An ecodistrict is a sustainable urban area designed to minimize environmental impact through energy efficiency, green infrastructure, and sustainable transportation. An ecozone refers to a specific geographic region characterized by distinct ecological features and biodiversity that guide conservation efforts. Discover how these concepts can transform your community by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
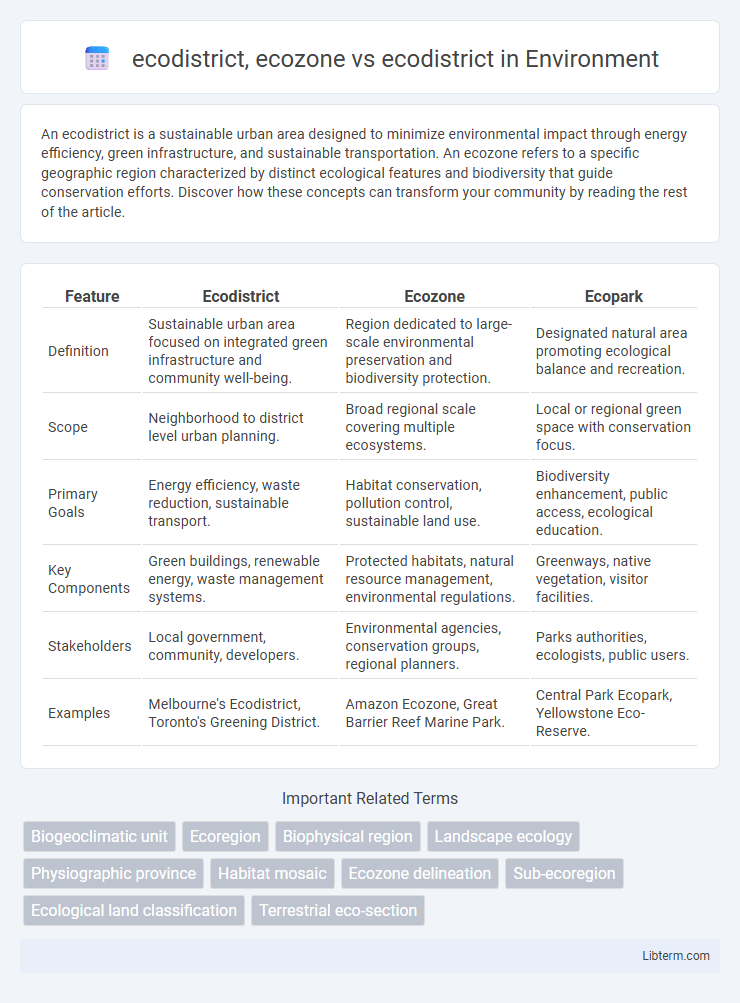
| Feature | Ecodistrict | Ecozone | Ecopark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sustainable urban area focused on integrated green infrastructure and community well-being. | Region dedicated to large-scale environmental preservation and biodiversity protection. | Designated natural area promoting ecological balance and recreation. |
| Scope | Neighborhood to district level urban planning. | Broad regional scale covering multiple ecosystems. | Local or regional green space with conservation focus. |
| Primary Goals | Energy efficiency, waste reduction, sustainable transport. | Habitat conservation, pollution control, sustainable land use. | Biodiversity enhancement, public access, ecological education. |
| Key Components | Green buildings, renewable energy, waste management systems. | Protected habitats, natural resource management, environmental regulations. | Greenways, native vegetation, visitor facilities. |
| Stakeholders | Local government, community, developers. | Environmental agencies, conservation groups, regional planners. | Parks authorities, ecologists, public users. |
| Examples | Melbourne's Ecodistrict, Toronto's Greening District. | Amazon Ecozone, Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. | Central Park Ecopark, Yellowstone Eco-Reserve. |
Introduction to Ecodistricts and Ecozones
Ecodistricts represent localized urban areas designed to integrate sustainable development principles, emphasizing efficient resource use, renewable energy, and green infrastructure to enhance community resilience and environmental quality. Ecozones, in contrast, often refer to broader geographical regions classified based on ecological factors like climate, vegetation, and wildlife, primarily used for environmental planning and conservation efforts. Understanding the distinction between ecodistricts as targeted urban sustainability projects and ecozones as ecological classification units is essential for effective environmental management and urban planning.
