Venting is an essential emotional release that helps reduce stress and improve mental clarity by expressing bottled-up feelings. Understanding healthy venting techniques can prevent misunderstandings and maintain positive relationships. Discover effective ways to vent constructively by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
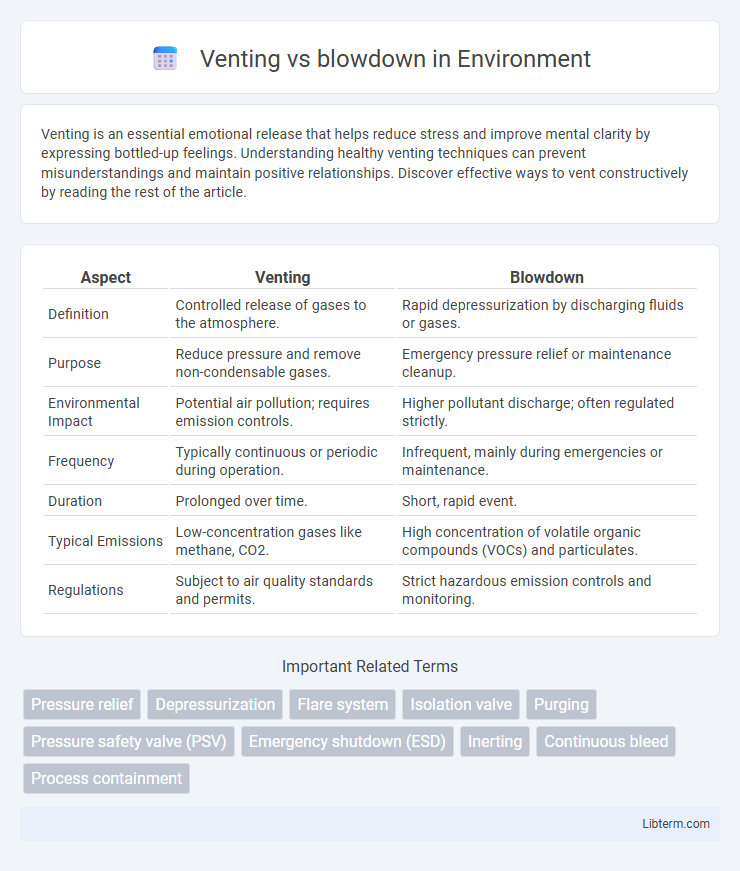
| Aspect | Venting | Blowdown |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled release of gases to the atmosphere. | Rapid depressurization by discharging fluids or gases. |
| Purpose | Reduce pressure and remove non-condensable gases. | Emergency pressure relief or maintenance cleanup. |
| Environmental Impact | Potential air pollution; requires emission controls. | Higher pollutant discharge; often regulated strictly. |
| Frequency | Typically continuous or periodic during operation. | Infrequent, mainly during emergencies or maintenance. |
| Duration | Prolonged over time. | Short, rapid event. |
| Typical Emissions | Low-concentration gases like methane, CO2. | High concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulates. |
| Regulations | Subject to air quality standards and permits. | Strict hazardous emission controls and monitoring. |
Introduction to Venting and Blowdown
Venting and blowdown are critical processes in industrial systems designed to manage pressure and ensure safety by releasing gases or liquids. Venting typically involves the controlled release of non-condensable gases or vapors to prevent overpressure, while blowdown refers to the deliberate discharge of liquid, steam, or gas to reduce pressure rapidly or remove contaminants. Understanding the differences between venting and blowdown is essential for optimizing pressure relief systems, maintaining environmental compliance, and protecting equipment integrity.
Understanding Gas Venting
Gas venting involves the controlled release of non-hazardous gases to the atmosphere, primarily to manage pressure and prevent equipment damage, whereas blowdown is a rapid depressurization process used to quickly evacuate gas or liquid from a system during emergency shutdowns or maintenance. Venting systems must comply with environmental regulations to minimize emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and greenhouse gases (GHGs), making gas composition and release rate critical factors. Accurate understanding of gas venting optimizes safety, reduces environmental impact, and ensures efficient system operation in industries such as oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and power generation.
What is Blowdown?
Blowdown is the controlled release of steam, water, or contaminants from a boiler or pressure vessel to maintain safe operating conditions and remove impurities that accumulate during operation. This process helps regulate pressure, prevent scaling, and ensure the efficiency and longevity of the equipment. Blowdown differs from venting in that it involves the removal of liquids and solids, not just gases, and is often performed periodically to manage system quality.
Key Differences Between Venting and Blowdown
Venting controls the gradual release of gases to maintain safe pressure levels, while blowdown involves rapid depressurization to quickly reduce pressure or remove contaminants. Venting usually results in continuous or intermittent gas discharge under controlled conditions, whereas blowdown is a sudden, high-flow event often used in emergency or maintenance situations. The key difference lies in their operational purpose: venting ensures system stability over time, while blowdown serves immediate pressure relief or cleanup.
Industrial Applications of Venting
Industrial venting systems are designed to safely release excess gases or vapors to prevent overpressure in equipment such as tanks, vessels, and pipelines. Venting controls the continuous or intermittent release of non-hazardous or low-pressure gases, whereas blowdown rapidly depressurizes systems to protect against dangerous pressure spikes. Proper venting in chemical plants, refineries, and power generation facilities ensures compliance with safety regulations and minimizes environmental impact by controlling emissions and preventing catastrophic failures.
Industrial Applications of Blowdown
Industrial blowdown involves controlled removal of water or steam to manage impurities and maintain optimal boiler efficiency and safety. It prevents scale buildup and corrosion by periodically discharging concentrated contaminants, ensuring the longevity of equipment in power plants and chemical processing facilities. This process is critical in maintaining operational stability and complying with regulatory standards for emissions and wastewater management.
Environmental Impact: Venting vs Blowdown
Venting releases unburned hydrocarbons directly into the atmosphere, significantly contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, whereas blowdown involves depressurizing equipment, often venting gas but sometimes flaring it to reduce environmental harm. Blowdown with flaring converts hydrocarbons into less harmful carbon dioxide and water, minimizing volatile organic compound (VOC) release compared to venting. Selecting blowdown systems with effective flaring technology is critical for reducing the environmental footprint of petrochemical and natural gas operations.
Safety Considerations in Venting and Blowdown
Safety considerations in venting and blowdown prioritize controlling pressure to prevent equipment failure and hazardous releases. Proper design ensures vent stacks and blowdown systems minimize exposure to toxic or flammable gases, reducing risks to personnel and the environment. Regular maintenance and monitoring of these systems are critical to detecting blockages or leaks that could compromise safety.
Regulatory Standards for Venting and Blowdown
Regulatory standards for venting and blowdown prioritize controlling emissions and ensuring safety during pressure relief operations in industrial systems. Venting regulations often mandate the use of vapor recovery units or flare systems to minimize atmospheric release of hazardous gases, complying with EPA's Clean Air Act and OSHA guidelines. Blowdown procedures must adhere to ANSI/API standards and local environmental regulations, requiring controlled depressurization methods to prevent overpressure incidents and limit pollutant discharge.
Best Practices for Managing Venting and Blowdown
Effective management of venting and blowdown in industrial systems involves implementing controlled release techniques to minimize environmental impact and ensure safety compliance. Utilizing advanced monitoring systems to regulate pressure and temperature during blowdown reduces emissions and equipment wear, while proper routing of vent gases through flares or scrubbers mitigates harmful pollutants. Regular maintenance schedules and operator training on venting protocols further optimize system performance and adhere to regulatory standards such as EPA and OSHA guidelines.
Venting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com