Reducing your carbon footprint is essential for mitigating climate change and preserving the environment. Small changes in daily habits, such as using energy-efficient appliances and reducing car travel, significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Discover practical tips to lower your impact and contribute to a greener planet by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
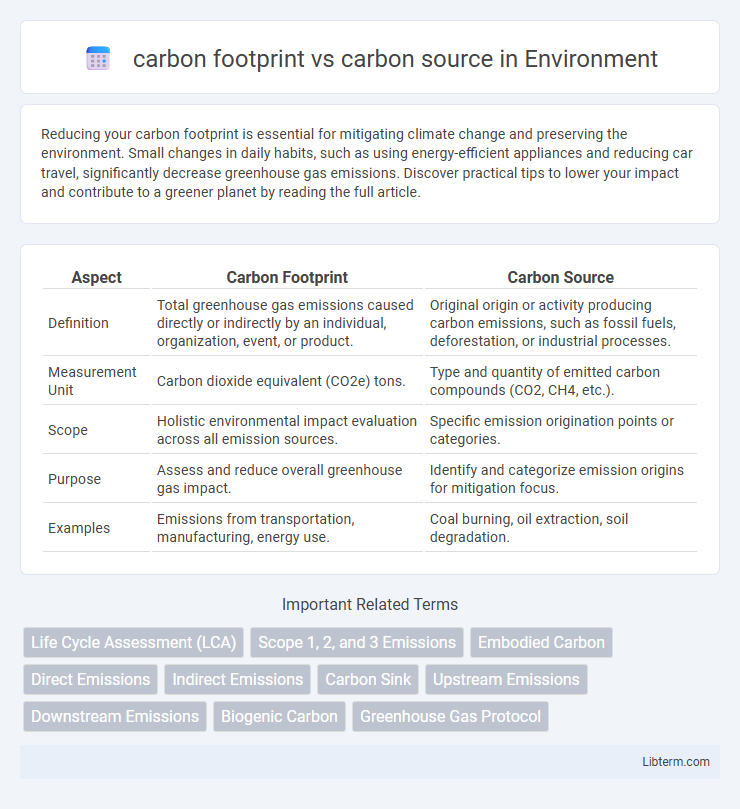
| Aspect | Carbon Footprint | Carbon Source |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by an individual, organization, event, or product. | Original origin or activity producing carbon emissions, such as fossil fuels, deforestation, or industrial processes. |
| Measurement Unit | Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) tons. | Type and quantity of emitted carbon compounds (CO2, CH4, etc.). |
| Scope | Holistic environmental impact evaluation across all emission sources. | Specific emission origination points or categories. |
| Purpose | Assess and reduce overall greenhouse gas impact. | Identify and categorize emission origins for mitigation focus. |
| Examples | Emissions from transportation, manufacturing, energy use. | Coal burning, oil extraction, soil degradation. |
Understanding Carbon Footprint: Definition and Importance
A carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, event, or product, expressed in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e). It quantifies human impact on climate change by accounting for carbon sources such as fossil fuel combustion, industrial processes, and deforestation that release CO2 into the atmosphere. Understanding carbon footprints is crucial for developing effective strategies to reduce emissions, mitigate global warming, and promote sustainable environmental practices.
What Is a Carbon Source?
A carbon source refers to any process, activity, or substance that releases carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Common carbon sources include fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial activities that emit significant amounts of CO2. Understanding carbon sources is crucial for managing and reducing overall carbon footprints to mitigate environmental impact.
Key Differences Between Carbon Footprint and Carbon Source
Carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by an individual, organization, event, or product, quantified in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e). Carbon source refers to any natural or artificial reservoir that releases carbon into the atmosphere, such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, or respiration. The key difference lies in carbon footprint being a metric of environmental impact, while carbon source identifies specific origins of carbon emissions contributing to atmospheric carbon levels.
How Carbon Footprints Are Measured
Carbon footprints are measured by quantifying the total greenhouse gas emissions produced directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, product, or activity, usually expressed in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e). This measurement involves calculating emissions from various carbon sources such as fossil fuel combustion, electricity usage, transportation, and industrial processes, using standardized protocols like the Greenhouse Gas Protocol or ISO 14064. Advanced tools and software analyze energy consumption, supply chain data, and waste generation to provide accurate carbon footprint assessments essential for mitigation strategies.
Common Examples of Carbon Sources
Common examples of carbon sources include burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which release significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Deforestation and land-use changes also act as major carbon sources by reducing the Earth's capacity to absorb CO2. Industrial processes, including cement production and chemical manufacturing, contribute further to carbon emissions, intensifying the overall carbon footprint.
The Role of Human Activity in Carbon Emissions
Human activities, particularly fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes, are primary carbon sources contributing significantly to global carbon emissions. The carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gases generated directly or indirectly by these activities, highlighting their impact on climate change. Reducing human-induced carbon sources is critical for minimizing the overall carbon footprint and mitigating global warming effects.
Reducing Your Carbon Footprint: Effective Strategies
Reducing your carbon footprint involves minimizing greenhouse gas emissions from activities such as transportation, energy consumption, and waste production. Key strategies include adopting renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency in homes and buildings, and choosing sustainable transportation options like electric vehicles or public transit. Behavioral changes like reducing meat consumption and promoting zero-waste practices further decrease reliance on carbon sources, effectively mitigating personal and community-level environmental impact.
Identifying Major Carbon Sources in Daily Life
Major carbon sources in daily life include transportation, energy consumption, and food production, each significantly contributing to an individual's carbon footprint. Vehicles powered by fossil fuels emit substantial amounts of carbon dioxide, while electricity generated from coal and natural gas increases household emissions. Dietary choices, particularly high meat consumption, also elevate carbon footprints due to methane emissions and deforestation associated with livestock farming.
The Global Impact of Carbon Footprints vs. Carbon Sources
The global impact of carbon footprints measures the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by individuals, organizations, or products, highlighting the cumulative effect on climate change. Carbon sources, including fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial activities, release significant amounts of CO2 and methane, driving global warming and environmental degradation. Understanding and mitigating both carbon footprints and carbon sources are critical to achieving global emission reduction targets and limiting temperature rise to below 1.5degC.
Future Trends: Innovations in Carbon Management
Future trends in carbon management emphasize advancing carbon capture technologies and renewable energy integration to reduce carbon footprints effectively. Enhanced monitoring systems leverage AI and blockchain for transparent tracking of carbon sources and emissions. Innovative materials and processes are emerging to convert carbon sources into valuable products, supporting a circular carbon economy.
carbon footprint Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com