The terminal is a powerful command-line interface that allows you to interact directly with your operating system by executing commands. Mastering terminal commands can significantly enhance your productivity and provide greater control over system tasks. Explore the rest of the article to unlock the full potential of your terminal usage.
Table of Comparison
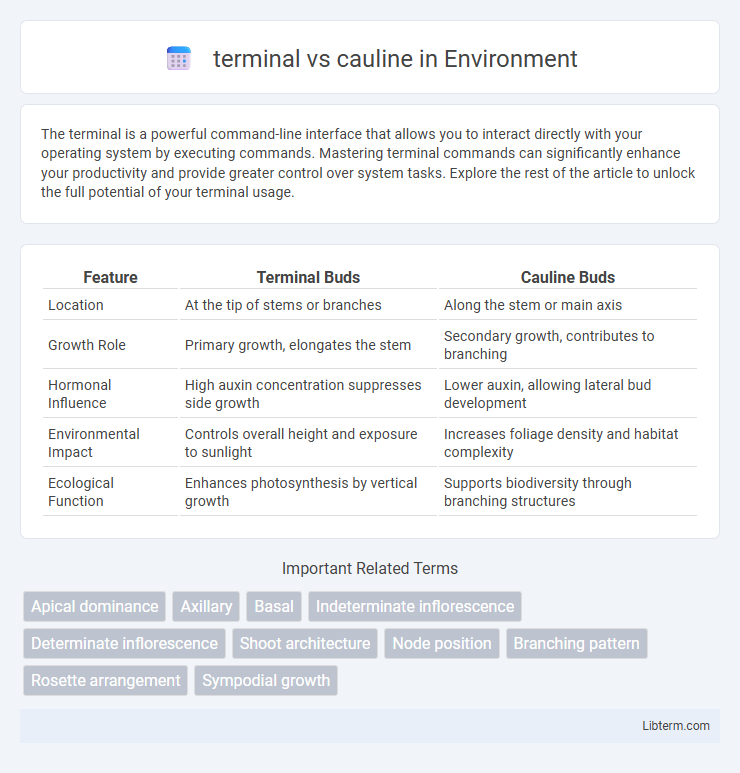
| Feature | Terminal Buds | Cauline Buds |
|---|---|---|
| Location | At the tip of stems or branches | Along the stem or main axis |
| Growth Role | Primary growth, elongates the stem | Secondary growth, contributes to branching |
| Hormonal Influence | High auxin concentration suppresses side growth | Lower auxin, allowing lateral bud development |
| Environmental Impact | Controls overall height and exposure to sunlight | Increases foliage density and habitat complexity |
| Ecological Function | Enhances photosynthesis by vertical growth | Supports biodiversity through branching structures |
Introduction to Terminal and Cauline Concepts
Terminal refers to the position of leaves or flowers located at the tip of a stem or branch, while cauline describes those attached along the stem. Understanding terminal and cauline arrangements provides key insights into plant morphology and growth patterns. These concepts are essential for botanists when classifying plant species and studying their development.
Defining Terminal and Cauline Structures
Terminal structures refer to organs or appendages located at the apex or tip of a stem or branch, such as terminal buds or flowers, crucial for primary growth and elongation. Cauline structures are those that emerge along the stem or main axis below the terminal point, including cauline leaves and lateral branches, playing key roles in photosynthesis and structural support. Differentiating these involves recognizing terminal elements at the stem's end versus cauline elements situated laterally along the stem's length.
Morphological Differences Between Terminal and Cauline
Terminal inflorescences develop at the apex of the main stem, often leading to determinate growth, while cauline inflorescences emerge from the stem's lateral nodes, supporting indeterminate growth patterns. Morphologically, terminal inflorescences tend to have a more prominent, compact flower cluster, whereas cauline flowers are distributed more evenly along the stem, often spaced apart by internodes. The presence of specialized bracts and variations in pedicel length further distinguish cauline from terminal inflorescences, influencing reproductive success and overall plant architecture.
Functions of Terminal and Cauline Parts
Terminal structures in plants primarily function as the main growth points responsible for elongation and the production of new leaves and flowers, while cauline parts, such as stem nodes and internodes, support nutrient transport and structural stability. Terminal buds often dominate apical growth through apical dominance, controlling the direction and extent of vertical growth. Cauline regions facilitate the distribution of water, minerals, and photosynthates between roots and leaves, contributing to overall plant vitality and development.
Examples of Terminal Structures in Plants
Terminal structures in plants refer to growth points located at the tip of a stem or branch, such as terminal buds, flowers, or inflorescences, which drive vertical growth. Examples include the apical bud found at the apex of sunflower stems, the flower clusters at the ends of tomato plant branches, and the terminal cones seen in conifer species like pine trees. These terminal structures play a crucial role in determining plant height and reproductive development.
Examples of Cauline Structures in Plants
Cauline structures in plants refer to leaves or branches that grow directly on the stem rather than at the tip of a branch or shoot, contrasting with terminal structures. Examples of cauline leaves include those of sunflowers (Helianthus annuus), where leaves emerge along the central stem, and maize (Zea mays), which displays prominent cauline leaves attached directly to the stalk. Cauline branches appear in plants like tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), producing lateral growths from the main stem rather than terminal tips.
Role in Plant Growth and Development
Terminal buds play a crucial role in the vertical growth of plants by producing primary shoots and hormones like auxins that suppress lateral bud growth, ensuring apical dominance. Cauline buds, located along the stem nodes, contribute to the lateral expansion and branching, promoting increased foliage and reproductive structures. The balance between terminal and cauline bud activity determines overall plant architecture, affecting height, branch density, and resource allocation.
Terminal vs Cauline in Plant Identification
Terminal leaves are located at the tip of a stem or branch, serving as key indicators in plant identification by marking growth points. Cauline leaves grow along the stem's length and aid in distinguishing species with varying leaf arrangements and stem structures. Examining the position and morphology of terminal versus cauline leaves helps botanists accurately classify and identify plants.
Importance in Horticulture and Agriculture
Terminal buds influence the primary growth and shape of plants, playing a crucial role in the development of fruit trees and ornamental shrubs by determining the main axis extension and flowering sites. Cauline leaves, positioned along the stem, contribute significantly to photosynthesis and nutrient distribution, impacting overall plant health and yield quality in crops like cereals and legumes. Understanding the interplay between terminal and cauline structures aids horticulturists and agriculturalists in optimizing pruning techniques, improving plant architecture, and enhancing productivity.
Summary: Terminal vs Cauline Key Takeaways
Terminal leaves grow at the tip of a stem or branch, playing a crucial role in the plant's vertical growth, while cauline leaves arise along the stem, contributing to photosynthesis and support. Terminal leaves are often larger and more complex, whereas cauline leaves tend to be smaller and simpler but more numerous. Understanding the differences between terminal and cauline leaves aids in identifying plant species and studying their growth patterns.
terminal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com