Nature reserves protect diverse ecosystems, preserving wildlife habitats and promoting biodiversity conservation. These protected areas offer opportunities for scientific research, eco-tourism, and environmental education. Discover how nature reserves contribute to a healthier planet and what role you can play by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
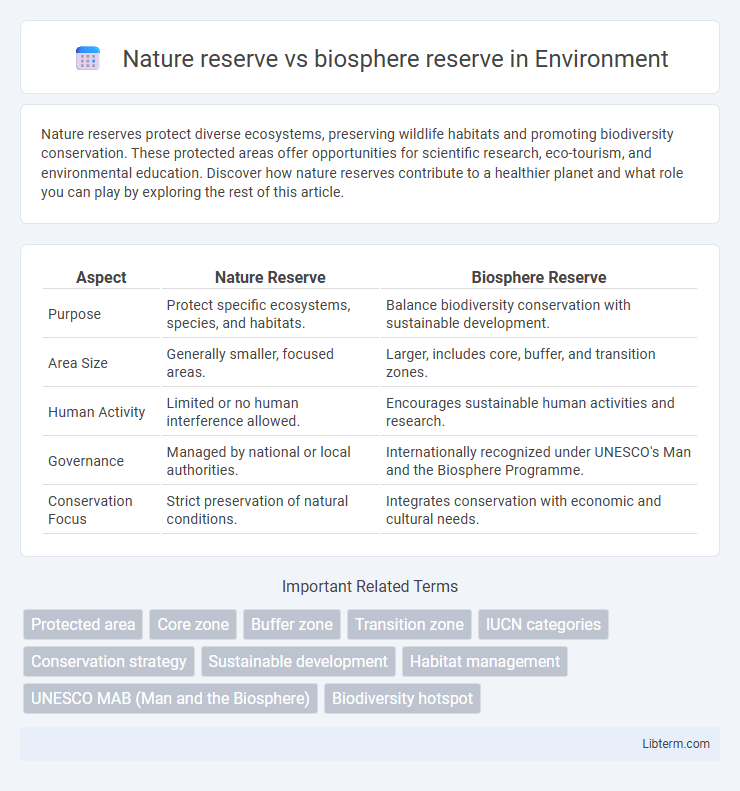
| Aspect | Nature Reserve | Biosphere Reserve |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protect specific ecosystems, species, and habitats. | Balance biodiversity conservation with sustainable development. |
| Area Size | Generally smaller, focused areas. | Larger, includes core, buffer, and transition zones. |
| Human Activity | Limited or no human interference allowed. | Encourages sustainable human activities and research. |
| Governance | Managed by national or local authorities. | Internationally recognized under UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere Programme. |
| Conservation Focus | Strict preservation of natural conditions. | Integrates conservation with economic and cultural needs. |
Introduction to Nature Reserves and Biosphere Reserves
Nature reserves are protected areas designated primarily for the conservation of wildlife and natural habitats, often restricting human activity to preserve biodiversity. Biosphere reserves, recognized by UNESCO, integrate conservation with sustainable development by combining core protected zones, buffer areas, and transition zones that support ecological research and community involvement. Both play crucial roles in preserving ecosystems, but biosphere reserves emphasize harmonizing human-nature interactions alongside strict conservation efforts.
Defining Nature Reserves
Nature reserves are protected areas designated primarily for the conservation of specific ecosystems, wildlife, and natural features, often restricting human activities to preserve biodiversity. These reserves prioritize the maintenance of habitats in their natural state, serving as critical sites for scientific research and environmental monitoring. In contrast, biosphere reserves integrate conservation with sustainable human development, promoting coexistence between people and nature through zoning that balances protection, sustainable use, and logistic support functions.
Defining Biosphere Reserves
Biosphere reserves are areas designated by UNESCO under the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme, aiming to reconcile biodiversity conservation with sustainable use of natural resources. Unlike nature reserves, which primarily focus on strict protection of ecosystems and wildlife, biosphere reserves integrate conservation, research, and community development through zonation into core, buffer, and transition areas. These reserves serve as living laboratories for testing and demonstrating sustainable development practices while preserving genetic diversity and ecosystem services.
Core Differences Between Nature and Biosphere Reserves
Nature reserves prioritize the protection of specific species and habitats with strict restrictions on human activities, emphasizing conservation and scientific research. Biosphere reserves integrate core protected areas with buffer and transition zones, promoting sustainable development alongside conservation efforts. The core difference lies in biosphere reserves incorporating human communities and sustainable use, while nature reserves focus primarily on preserving natural ecosystems with minimal human interference.
Conservation Goals and Approaches
Nature reserves prioritize strict protection of flora and fauna through limited human intervention, aiming to preserve biodiversity and maintain natural habitats intact. Biosphere reserves integrate conservation with sustainable development by combining core protected areas, buffer zones, and zones for human activity, promoting ecosystem restoration alongside community engagement. Conservation approaches in biosphere reserves emphasize balancing ecological preservation with socio-economic wellbeing, contrasting with the primarily preservation-focused strategies of nature reserves.
Levels of Protection and Human Activity
Nature reserves offer stringent protection by limiting human activities primarily to conservation and scientific research, ensuring minimal ecological disturbance. Biosphere reserves balance conservation with sustainable human activities, integrating core protected areas with surrounding zones that allow controlled resource use and community engagement. This zoned approach in biosphere reserves promotes biodiversity preservation alongside traditional livelihoods and environmental education.
Role in Biodiversity Preservation
Nature reserves serve as protected areas primarily focused on conserving specific species and their natural habitats, ensuring minimal human disturbance to maintain ecological balance. Biosphere reserves encompass broader zones that integrate core protected areas with buffer and transition zones, promoting sustainable development alongside biodiversity conservation. These reserves play a critical role in preserving genetic diversity, supporting ecosystem services, and facilitating research on sustainable interactions between humans and nature.
Management and Governance Structures
Nature reserves operate under local or national management with strict conservation regulations enforced by government agencies or NGOs, emphasizing habitat protection and species preservation. Biosphere reserves follow a zoning system integrating core protected areas with buffer zones and transition areas, managed through collaborative governance involving multiple stakeholders including local communities, scientists, and policymakers. This multi-layered management approach in biosphere reserves promotes sustainable development alongside biodiversity conservation, contrasting with the more rigid, protection-focused governance of nature reserves.
International Recognition and UNESCO’s Role
Nature reserves primarily emphasize local or national biodiversity protection with limited international status, whereas biosphere reserves receive formal recognition under UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme, highlighting their global significance in conservation and sustainable development. UNESCO designates biosphere reserves to promote interdisciplinary research, education, and collaboration across international borders, integrating human activity with biodiversity conservation. This international recognition elevates biosphere reserves as exemplary models of balancing ecological preservation with social and economic needs, a status not typically granted to nature reserves.
Choosing Between a Nature Reserve and Biosphere Reserve
Choosing between a nature reserve and a biosphere reserve depends on conservation goals and land use priorities; nature reserves emphasize strict protection of biodiversity with limited human interference, while biosphere reserves integrate conservation with sustainable development and research activities. Nature reserves prioritize preserving specific habitats or species in pristine conditions, often prohibiting resource extraction and public access. Biosphere reserves balance ecological preservation with learning and cooperation by zoning areas for core conservation, buffer activities, and sustainable human interaction.
Nature reserve Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com