integrating green infrastructure, adaptive reuse, and technology-driven planning to create sustainable, flexible cities capable of withstanding climate change and population pressures.
Smart growth Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com