Transpiration is the process by which water vapor is released from plants into the atmosphere, playing a crucial role in the water cycle and plant health. This natural mechanism helps regulate temperature and maintain nutrient flow within your plants. Explore the rest of the article to understand how transpiration impacts ecosystems and agriculture.
Table of Comparison
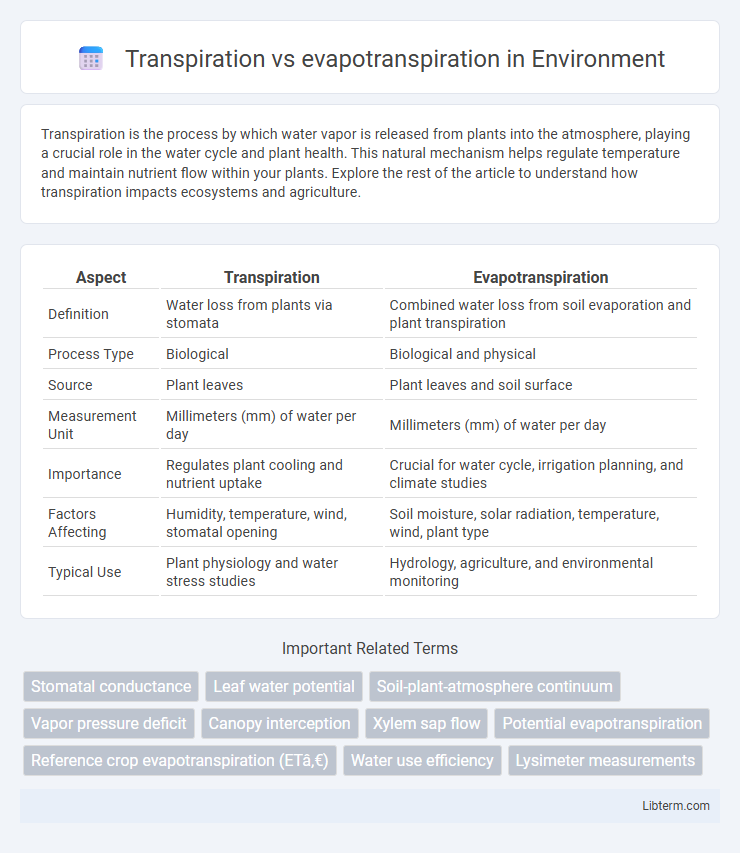
| Aspect | Transpiration | Evapotranspiration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water loss from plants via stomata | Combined water loss from soil evaporation and plant transpiration |
| Process Type | Biological | Biological and physical |
| Source | Plant leaves | Plant leaves and soil surface |
| Measurement Unit | Millimeters (mm) of water per day | Millimeters (mm) of water per day |
| Importance | Regulates plant cooling and nutrient uptake | Crucial for water cycle, irrigation planning, and climate studies |
| Factors Affecting | Humidity, temperature, wind, stomatal opening | Soil moisture, solar radiation, temperature, wind, plant type |
| Typical Use | Plant physiology and water stress studies | Hydrology, agriculture, and environmental monitoring |
Introduction to Transpiration and Evapotranspiration
Transpiration is the process where water is absorbed by plant roots, moves through the plant, and evaporates from stomata in leaves, playing a key role in the water cycle and plant physiology. Evapotranspiration combines transpiration and evaporation from soil and plant surfaces, representing a major component of water loss in ecosystems. Understanding the differences between these processes is crucial for agricultural water management, climate modeling, and ecosystem sustainability.
Defining Transpiration
Transpiration is the biological process by which moisture is absorbed by plant roots, transported through the plant, and released as water vapor through stomata in leaves. It plays a critical role in regulating plant temperature and maintaining nutrient flow within the plant system. Unlike evapotranspiration, which combines both evaporation from soil and transpiration from plants, transpiration specifically refers to water movement through and from plants.
Defining Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration combines the processes of transpiration from plants and evaporation from soil and water surfaces, representing the total water vapor flux from the land to the atmosphere. It is a key component in the hydrological cycle, influencing water balance, crop growth, and climate models. Accurate measurement of evapotranspiration is essential for effective irrigation management, drought assessment, and environmental monitoring.
Key Differences Between Transpiration and Evapotranspiration
Transpiration refers specifically to the process by which water is absorbed by plant roots, moves through plants, and evaporates from leaf surfaces. Evapotranspiration encompasses both transpiration and evaporation from soil and other surfaces, representing the total water loss to the atmosphere in a given area. Key differences include that transpiration is a biological process limited to plants, whereas evapotranspiration combines biological and physical water loss mechanisms affecting the entire ecosystem.
Scientific Processes Involved
Transpiration is the process by which water is absorbed by plant roots, moves through the plant, and evaporates from small pores called stomata on leaves, playing a critical role in nutrient uptake and temperature regulation. Evapotranspiration combines transpiration and evaporation from soil and other surfaces, representing the total water vapor flux from the land to the atmosphere. Scientific analysis of these processes involves measuring stomatal conductance, leaf water potential, and soil moisture content to understand water cycling and energy balance in ecosystems.
Factors Influencing Transpiration
Transpiration is primarily influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and light intensity, which regulate the opening and closing of stomata in plant leaves. Soil moisture availability directly impacts the rate of transpiration by affecting root water uptake. Plant species characteristics, including leaf area and stomatal density, also play crucial roles in determining transpiration rates compared to the combined process of evapotranspiration that includes soil evaporation.
Factors Influencing Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration rates are primarily influenced by factors such as temperature, solar radiation, humidity, wind speed, and soil moisture availability. Vegetation type and density also play a crucial role, as different plants exhibit varying transpiration rates based on leaf area and stomatal conductance. Understanding these elements is essential for accurate water cycle modeling and irrigation management in agriculture.
Importance in the Water Cycle
Transpiration is the process where plants release water vapor from their leaves, significantly contributing to atmospheric moisture and local humidity. Evapotranspiration combines transpiration and evaporation from soil and plant surfaces, representing a critical component in the hydrological cycle by regulating water transfer between land and atmosphere. Understanding evapotranspiration rates helps in water resource management, agricultural planning, and predicting climate patterns due to its role in balancing soil moisture and atmospheric water content.
Applications in Agriculture and Environmental Science
Transpiration, the process by which plants release water vapor through stomata, directly influences crop water requirements and irrigation scheduling in agriculture. Evapotranspiration, combining soil evaporation and plant transpiration, serves as a critical metric for managing water resources and predicting drought impacts in environmental science. Accurate measurement of evapotranspiration supports precision agriculture by optimizing water use efficiency and enhancing sustainable land management practices.
Summary and Comparative Analysis
Transpiration is the process where plants release water vapor through stomata, playing a crucial role in the water cycle and plant physiology. Evapotranspiration combines transpiration and evaporation from soil and plant surfaces, representing the total water loss to the atmosphere in ecosystems. Comparative analysis highlights that evapotranspiration provides a holistic measure of water flux in agricultural and natural environments, whereas transpiration specifically quantifies plant-driven water vapor exchange.
Transpiration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com