An aquifuge is a geological formation that completely resists the flow of groundwater due to its extremely low permeability. It acts as a barrier, preventing water from passing through layers of rock or sediment, which significantly affects the movement and storage of groundwater in aquifers. Discover how understanding aquifuges can help You better manage water resources by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
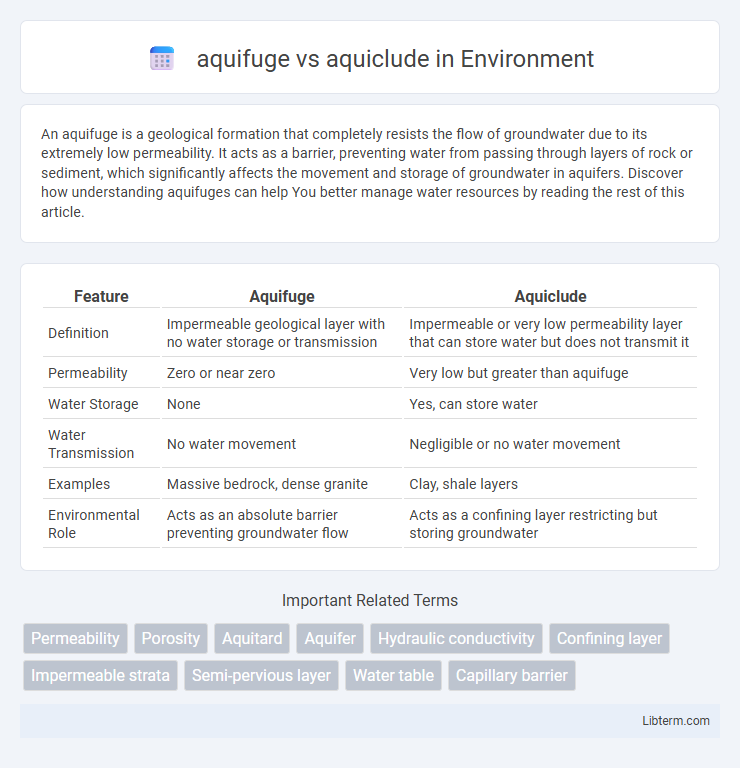
| Feature | Aquifuge | Aquiclude |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Impermeable geological layer with no water storage or transmission | Impermeable or very low permeability layer that can store water but does not transmit it |
| Permeability | Zero or near zero | Very low but greater than aquifuge |
| Water Storage | None | Yes, can store water |
| Water Transmission | No water movement | Negligible or no water movement |
| Examples | Massive bedrock, dense granite | Clay, shale layers |
| Environmental Role | Acts as an absolute barrier preventing groundwater flow | Acts as a confining layer restricting but storing groundwater |
Introduction to Aquifuge and Aquiclude
An aquifuge is a geological formation that is completely impermeable, preventing any water flow or storage, often composed of dense, non-porous rock like granite or marble. In contrast, an aquiclude is a permeable layer that contains water but restricts its flow due to low permeability, commonly made up of shale or claystone. Both aquifuges and aquicludes play crucial roles in hydrogeology by influencing groundwater movement and availability in subsurface environments.
Definition of Aquifuge
An aquifuge is a geological formation that neither contains nor transmits groundwater due to its impermeable nature, effectively acting as a barrier to water flow. In contrast, an aquiclude also restricts water movement but may contain some water within its pores, making it a confining layer rather than a completely impermeable one. Understanding the distinction between aquifuge and aquiclude is crucial for hydrogeological studies and groundwater management.
Definition of Aquiclude
An aquiclude is a geological formation that acts as an impermeable barrier, preventing the flow of groundwater due to its low porosity and permeability. In contrast, an aquifuge is a rock or sediment unit that is completely impermeable and does not store or transmit water at all. Understanding the definition of an aquiclude is crucial for groundwater management, as it helps delineate boundaries of aquifers and controls water movement below the surface.
Key Differences Between Aquifuge and Aquiclude
An aquifuge is a geological formation that neither transmits nor stores groundwater due to its impermeable and non-porous nature, effectively blocking water flow. In contrast, an aquiclude has very low permeability but can store water within its porous spaces, allowing it to act as a barrier that restricts groundwater movement without completely obstructing it. The primary key difference lies in aquifuges lacking porosity and permeability, while aquicludes possess porosity but exhibit minimal permeability.
Geological Formation Processes
Aquifuges form through lithification and cementation, creating impermeable layers such as shale or unfractured crystalline rocks that prevent water flow entirely. Aquicludes develop from fine-grained sediments like clay or silt deposited in low-energy environments, resulting in low permeability but occasional minor water passage. Both play critical roles in hydrogeology by influencing groundwater movement and storage within sedimentary basins and crystalline bedrock settings.
Water Movement and Storage Characteristics
Aquifuges are impermeable geologic formations that both prevent water movement and lack water storage capacity, effectively acting as barriers to groundwater flow. Aquicludes, while also impermeable or nearly impermeable, may contain small amounts of water but allow negligible water movement, thereby restricting groundwater transmission. The key difference lies in their ability to store minimal water in aquicludes versus the complete absence of water storage in aquifuges, influencing groundwater recharge and flow dynamics.
Examples of Aquifuge in Nature
Aquifuges are geological formations that prevent water movement by being completely impermeable and unsaturated, such as granite and unfractured basalt. Unlike aquicludes, which can store water but hinder its flow, aquifuges do not hold water at all due to their extremely low porosity and permeability. Examples of natural aquifuges include massive crystalline rocks and dense claystone layers that act as barriers to groundwater flow.
Examples of Aquiclude in Nature
Aquicludes are geological formations that completely restrict water flow due to their impermeable properties, with common natural examples including clay, shale, and unfractured granite. These materials prevent groundwater movement and serve as barriers in hydrogeological systems, contrasting with aquifuges, which are impermeable but may not contain water. In nature, clay layers within sedimentary basins and thick shale formations in mountainous regions often act as effective aquicludes by sealing off aquifers.
Importance in Hydrogeology and Water Management
Aquifuges and aquicludes differ in their ability to transmit water, with aquifuges being completely impermeable and aquicludes allowing minimal water passage, making aquiculdes crucial for confining aquifers and directing groundwater flow. Understanding these distinctions drives effective well placement, aquifer recharge, and contamination prevention strategies in hydrogeology. Proper identification of aquifuges and aquicludes enables sustainable water management by controlling groundwater movement and protecting water resources.
Summary: Aquifuge vs Aquiclude
An aquifuge is a geological formation that neither contains nor transmits water due to its impermeable nature, acting as a complete barrier to groundwater flow. In contrast, an aquiclude is a water-bearing formation that holds water but has very low permeability, significantly restricting the movement of groundwater. Understanding the differences between aquifuges and aquicludes is crucial for hydrogeological assessments and groundwater management.
aquifuge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com