The Capitalocene describes the current epoch shaped by capitalism's impact on the environment, highlighting how economic systems drive ecological change and degradation. This concept challenges traditional geological timeframes by emphasizing human-induced alterations rooted in capital accumulation and industrial exploitation. Discover how the Capitalocene reshapes our understanding of environmental crises and what it means for Your role in addressing these urgent challenges in the full article.
Table of Comparison
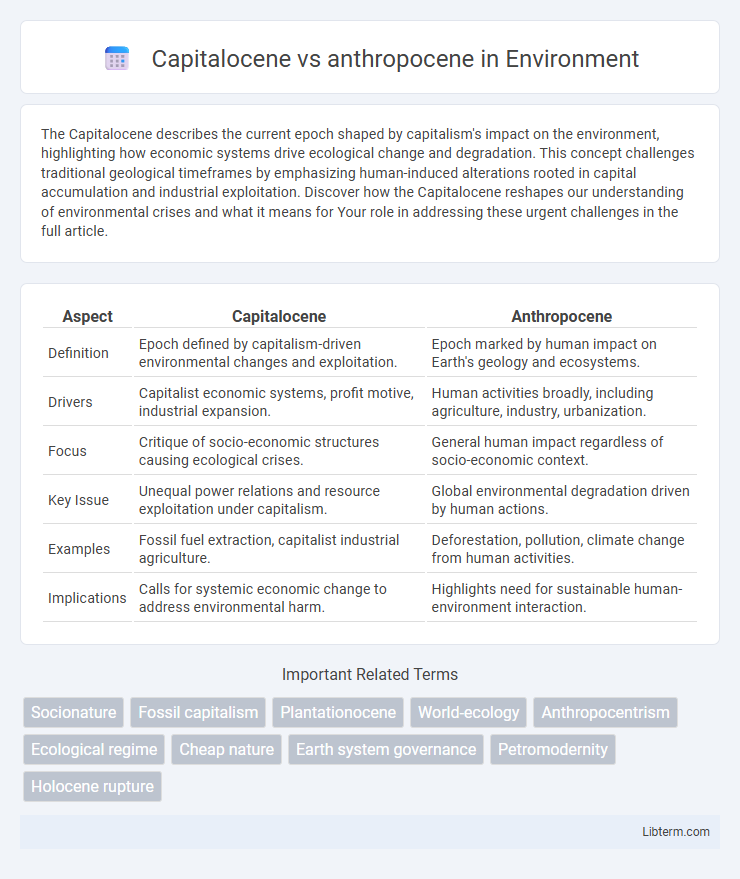
| Aspect | Capitalocene | Anthropocene |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Epoch defined by capitalism-driven environmental changes and exploitation. | Epoch marked by human impact on Earth's geology and ecosystems. |
| Drivers | Capitalist economic systems, profit motive, industrial expansion. | Human activities broadly, including agriculture, industry, urbanization. |
| Focus | Critique of socio-economic structures causing ecological crises. | General human impact regardless of socio-economic context. |
| Key Issue | Unequal power relations and resource exploitation under capitalism. | Global environmental degradation driven by human actions. |
| Examples | Fossil fuel extraction, capitalist industrial agriculture. | Deforestation, pollution, climate change from human activities. |
| Implications | Calls for systemic economic change to address environmental harm. | Highlights need for sustainable human-environment interaction. |
Understanding the Anthropocene: Defining a New Epoch
The Anthropocene marks a geological epoch defined by significant human impact on Earth's systems, highlighting widespread environmental changes such as climate alteration and biodiversity loss. The Capitalocene concept reinterprets this epoch by emphasizing capitalism's role in driving unequal resource exploitation and environmental degradation. Understanding these frameworks clarifies the socio-economic drivers behind planetary shifts, essential for developing sustainable policies and mitigating ecological crises.
The Rise of the Capitalocene Perspective
The Capitalocene perspective emphasizes the central role of capitalism in driving ecological destruction and climate change, challenging the Anthropocene narrative that attributes environmental impacts to humanity as a whole. It highlights the historical rise of capital accumulation and industrial capitalism since the 15th century as key factors in accelerating carbon emissions and resource exploitation. Scholars argue that understanding global environmental crises requires analyzing socio-economic systems and power relations inherent to the capitalist mode of production.
