A scrubber is an essential air pollution control device that removes harmful contaminants from industrial exhaust streams, improving air quality and ensuring regulatory compliance. By utilizing chemical or physical processes, scrubbers effectively capture particles, gases, and vapors before they are released into the atmosphere. Explore the rest of this article to learn how scrubbers work and how they can benefit your facility.
Table of Comparison
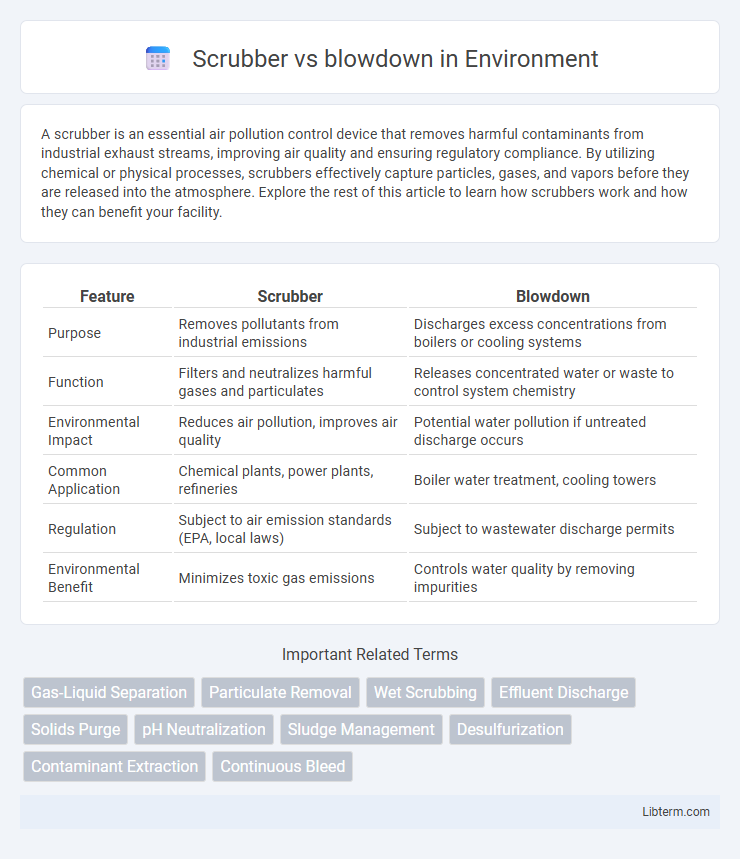
| Feature | Scrubber | Blowdown |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Removes pollutants from industrial emissions | Discharges excess concentrations from boilers or cooling systems |
| Function | Filters and neutralizes harmful gases and particulates | Releases concentrated water or waste to control system chemistry |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces air pollution, improves air quality | Potential water pollution if untreated discharge occurs |
| Common Application | Chemical plants, power plants, refineries | Boiler water treatment, cooling towers |
| Regulation | Subject to air emission standards (EPA, local laws) | Subject to wastewater discharge permits |
| Environmental Benefit | Minimizes toxic gas emissions | Controls water quality by removing impurities |
Introduction to Scrubbers and Blowdown Systems
Scrubbers are air pollution control devices designed to remove harmful particulates and gases from industrial exhaust streams through liquid absorption or chemical reaction. Blowdown systems manage the discharge of wastewater or contaminants from boilers, cooling towers, and other water treatment processes to maintain system efficiency and regulatory compliance. Both systems play critical roles in environmental protection by controlling industrial emissions and wastewater quality.
Purpose and Functionality of Scrubbers
Scrubbers primarily function to remove pollutants such as sulfur oxides, particulates, and acidic gases from industrial exhaust streams, improving air quality and complying with environmental regulations. They achieve this by using a liquid, often water or a chemical solution, to capture and neutralize harmful emissions before they are released into the atmosphere. In contrast, blowdown refers to the process of removing concentrated water containing impurities from boilers or cooling towers to maintain system efficiency and prevent scale buildup.
