A producer oversees the creation and development of various projects in film, television, music, or other media, ensuring that all aspects run smoothly from concept to completion. They manage budgets, coordinate teams, and make critical decisions to bring a vision to life effectively. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how a producer's role can shape your favorite entertainment.
Table of Comparison
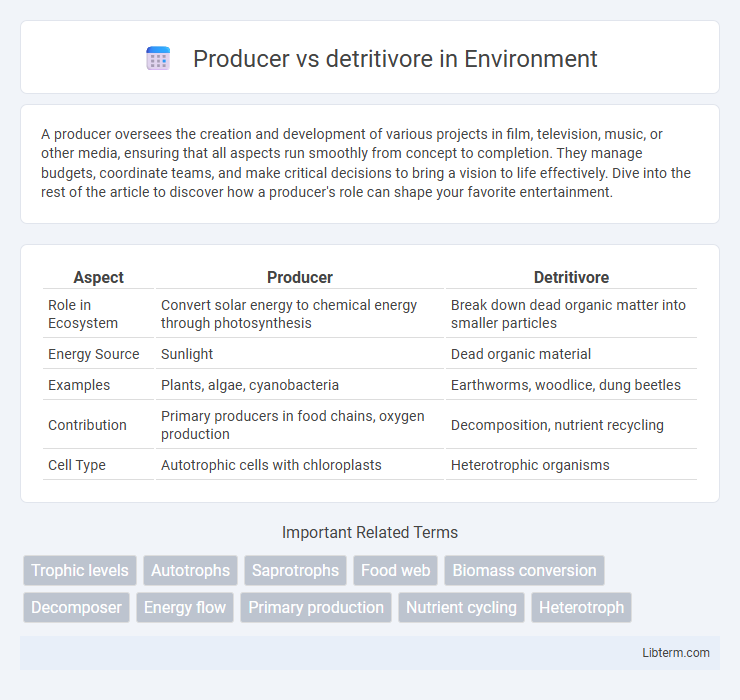
| Aspect | Producer | Detritivore |
|---|---|---|
| Role in Ecosystem | Convert solar energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis | Break down dead organic matter into smaller particles |
| Energy Source | Sunlight | Dead organic material |
| Examples | Plants, algae, cyanobacteria | Earthworms, woodlice, dung beetles |
| Contribution | Primary producers in food chains, oxygen production | Decomposition, nutrient recycling |
| Cell Type | Autotrophic cells with chloroplasts | Heterotrophic organisms |
Understanding Producers and Detritivores
Producers, predominantly green plants and algae, convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food chain and supporting ecosystem energy flow. Detritivores, such as earthworms and certain insect larvae, consume decomposing organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil and maintaining ecosystem nutrient cycles. Understanding the distinct roles of producers and detritivores is essential for grasping energy transfer and nutrient recycling within ecosystems.
Defining Producers: The Foundation of Ecosystems
Producers, primarily green plants and algae, use photosynthesis to convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into organic matter, forming the foundation of ecosystems by supplying energy for all trophic levels. Unlike detritivores, which consume decomposing organic material, producers generate new biomass that supports herbivores and indirectly sustains higher consumers. This primary production drives energy flow and nutrient cycling, making producers essential for ecosystem stability and productivity.
What Are Detritivores? Nature’s Recyclers
Detritivores are organisms, such as earthworms, woodlice, and certain insects, that consume decomposing organic matter, playing a crucial role in nutrient recycling within ecosystems. Unlike producers, which synthesize energy through photosynthesis, detritivores break down dead plant and animal material, facilitating soil enrichment and maintaining ecosystem health. Their activity accelerates decomposition, ensuring the continuous availability of essential nutrients for producers and other organisms.
Roles of Producers in Energy Flow
Producers, primarily autotrophic organisms such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, play a critical role in energy flow by converting solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis. They form the base of the food chain, supplying organic compounds and oxygen that support heterotrophic organisms, including consumers and detritivores. By synthesizing organic matter from inorganic substances, producers create the primary energy source that sustains ecosystems and drives biogeochemical cycles.
How Detritivores Facilitate Nutrient Cycling
Detritivores play a crucial role in nutrient cycling by breaking down dead organic matter and converting it into simpler inorganic compounds accessible to producers like plants and algae. This decomposition process releases essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium back into the soil or aquatic environments, promoting ecosystem productivity and maintaining soil fertility. By accelerating the recycling of nutrients, detritivores ensure the continuity of energy flow and support the growth of primary producers.
Key Differences Between Producers and Detritivores
Producers, primarily plants and algae, generate organic matter through photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy and forming the base of the food chain. Detritivores, such as earthworms and certain insects, consume decomposing organic material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Unlike producers that create energy-rich compounds, detritivores specialize in breaking down dead matter, facilitating nutrient cycling and soil fertility.
Examples of Producers in Various Ecosystems
Producers in various ecosystems include green plants like oak trees in forests, phytoplankton in aquatic environments, and algae in freshwater and marine habitats, all of which utilize photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy. These primary producers form the base of the food web, supplying organic matter and oxygen essential for consumer survival. In contrast, detritivores such as earthworms and certain crustaceans feed on decomposing organic material, playing a critical role in nutrient cycling rather than energy production.
Common Detritivores and Their Functions
Common detritivores such as earthworms, woodlice, and dung beetles play a crucial role in breaking down dead organic material, facilitating nutrient recycling in ecosystems. These organisms consume decomposing plant and animal matter, accelerating decomposition and releasing essential nutrients back into the soil, which supports primary producers like plants. Unlike producers that synthesize energy through photosynthesis, detritivores depend on organic matter, making them vital for maintaining soil fertility and ecosystem health.
Ecological Importance of Producer-Detritivore Interactions
Producers, primarily autotrophic plants and algae, generate organic matter through photosynthesis, forming the base of ecosystems' energy flow, while detritivores like earthworms and fungi play a critical role in decomposing dead organic material, recycling nutrients back into the soil. This interaction enhances soil fertility and supports primary production by maintaining nutrient cycles and reducing organic waste accumulation. Efficient producer-detritivore relationships are essential for ecosystem sustainability, promoting biodiversity and stabilizing food webs in terrestrial and aquatic environments.
Impact of Producers and Detritivores on Ecosystem Health
Producers, such as plants and algae, play a crucial role in ecosystem health by converting solar energy into organic matter through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food web and supporting biodiversity. Detritivores, including earthworms and certain insects, enhance nutrient cycling by breaking down dead organic material, which enriches soil fertility and promotes plant growth. The combined activities of producers and detritivores maintain ecosystem stability and productivity by regulating energy flow and nutrient availability.
Producer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com