Historical Origins: From Agriculture to Industrialization
The Capitalocene concept highlights the historical origins of environmental change rooted in the rise of capitalism, tracing its impact from early agricultural practices to industrialization. Unlike the Anthropocene, which attributes ecological crisis broadly to human activity, the Capitalocene emphasizes the role of capitalist modes of production and accumulation since the 15th century. This perspective connects industrialization's reliance on fossil fuels and colonial exploitation to systemic environmental transformation and social inequality.
Capitalism’s Role in Shaping the Planet
Capitalocene frames environmental degradation as a consequence of capitalist modes of production prioritizing profit over ecological balance, contrasting with the Anthropocene's broader attribution to human activity. Capitalism's expansion drives resource extraction and carbon emissions, intensifying climate change and biodiversity loss through industrial-scale exploitation. This perspective highlights systemic economic incentives as central to planetary crises, urging structural changes beyond individual behaviors.
Human Impact vs. Systemic Drivers of Change
The Anthropocene emphasizes human impact on the environment as a collective species, highlighting alterations in climate, biodiversity, and geochemical cycles driven by population growth and consumption patterns. In contrast, the Capitalocene centers on systemic drivers, attributing ecological degradation to capitalist modes of production, profit maximization, and resource extraction that prioritize economic growth over sustainability. This distinction underscores how structural socio-economic factors, rather than humanity as a whole, are critical in shaping environmental crises.
Debates and Controversies: Anthropocene or Capitalocene?
The debate between Anthropocene and Capitalocene centers on whether the current geological epoch is driven by humanity as a whole or specifically by capitalist systems and their environmental impacts. Proponents of the Anthropocene emphasize broad human influence on Earth's geology and ecosystems, while advocates for the Capitalocene highlight the role of capitalist exploitation, colonialism, and socio-economic inequalities in shaping environmental degradation. This controversy reflects deeper disagreements about the causes of ecological crises and the potential pathways for sustainable futures.
Environmental Consequences of Capital Accumulation
The Capitalocene framework emphasizes how capitalist-driven capital accumulation intensifies environmental degradation through relentless resource extraction and ecosystem exploitation, surpassing the general anthropogenic impacts described by the Anthropocene. This paradigm highlights the systemic prioritization of profit maximization, leading to deforestation, biodiversity loss, and increased greenhouse gas emissions predominantly from industrialized production processes. Such dynamics underscore the critique that environmental crises are rooted in socio-economic structures rather than merely human presence on the planet.
Reframing Accountability: Who Drives Ecological Crisis?
The Capitalocene framework reframes accountability by attributing ecological crisis primarily to capitalist modes of production and their relentless drive for profit, contrasting with the broader Anthropocene concept that implicates humanity as a whole. This perspective highlights systemic economic structures and power dynamics as the root causes of environmental degradation, shifting focus from individual actions to corporate and governmental responsibilities. Recognizing the Capitalocene emphasizes the need for transformative policies targeting capitalism's extractive practices to address climate change and biodiversity loss effectively.
Moving Beyond Labels: Implications for Environmental Policy
The Capitalocene framework reframes environmental degradation as a consequence of capitalist exploitation and systemic economic growth rather than human activity in general, offering a more precise critique than the Anthropocene concept. This perspective encourages environmental policies that target structural inequalities, corporate accountability, and sustainable economic reforms instead of solely focusing on technological fixes or individual behavioral change. Emphasizing the Capitalocene can drive transformative climate justice initiatives that address root causes and promote equitable resource management.
Imagining Futures: Solutions in the Anthropocene and Capitalocene
Imagining futures in the Anthropocene emphasizes sustainable practices that address human-induced environmental changes through technological innovation and global cooperation. In contrast, solutions in the Capitalocene critique prioritize dismantling capitalist systems driving ecological destruction, advocating for systemic social and economic transformations. Both perspectives highlight the urgent need for equitable and effective strategies to mitigate climate change and promote planetary health.
Capitalocene Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com