Retention ponds manage stormwater by collecting and holding runoff to prevent flooding and improve water quality. These ponds allow sediment and pollutants to settle, protecting local waterways from contamination. Explore the rest of the article to learn how retention ponds can benefit your property and community.
Table of Comparison
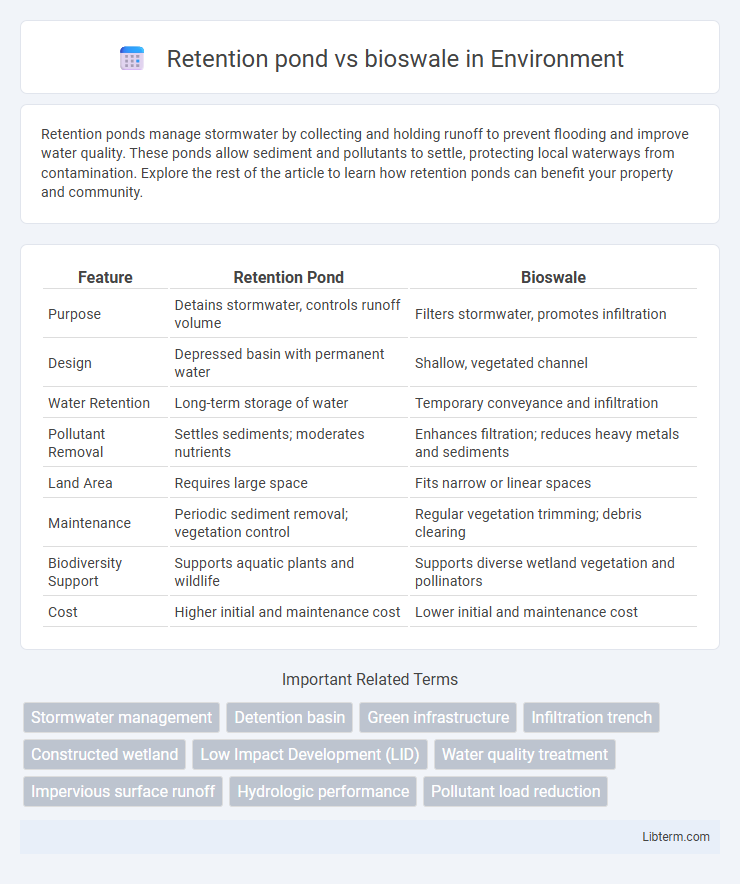
| Feature | Retention Pond | Bioswale |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detains stormwater, controls runoff volume | Filters stormwater, promotes infiltration |
| Design | Depressed basin with permanent water | Shallow, vegetated channel |
| Water Retention | Long-term storage of water | Temporary conveyance and infiltration |
| Pollutant Removal | Settles sediments; moderates nutrients | Enhances filtration; reduces heavy metals and sediments |
| Land Area | Requires large space | Fits narrow or linear spaces |
| Maintenance | Periodic sediment removal; vegetation control | Regular vegetation trimming; debris clearing |
| Biodiversity Support | Supports aquatic plants and wildlife | Supports diverse wetland vegetation and pollinators |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower initial and maintenance cost |
Introduction to Retention Ponds and Bioswales
Retention ponds and bioswales are essential stormwater management systems designed to control runoff and improve water quality. Retention ponds temporarily store stormwater, allowing sediments and pollutants to settle before gradual release, while bioswales use vegetation and soil to filter and absorb runoff along defined channels. Both systems reduce flooding risks and enhance groundwater recharge, but retention ponds emphasize detention capacity, and bioswales prioritize filtration through natural processes.
Key Differences Between Retention Ponds and Bioswales
Retention ponds are designed to collect and store stormwater, allowing sediment and pollutants to settle out before controlled release, whereas bioswales promote infiltration through vegetated, sloped channels that filter runoff naturally. Retention ponds typically have a permanent pool of water, serving as a detention basin, while bioswales operate as linear landscapes relying on soil and plants for water treatment. The key differences lie in water storage duration, structural design, and mechanisms of pollutant removal.
How Retention Ponds Work
Retention ponds function by collecting and holding stormwater runoff in a designed basin, allowing sediments and pollutants to settle before the water slowly infiltrates into the ground or is released at a controlled rate. These ponds reduce flood risk and improve water quality by trapping contaminants and promoting biological processes like sedimentation and microbial breakdown. Unlike bioswales, retention ponds maintain a permanent pool of water, enabling continuous treatment and habitat provision.
How Bioswales Work
Bioswales function as engineered channels designed to manage stormwater runoff by filtering pollutants through vegetation and engineered soil. These systems slow water flow, promoting infiltration and sediment capture, which reduces contamination before water enters natural waterways. Unlike retention ponds that primarily store water, bioswales actively treat runoff using plants and microbial activity to improve water quality.
Benefits of Retention Ponds
Retention ponds effectively manage stormwater by temporarily storing runoff, reducing flood risks, and improving water quality through sedimentation and pollutant removal. They provide extended water retention times, allowing natural infiltration and supporting groundwater recharge. Retention ponds also create valuable habitats for wildlife, enhance aesthetic appeal in urban planning, and require relatively low maintenance compared to other stormwater management systems.
Advantages of Bioswales
Bioswales offer superior stormwater management by enhancing groundwater recharge through natural infiltration processes, reducing runoff volume and pollutant loads more effectively than retention ponds. Their vegetated design promotes habitat creation and improves water quality by filtering sediments and contaminants before they reach water bodies. Maintenance of bioswales is generally lower cost and less intensive, supporting sustainable urban drainage systems and contributing to green infrastructure goals.
Suitability for Urban and Rural Environments
Retention ponds are highly suitable for both urban and rural environments, effectively managing large volumes of stormwater while providing flood control and water quality benefits. Bioswales, with their narrow, vegetated channels, are particularly well-suited for urban areas where space is limited and they can integrate seamlessly into streetscapes and parking lots. In rural settings, retention ponds are preferred due to their larger footprint and ability to support local wildlife habitats, whereas bioswales may require more maintenance and space constraints.
Cost Comparison: Retention Pond vs Bioswale
Retention ponds generally require higher initial construction costs due to extensive excavation, liner installation, and larger land requirements, while bioswales often involve lower upfront expenses by utilizing natural vegetation and minimal earthwork. Maintenance costs for retention ponds can be substantial, as they need regular sediment removal, water quality monitoring, and structural repairs; bioswales typically demand less intensive maintenance focused on plant care and debris removal. Overall, bioswales offer a cost-effective stormwater management solution for urban areas with limited space, whereas retention ponds are more suitable for large-scale developments with available land and budget.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Retention ponds reduce stormwater runoff by capturing and slowly releasing water, aiding in flood control and sediment settling, but can create stagnant water habitats that may detrimentally affect local ecosystems. Bioswales enhance sustainability by using vegetation and soil to filter pollutants, promote groundwater recharge, and support biodiversity, making them effective for improving water quality and reducing urban heat island effects. Both systems contribute to environmental management, but bioswales offer superior ecological benefits through natural filtration and habitat provision.
Choosing the Best Stormwater Management Solution
Retention ponds provide long-term stormwater storage by holding runoff to prevent flooding and allow sedimentation, making them ideal for large-scale developments with significant impervious surfaces. Bioswales offer enhanced pollutant filtration through vegetation and soil, promoting infiltration and groundwater recharge, suitable for urban areas aiming to improve water quality and reduce stormwater volume. Selecting between retention ponds and bioswales depends on site constraints, maintenance capacity, regulatory requirements, and desired environmental benefits.
Retention pond Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com