How Blowdown Systems Operate
Blowdown systems operate by removing concentrated dissolved solids and impurities from boiler water to maintain optimal water chemistry, prevent scaling, and reduce corrosion. This process involves periodically releasing a portion of water from the boiler, either continuously or intermittently, to control the concentration of contaminants. Effective blowdown control enhances boiler efficiency and extends equipment lifespan by maintaining proper water quality.
Key Differences Between Scrubber and Blowdown
Scrubber systems primarily remove pollutants and particulate matter from industrial exhaust gases, improving air quality by capturing harmful substances like sulfur dioxide (SO2) and particulate emissions. Blowdown refers to the controlled removal of water containing high concentrations of dissolved solids from boilers or cooling towers to maintain optimal water chemistry and prevent scale or corrosion. While scrubbers focus on gas pollution control, blowdown centers on maintaining water quality in industrial processes; both are essential for environmental compliance but address different types of contaminants.
Advantages of Using Scrubbers
Scrubbers offer efficient removal of harmful gases and particulates from industrial exhaust streams, significantly reducing air pollution and complying with environmental regulations. Unlike blowdown systems that handle water discharge from boilers, scrubbers provide continuous air pollution control and can capture a wide range of pollutants, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. Their ability to recycle water and minimize hazardous waste disposal enhances operational sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Benefits and Limitations of Blowdown
Blowdown effectively removes dissolved solids and contaminants from boilers, preventing scale buildup and corrosion, which enhances operational efficiency and prolongs equipment life. However, frequent blowdown leads to water, energy, and chemical losses, increasing operational costs and environmental impact due to wastewater discharge. While it is essential for maintaining water quality, blowdown requires careful management to balance system cleanliness with resource conservation and regulatory compliance.
Environmental Impact: Scrubber vs Blowdown
Scrubbers significantly reduce environmental pollution by removing harmful gases and particulate matter from industrial emissions, thereby lowering sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide levels that contribute to acid rain and smog. Blowdown water from industrial processes, if not properly treated, can contain high concentrations of heavy metals and chemical contaminants, posing risks to aquatic ecosystems and water quality. Effective management of scrubber outputs and blowdown effluents is critical to minimizing their respective environmental footprints and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Efficiency and Cost Comparison
Scrubbers offer high efficiency in removing contaminants from industrial gases, with removal rates often exceeding 90%, but involve significant upfront capital and maintenance costs due to complex components and chemical usage. Blowdown systems, primarily used for controlling boiler water chemistry, provide lower operational costs and simpler maintenance but are less efficient in pollutant removal, focusing instead on preventing scale and corrosion. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, scrubbers excel in stringent emission control scenarios despite higher expenses, while blowdown is more economical for routine water treatment and process stability.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases
Scrubbers are crucial in industrial applications for removing pollutants and contaminants from exhaust gases, enhancing air quality and regulatory compliance in sectors like power plants and chemical manufacturing. Blowdown systems manage the concentration of dissolved solids in boilers by periodically discharging water, preventing scaling and corrosion to maintain efficient steam generation in industries such as oil refineries and pulp mills. The integration of scrubber technology with blowdown processes optimizes emission control and water treatment, supporting sustainable industrial operations.
Choosing the Right System for Your Operation
Selecting the right system for your operation requires a clear understanding of scrubber and blowdown technologies, as scrubbers efficiently remove contaminants from gases while blowdown systems manage the water quality in boilers or cooling towers by discharging concentrated waste. Operators must consider factors such as operational costs, environmental regulations, and maintenance requirements, with scrubbers benefiting air quality compliance in industrial emissions and blowdown systems ensuring prolonged equipment lifespan and safety. Evaluating specific process needs, including waste composition and regulatory standards, enables informed decisions that optimize performance and sustainability for your facility.
Scrubber Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com