Defining Ecodistricts: Key Characteristics
Ecodistricts are defined by integrated sustainability goals, emphasizing energy efficiency, waste reduction, and green infrastructure within a cohesive urban area, often smaller and community-focused compared to ecozones. Unlike ecozones, which primarily denote environmentally regulated regions with specific land-use controls, ecodistricts foster active community engagement and innovative urban planning to create resilient, livable neighborhoods. Their key characteristics include multi-sector collaboration, localized resource management, and adaptive design strategies that promote environmental, economic, and social well-being.
Understanding Ecozones: Scope and Scale
Ecozones represent broad geographic regions defined by distinct ecological characteristics, encompassing multiple ecosystems and larger scales of biodiversity and climate patterns. In contrast, ecodistricts are smaller, more localized units within ecozones focused on site-specific environmental management and sustainable development practices. Understanding the scope and scale of ecozones is essential for effective regional planning, conservation strategies, and resource allocation in environmental governance.
Major Differences Between Ecozones and Ecodistricts
Ecodistricts are localized urban areas designed with integrated sustainability goals, focusing on energy efficiency, green infrastructure, and community resilience, whereas ecozones represent broader geographic regions designated primarily for environmental protection and conservation. Ecodistricts emphasize human-centered design and urban regeneration with measurable impacts on transportation, waste management, and social equity. Ecozones typically regulate land use to preserve biodiversity and natural resources, often limiting development to maintain ecological balance at a macro scale.
Functions and Objectives of Ecodistricts
Ecodistricts are designed to integrate sustainable urban planning principles with localized environmental, social, and economic objectives, focusing on reducing carbon footprints, promoting renewable energy, and enhancing community well-being. Unlike ecozones, which prioritize environmental protection through regulatory measures, ecodistricts emphasize multifunctional urban spaces that combine green infrastructure, mixed-use development, and participatory governance to foster resilient and adaptable neighborhoods. Key functions of ecodistricts include optimizing resource efficiency, improving air and water quality, and creating socially inclusive environments that support sustainable growth and climate adaptation.
Geographic and Administrative Boundaries Explained
Ecodistricts are defined by clear geographic boundaries that integrate sustainable urban planning within existing administrative jurisdictions, promoting localized environmental goals. Ecozones, often broader, encompass larger geographic areas focused primarily on ecological or biogeographical characteristics rather than administrative limits. The key distinction lies in ecodistricts aligning sustainability initiatives with municipal governance, whereas ecozones prioritize natural ecosystem conservation across potentially multiple administrative regions.
Environmental Impact: Ecodistricts vs. Ecozones
Ecodistricts are designed as integrated urban areas that prioritize sustainable practices, reducing environmental impact through energy-efficient buildings, green infrastructure, and waste reduction strategies. Ecozones typically refer to broader geographical regions with distinct ecological characteristics, focusing on conservation and natural resource management rather than urban sustainability. Ecodistricts actively mitigate urban environmental issues by lowering carbon emissions and enhancing biodiversity within city contexts, while ecozones primarily aim to preserve natural habitats and maintain ecological balance on a larger, often rural scale.
Real-World Examples of Ecodistricts
Ecodistricts prioritize sustainable urban development through integrated systems of energy, water, and transportation, exemplified by projects like the Vauban district in Freiburg, Germany, which features car-free zones and energy-efficient buildings. Ecozones typically refer to broader ecological or geographical areas designated for environmental protection, while ecodistricts emphasize localized urban planning and community engagement to reduce carbon footprints. The Portland EcoDistrict in Oregon showcases successful community-led initiatives promoting renewable energy, green infrastructure, and waste reduction within a defined urban neighborhood.
Implementing Sustainable Practices in Ecodistricts
Ecodistricts prioritize integrated sustainable practices by combining energy-efficient infrastructure, renewable energy systems, and green building standards to reduce carbon footprints. In contrast, ecozones often focus on designated regulatory frameworks to encourage environmental compliance and resource management within specific geographic areas. Implementing sustainable practices in ecodistricts involves community engagement, smart technology integration, and circular economy principles to enhance resilience and improve urban livability.
Choosing the Right Approach: Ecozone or Ecodistrict?
Choosing between an ecozone and an ecodistrict depends on the scale and goals of the sustainability initiative. Ecozones typically cover larger geographic areas with integrated policies targeting regional environmental impacts, while ecodistricts focus on smaller urban neighborhoods emphasizing localized energy efficiency, waste reduction, and community engagement. Understanding the specific environmental, social, and economic contexts helps determine whether an ecozone's broad regulatory framework or an ecodistrict's targeted, participatory approach better aligns with project objectives.
ecodistrict, ecozone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com