A unit hydrograph represents the direct runoff response of a watershed to a unit depth of rainfall over a specified duration, serving as a fundamental tool in hydrologic modeling and flood prediction. It helps you estimate streamflow resulting from rainfall events, making it essential for water resource management and infrastructure design. Explore the rest of the article to understand how unit hydrographs are derived and applied in practical scenarios.
Table of Comparison
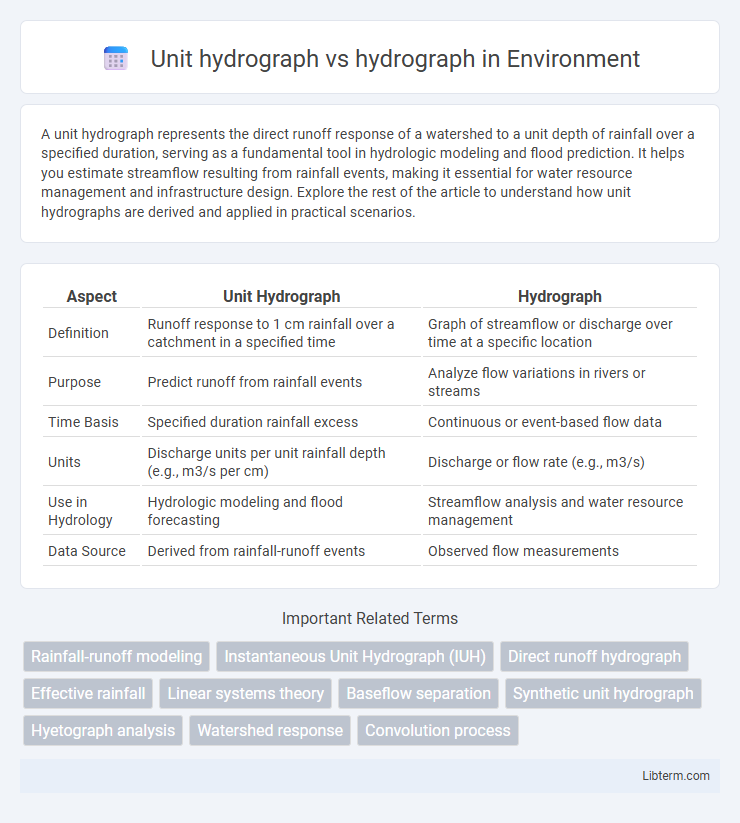
| Aspect | Unit Hydrograph | Hydrograph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Runoff response to 1 cm rainfall over a catchment in a specified time | Graph of streamflow or discharge over time at a specific location |
| Purpose | Predict runoff from rainfall events | Analyze flow variations in rivers or streams |
| Time Basis | Specified duration rainfall excess | Continuous or event-based flow data |
| Units | Discharge units per unit rainfall depth (e.g., m3/s per cm) | Discharge or flow rate (e.g., m3/s) |
| Use in Hydrology | Hydrologic modeling and flood forecasting | Streamflow analysis and water resource management |
| Data Source | Derived from rainfall-runoff events | Observed flow measurements |
Introduction to Hydrographs
Hydrographs represent the variation of river discharge over time at a specific location, capturing the response to precipitation events. A unit hydrograph specifically describes the direct runoff response to a unit depth of rainfall occurring uniformly over the watershed in a given duration, serving as a fundamental tool in hydrologic modeling. Understanding the distinction between general hydrographs and unit hydrographs is essential for effective flood forecasting and watershed management.
What is a Unit Hydrograph?
A unit hydrograph represents the direct runoff response of a watershed to a unit depth of effective rainfall occurring uniformly over a specified duration. It is a fundamental tool in hydrology used to predict streamflow hydrographs from rainfall events by scaling and superimposing unit hydrographs. Unlike a general hydrograph, which shows observed streamflow over time, the unit hydrograph isolates the watershed's response to a standardized rainfall input, enabling flood forecasting and water resource management.
What is a Hydrograph?
A hydrograph is a graphical representation showing how river discharge changes over time in response to precipitation. It illustrates the relationship between rainfall and streamflow, capturing the timing, magnitude, and duration of runoff. The unit hydrograph, in contrast, represents the runoff resulting from one unit of effective rainfall over a specific area and duration, serving as a fundamental tool for predicting hydrograph responses to varied rainfall events.
Key Differences: Unit Hydrograph vs Hydrograph
The unit hydrograph represents the direct runoff response to a unit depth of effective rainfall over a specific drainage area and time duration, serving as a tool for flood forecasting and watershed management. In contrast, a hydrograph is a graphical representation of river discharge over time, encompassing both baseflow and direct runoff components without isolating specific rainfall events. Key differences include the unit hydrograph's basis on standardized rainfall excess and discrete rainfall events, whereas the general hydrograph reflects continuous flow variations influenced by multiple hydrologic factors.
Applications of Unit Hydrographs
Unit hydrographs provide crucial data for hydrologists to predict direct runoff from rainfall events, enabling accurate flood forecasting and watershed management. These hydrographs are widely used in urban drainage design, stormwater management, and reservoir operation planning to optimize water resource allocation and minimize flood risks. Unlike general hydrographs, unit hydrographs specifically quantify the temporal distribution of runoff for a unit of rainfall, making them essential for hydrologic modeling and infrastructure development.
Applications of Hydrographs
Hydrographs are essential tools in hydrology for analyzing streamflow variations over time, aiding in flood prediction, water resource management, and watershed planning. Unit hydrographs specifically model how a watershed responds to a unit of rainfall excess, making them crucial for designing drainage systems and estimating runoff from storm events. Both hydrograph types support applications in flood forecasting, reservoir operation, and urban stormwater management by providing insights into rainfall-runoff relationships.
Advantages of Using Unit Hydrographs
Unit hydrographs provide a clear and quantifiable method to predict runoff response from specific rainfall events, enhancing the accuracy of flood forecasting. They simplify complex watershed behavior by assuming linearity and time invariance, allowing for easier modeling and analysis compared to conventional hydrographs. Using unit hydrographs facilitates the design of efficient stormwater management systems by enabling precise runoff calculations for varied rainfall intensities.
Limitations of Unit Hydrographs
Unit hydrographs simplify streamflow prediction by assuming linearity and time invariance, which limits their accuracy in complex or non-uniform rainfall events. They often fail to account for watershed heterogeneity, changing land use, and soil saturation conditions, resulting in less reliable runoff estimates. These limitations restrict their application in basins with significant spatial variability or during extreme hydrologic conditions.
Selecting the Appropriate Hydrograph Method
Selecting the appropriate hydrograph method depends on watershed size, rainfall characteristics, and data availability. Unit hydrographs are ideal for small to medium catchments with uniform rainfall, facilitating the conversion of direct runoff into flow rates. Complex or non-uniform rainfall events and larger basins often require a composite or synthetic hydrograph for accurate flood forecasting and water resource management.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Unit Hydrograph and Hydrograph
Selecting between a unit hydrograph and a hydrograph depends on the specific hydrological analysis and application requirements. Unit hydrographs provide a standardized method to estimate runoff response from rainfall events, ideal for modeling and watershed management. In contrast, hydrographs offer actual observed data, essential for real-time flood forecasting and detailed water resource assessments.
Unit hydrograph Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com