Direct push sampling offers a rapid and efficient method for collecting soil and groundwater samples by directly advancing a probe into subsurface materials. This technique minimizes disturbance and provides reliable data crucial for environmental assessments and contamination investigations. Explore the rest of the article to understand how this method can enhance your site characterization efforts.
Table of Comparison
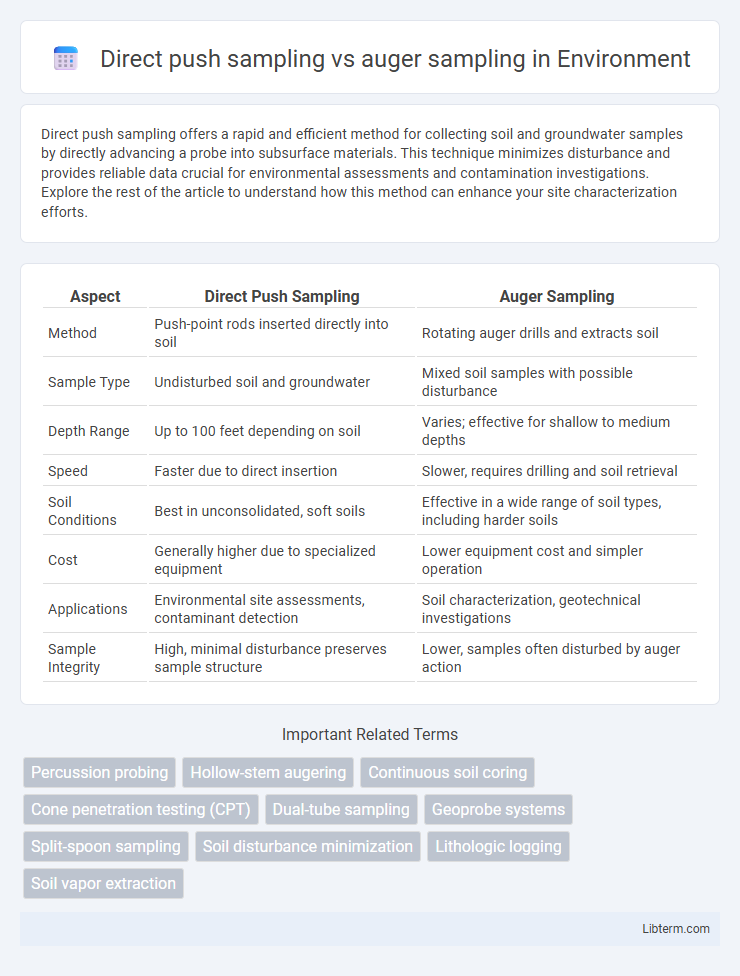
| Aspect | Direct Push Sampling | Auger Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Push-point rods inserted directly into soil | Rotating auger drills and extracts soil |
| Sample Type | Undisturbed soil and groundwater | Mixed soil samples with possible disturbance |
| Depth Range | Up to 100 feet depending on soil | Varies; effective for shallow to medium depths |
| Speed | Faster due to direct insertion | Slower, requires drilling and soil retrieval |
| Soil Conditions | Best in unconsolidated, soft soils | Effective in a wide range of soil types, including harder soils |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized equipment | Lower equipment cost and simpler operation |
| Applications | Environmental site assessments, contaminant detection | Soil characterization, geotechnical investigations |
| Sample Integrity | High, minimal disturbance preserves sample structure | Lower, samples often disturbed by auger action |
Introduction to Soil Sampling Methods
Direct push sampling uses a hydraulic-powered rig to drive sampling tools into the ground, capturing continuous soil cores for detailed stratigraphic analysis and contaminant profiling. Auger sampling involves rotating a helical screw into the soil to extract samples, commonly used for shallow depths and coarse material identification. Selection between direct push and auger sampling depends on factors like soil type, depth, site conditions, and desired data resolution in environmental and geotechnical investigations.
