Understanding hydrology is essential for managing water resources, predicting floods, and preserving ecosystems. It studies the movement, distribution, and quality of water throughout the Earth, including the hydrological cycle and groundwater flow. Discover more about how your knowledge of hydrology can impact environmental sustainability in the rest of this article.
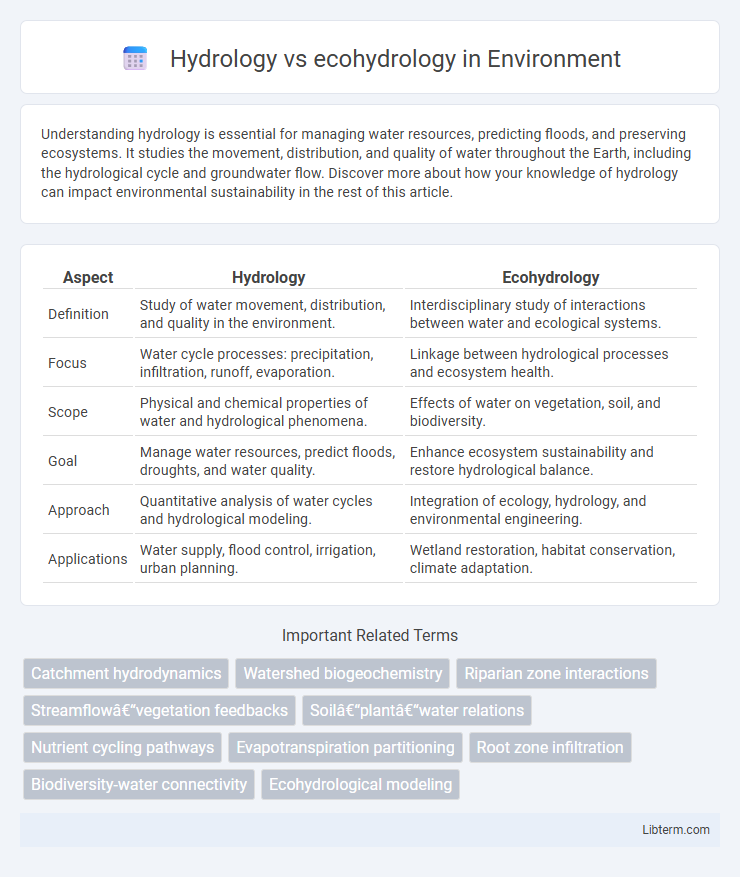
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hydrology | Ecohydrology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of water movement, distribution, and quality in the environment. | Interdisciplinary study of interactions between water and ecological systems. |
| Focus | Water cycle processes: precipitation, infiltration, runoff, evaporation. | Linkage between hydrological processes and ecosystem health. |
| Scope | Physical and chemical properties of water and hydrological phenomena. | Effects of water on vegetation, soil, and biodiversity. |
| Goal | Manage water resources, predict floods, droughts, and water quality. | Enhance ecosystem sustainability and restore hydrological balance. |
| Approach | Quantitative analysis of water cycles and hydrological modeling. | Integration of ecology, hydrology, and environmental engineering. |
| Applications | Water supply, flood control, irrigation, urban planning. | Wetland restoration, habitat conservation, climate adaptation. |
Introduction to Hydrology and Ecohydrology
Hydrology focuses on the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth, encompassing processes such as precipitation, infiltration, runoff, and evaporation. Ecohydrology integrates ecological and hydrological sciences to understand interactions between water dynamics and ecosystems, emphasizing how vegetation and biota influence and respond to the water cycle. This interdisciplinary approach helps in managing water resources sustainably, considering both hydrological processes and ecological health.
