Stormwater management is essential for preventing flooding, reducing pollution, and protecting natural water bodies in urban areas. Effective systems capture and treat runoff to minimize environmental impact and enhance water quality. Explore the full article to learn how you can implement practical stormwater solutions for your property.
Table of Comparison
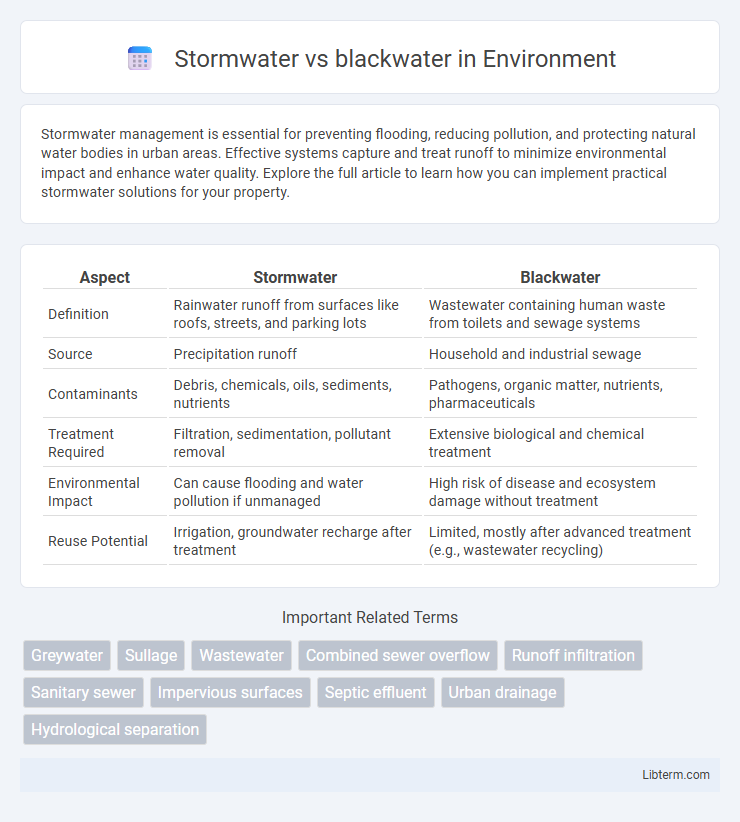
| Aspect | Stormwater | Blackwater |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rainwater runoff from surfaces like roofs, streets, and parking lots | Wastewater containing human waste from toilets and sewage systems |
| Source | Precipitation runoff | Household and industrial sewage |
| Contaminants | Debris, chemicals, oils, sediments, nutrients | Pathogens, organic matter, nutrients, pharmaceuticals |
| Treatment Required | Filtration, sedimentation, pollutant removal | Extensive biological and chemical treatment |
| Environmental Impact | Can cause flooding and water pollution if unmanaged | High risk of disease and ecosystem damage without treatment |
| Reuse Potential | Irrigation, groundwater recharge after treatment | Limited, mostly after advanced treatment (e.g., wastewater recycling) |
Understanding Stormwater: Definition and Sources
Stormwater is precipitation runoff generated from rain or melting snow that flows over surfaces like roads, rooftops, and land, often carrying pollutants into water bodies. Key sources include impervious surfaces such as urban areas, parking lots, and highways, which prevent infiltration and increase runoff volume. Managing stormwater is essential to reduce flooding, erosion, and contamination of rivers, lakes, and coastal waters.
What is Blackwater? Key Characteristics
Blackwater refers to wastewater that contains human waste, including feces, urine, and flush water from toilets, often mixed with septic tank effluent and household sewage. It is characterized by high levels of pathogens, organic matter, and nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, posing significant health and environmental risks if untreated. Managing blackwater requires specialized treatment processes like anaerobic digestion, membrane filtration, or biological treatment to safely remove contaminants before disposal or reuse.
