Abiotic factors encompass non-living elements like temperature, sunlight, water, and soil composition that significantly influence ecosystems and organism survival. Understanding these components is crucial for grasping how environments function and change over time. Explore the rest of the article to discover how abiotic factors shape the natural world around you.
Table of Comparison
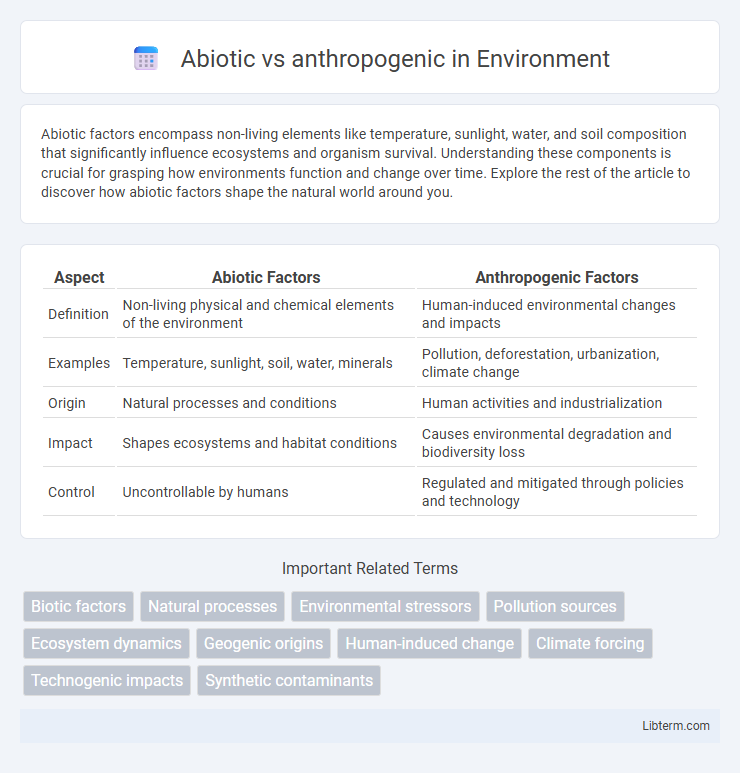
| Aspect | Abiotic Factors | Anthropogenic Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-living physical and chemical elements of the environment | Human-induced environmental changes and impacts |
| Examples | Temperature, sunlight, soil, water, minerals | Pollution, deforestation, urbanization, climate change |
| Origin | Natural processes and conditions | Human activities and industrialization |
| Impact | Shapes ecosystems and habitat conditions | Causes environmental degradation and biodiversity loss |
| Control | Uncontrollable by humans | Regulated and mitigated through policies and technology |
Understanding Abiotic and Anthropogenic Factors
Abiotic factors refer to non-living physical and chemical elements such as temperature, sunlight, and soil composition that shape ecosystems and influence species survival. Anthropogenic factors involve human activities like deforestation, pollution, and urbanization, which significantly impact environmental balance and biodiversity. Understanding the distinction between abiotic and anthropogenic factors is crucial for effective environmental management and sustainable development strategies.
Defining Abiotic Influences in Ecosystems
Abiotic influences in ecosystems refer to non-living physical and chemical factors such as sunlight, temperature, water availability, soil composition, and atmospheric gases that shape habitat conditions and affect organism survival. These abiotic elements regulate energy flow, nutrient cycling, and ecosystem productivity by creating environmental constraints and opportunities for various species. Understanding abiotic factors is crucial for distinguishing natural ecosystem dynamics from anthropogenic impacts caused by human activities like pollution and habitat alteration.
Anthropogenic Impact: What Does It Mean?
Anthropogenic impact refers to the environmental changes caused directly or indirectly by human activities such as deforestation, industrial pollution, and urbanization. These impacts result in habitat destruction, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and loss of biodiversity, significantly altering natural ecosystems. Understanding anthropogenic factors is critical for developing sustainable practices and mitigating climate change effects.
Key Differences Between Abiotic and Anthropogenic Factors
Abiotic factors refer to non-living physical and chemical elements in the environment such as temperature, sunlight, and soil composition, while anthropogenic factors result from human activities including pollution, deforestation, and urbanization. Abiotic factors naturally regulate ecosystem functions, whereas anthropogenic factors often disrupt ecological balance leading to environmental degradation. The key distinction lies in the origin: abiotic factors are natural environmental components, and anthropogenic factors are human-induced changes impacting habitats and climate.
Examples of Abiotic Forces Affecting the Environment
Abiotic forces affecting the environment include natural phenomena such as volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, earthquakes, and droughts, which can drastically alter ecosystems and landscape formations. These non-living factors influence soil composition, water availability, and atmospheric conditions, impacting plant and animal life. Unlike anthropogenic forces caused by human activities, abiotic factors operate independently of human influence and drive natural environmental changes.
Human Activities and Their Environmental Consequences
Human activities such as deforestation, fossil fuel combustion, and industrial processes contribute significantly to anthropogenic environmental changes, including increased greenhouse gas emissions and habitat destruction. These activities accelerate climate change, leading to more extreme weather patterns and biodiversity loss, which differ from natural abiotic processes like volcanic eruptions or solar radiation fluctuations. Understanding the scale and impact of human-induced changes is crucial for developing sustainable practices to mitigate environmental consequences.
Interactions Between Abiotic and Anthropogenic Elements
Interactions between abiotic and anthropogenic elements shape ecosystems by altering natural processes such as nutrient cycling, water availability, and soil composition. Anthropogenic activities like urbanization, deforestation, and pollution modify abiotic factors including temperature, pH, and atmospheric gases, resulting in changes to biodiversity and ecosystem services. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for developing sustainable environmental management and mitigating human impact on natural systems.
Measuring the Effects of Abiotic vs Anthropogenic Factors
Measuring the effects of abiotic versus anthropogenic factors involves analyzing environmental indicators such as temperature fluctuations, soil composition, pollutant concentrations, and biodiversity changes. Remote sensing technologies and geographic information systems (GIS) provide precise spatial and temporal data to distinguish natural variability from human-induced alterations. Long-term monitoring and statistical models help quantify the relative impact of climate variability, volcanic activity, and industrial emissions on ecosystems.
Mitigation Strategies for Anthropogenic Impacts
Mitigation strategies for anthropogenic impacts concentrate on reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy adoption, enhancing energy efficiency, and implementing carbon capture technologies. Urban planning improvements, such as green infrastructure and sustainable transportation, play a crucial role in minimizing human-induced environmental degradation. Policy frameworks like carbon pricing, emission regulations, and international agreements further support the reduction of anthropogenic environmental stressors.
Future Trends in Managing Environmental Influences
Future trends in managing environmental influences emphasize advanced monitoring technologies to differentiate between abiotic and anthropogenic factors affecting ecosystems. Sustainable development initiatives leverage big data and AI to predict and mitigate human-driven environmental changes while preserving natural abiotic processes. Increased investment in green infrastructure and regulatory frameworks aims to balance economic growth with the reduction of anthropogenic impacts on climate and biodiversity.
Abiotic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com