Defining Hydrology: Scope and Principles
Hydrology encompasses the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water throughout the Earth's atmosphere, surface, and subsurface environments, focusing on processes such as precipitation, evaporation, infiltration, and runoff. Ecohydrology integrates ecological principles with hydrological processes to understand the interactions between water and living organisms, emphasizing the role of vegetation, soil biota, and ecosystems in regulating water cycles. Defining hydrology's scope involves analyzing hydrological pathways and equilibrium, while ecohydrology assesses feedback mechanisms between ecological systems and hydrological dynamics for sustainable water resource management.
What is Ecohydrology? Core Concepts
Ecohydrology examines the interactions between water and ecosystems, emphasizing how hydrological processes influence biological components and vice versa. Core concepts include the study of water fluxes, nutrient cycling, and ecosystem dynamics to understand ecosystem sustainability and resilience. It integrates hydrology, ecology, and environmental sciences to optimize water resource management in natural and managed landscapes.
Key Differences Between Hydrology and Ecohydrology
Hydrology primarily studies the movement, distribution, and quality of water in the Earth's atmosphere, surface, and underground, focusing on physical and chemical processes. Ecohydrology integrates ecological principles with hydrological processes, emphasizing the interactions between water and ecosystems to understand how water availability affects biological communities and vice versa. Key differences include hydrology's focus on pure water cycle dynamics versus ecohydrology's focus on water-ecosystem feedback mechanisms and their influence on environmental sustainability.
The Role of Water in Ecosystem Functioning
Hydrology studies the distribution, movement, and quality of water in natural systems, emphasizing physical processes like precipitation, runoff, and groundwater flow. Ecohydrology integrates ecological and hydrological principles to understand how water availability and dynamics influence ecosystem structure, function, and biodiversity. The role of water in ecosystem functioning includes regulating nutrient cycling, facilitating habitat connectivity, and sustaining species populations through dynamic water fluxes.
Hydrological Processes vs Ecohydrological Processes
Hydrological processes involve the movement, distribution, and quality of water in the Earth's atmosphere, surface, and subsurface, including precipitation, infiltration, runoff, and evapotranspiration. Ecohydrological processes integrate these hydrological dynamics with ecological functions, emphasizing interactions between water availability, vegetation growth, and ecosystem health. Understanding the distinctions between traditional hydrological processes and ecohydrological feedback mechanisms is crucial for sustainable water resource management and ecological conservation.
Applications of Hydrology in Water Resource Management
Hydrology plays a crucial role in water resource management by analyzing precipitation, surface runoff, and groundwater flow to optimize water allocation and mitigate flood risks. Hydrologic models support sustainable irrigation practices, urban water supply planning, and reservoir operation, ensuring reliable access to freshwater. Ecohydrology integrates ecological processes with hydrologic cycles, enhancing ecosystem restoration and biodiversity conservation in watershed management.
Ecohydrology for Biodiversity Conservation
Ecohydrology integrates hydrological processes with ecological dynamics to enhance biodiversity conservation by promoting sustainable water management in natural habitats. It examines the interactions between water availability, vegetation patterns, and wildlife populations, enabling restoration of ecosystems and protection of endangered species. This approach supports resilient landscapes by maintaining the ecological functions essential for diverse biological communities.
Integrating Hydrology and Ecohydrology for Sustainability
Hydrology studies the distribution and movement of water in the environment, while ecohydrology emphasizes interactions between water and ecosystems, focusing on sustaining ecological functions. Integrating hydrology and ecohydrology enhances water resource management by aligning hydrological processes with ecosystem health, promoting biodiversity and resilience. This interdisciplinary approach supports sustainable development through balanced water use, conservation, and restoration strategies that address both human and ecological needs.
Future Directions in Hydrology and Ecohydrology Research
Emerging research in hydrology emphasizes integrating advanced remote sensing technologies and machine learning algorithms to improve watershed modeling and flood prediction accuracy. Ecohydrology studies are increasingly focusing on climate change impacts on water-vegetation interactions and developing sustainable water management strategies that enhance ecosystem resilience. Future directions prioritize interdisciplinary approaches combining hydrological data with ecological processes to address global water scarcity and biodiversity loss.
Hydrology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com