Overview of Direct Push Sampling
Direct push sampling involves driving a hollow rod or probe directly into the subsurface to collect soil, groundwater, or vapor samples without the need for drilling fluids. This method provides rapid data collection and minimal site disturbance, making it ideal for environmental assessments and site characterization. Its precision in obtaining discrete samples at specific depths offers significant advantages over auger sampling, which often disturbs stratigraphy and generates waste cuttings.
Overview of Auger Sampling
Auger sampling involves using a helical screw blade to extract soil samples from shallow depths, providing quick and continuous collection of soil profiles. This method is highly effective for heterogeneous soil environments where detailed stratigraphic information is needed, offering better precision than direct push sampling in non-cohesive soils. Auger sampling is widely used in environmental investigations, geotechnical studies, and mineral exploration due to its simplicity and ability to recover relatively undisturbed samples.
Key Differences Between Direct Push and Auger Sampling
Direct push sampling utilizes a hydraulic ram to drive sampling tools into the subsurface quickly, offering high-resolution vertical profiling of soil and groundwater contaminants. Auger sampling relies on a helical screw to extract soil samples, providing larger, more discrete soil intervals but with slower penetration and potential for sample disturbance. Key differences include the speed and precision of sample collection, sample integrity, and suitability for varying soil types and contamination conditions.
Advantages of Direct Push Sampling
Direct push sampling offers faster and more cost-effective site characterization compared to auger sampling by minimizing soil disturbance and reducing the need for drilling fluid. This method enables real-time data collection and precise placement of sensors or samplers, enhancing accuracy in volatile or liquid contamination assessments. Its adaptability to various subsurface conditions makes it ideal for shallow to medium-depth environmental investigations.
Advantages of Auger Sampling
Auger sampling offers significant advantages such as deeper penetration into soil layers, providing more continuous and undisturbed core samples compared to direct push sampling. This method enables accurate stratigraphic profiling and is effective in both soft and compacted soils, enhancing data reliability for geotechnical and environmental analysis. Auger sampling also allows for larger sample volumes, facilitating comprehensive laboratory testing and contaminant assessment.
Limitations of Each Sampling Technique
Direct push sampling often encounters limitations in coarse-grained or highly compacted soils where probe advancement is difficult, leading to potential sample disturbance and biased results. Auger sampling is constrained by the inability to obtain uncontaminated or representative samples in saturated or loose sediments due to soil mixing and sample loss during auger rotation. Both methods may fail to capture accurate stratigraphic boundaries in heterogeneous subsurface conditions, impacting the reliability of soil property assessments.
Applications in Environmental Site Assessment
Direct push sampling enables rapid collection of continuous soil and groundwater samples, making it ideal for delineating contamination plumes and assessing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in environmental site assessments. Auger sampling provides discrete soil samples useful for identifying stratigraphy and assessing heavy metal concentrations, especially in sites with heterogeneous subsurface conditions. Combining direct push and auger methods enhances data reliability for comprehensive contaminant characterization and risk evaluation.
Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Direct push sampling offers lower operational costs and faster deployment compared to auger sampling, making it ideal for shallow subsurface investigations where rapid data collection is essential. Auger sampling typically incurs higher expenses due to the need for more specialized equipment and longer setup times but provides deeper sample extraction capabilities. Efficiency in direct push methods is enhanced by minimal soil disturbance and quicker turnaround, while auger sampling excels in heterogeneous soil conditions requiring comprehensive sample profiles.
Choosing the Right Soil Sampling Method
Direct push sampling offers rapid collection of undisturbed soil cores with high resolution in stratified soil profiles, ideal for environmental site assessments and contamination delineation. Auger sampling allows deeper soil penetration and is effective in a variety of soil types, making it suitable for agricultural surveys and geotechnical investigations. Selecting the right soil sampling method depends on factors such as soil type, depth requirements, site conditions, and the specific objectives of the soil analysis.
Direct push sampling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com