Differences Between Stormwater and Blackwater
Stormwater consists of rainwater or melted snow that flows over surfaces like roads and rooftops, carrying debris and contaminants but generally lacking human waste. Blackwater is wastewater from toilets, containing fecal matter, urine, and pathogens that require specialized treatment to prevent health hazards. The main difference lies in their composition and treatment processes: stormwater is primarily concerned with pollution control in natural water bodies, while blackwater demands comprehensive sanitation measures to protect public health.
Composition and Contaminants of Stormwater
Stormwater primarily contains rainwater runoff mixed with various contaminants such as sediments, nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus), heavy metals (lead, zinc, copper), hydrocarbons from vehicle emissions, and pathogens from animal waste. Unlike blackwater, which originates from sewage and contains high levels of organic matter and pathogens, stormwater's composition varies widely depending on land use and weather conditions, often carrying pollutants from urban, industrial, and agricultural surfaces. Key contaminants in stormwater also include pesticides, oils, greases, and debris, contributing to water quality degradation in receiving bodies if untreated.
Health and Environmental Impacts of Blackwater
Blackwater contains human waste, pathogens, and contaminants that pose significant health risks, including the spread of waterborne diseases like cholera and dysentery, when improperly managed. In contrast to stormwater, which mainly includes rainwater runoff, blackwater demands advanced treatment to prevent environmental pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems from nutrient overload and toxic substances. Effective blackwater management reduces public health hazards and minimizes the contamination of soil and groundwater resources.
Treatment Methods for Stormwater Management
Stormwater treatment methods primarily involve physical, chemical, and biological processes designed to reduce pollutants from runoff before it reaches natural water bodies. Common techniques include detention basins, infiltration trenches, constructed wetlands, and bio-retention systems, which help manage flow rates and filter contaminants through sedimentation, filtration, and microbial degradation. These stormwater management practices aim to control flooding, improve water quality, and protect aquatic ecosystems by effectively treating pollutants such as sediments, nutrients, heavy metals, and organic matter.
Blackwater Treatment and Disposal Solutions
Blackwater treatment and disposal solutions prioritize advanced biological and chemical processes to effectively remove pathogens, organic waste, and nutrients from sewage water originating from toilets and kitchen drains. Technologies such as activated sludge systems, membrane bioreactors, and anaerobic digesters are commonly employed to ensure safe, environmentally compliant discharge or reuse. Decentralized treatment units and septic systems also provide scalable options for blackwater management in urban and rural settings, minimizing groundwater contamination and promoting sustainable sanitation.
Legal Regulations for Stormwater and Blackwater
Stormwater and blackwater are regulated under distinct legal frameworks due to their different sources and contamination levels. Stormwater, primarily rainwater runoff, is managed by environmental protection agencies through permits like the NPDES (National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System) to control pollutants entering water bodies. Blackwater, originating from sewage and containing human waste, is subject to stringent wastewater treatment and disposal regulations under the Clean Water Act and local health codes to prevent public health hazards.
Sustainable Practices for Managing Urban Water
Stormwater management in urban areas emphasizes techniques like green roofs, permeable pavements, and rain gardens to reduce runoff and filter pollutants naturally. Blackwater requires advanced treatment processes such as septic systems or wastewater recycling to safely remove contaminants and pathogens before reuse or discharge. Implementing sustainable practices for both stormwater and blackwater enhances urban water quality, conserves resources, and mitigates flooding risks.
Future Trends in Water Management Technologies
Stormwater and blackwater management technologies are evolving with innovations such as smart sensors and AI-driven treatment systems that optimize water quality monitoring and reduce contamination risks. Emerging green infrastructure, including permeable pavements and bio-retention systems, enhances stormwater infiltration and mitigates urban flooding while improving ecosystem health. Future trends indicate integrated water recycling solutions merging stormwater capture with advanced blackwater treatment to promote sustainable water reuse in urban environments.
Stormwater Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com