A hygrometer accurately measures the humidity level in the air, essential for maintaining optimal indoor comfort and preventing moisture-related damage. Understanding how to read and use a hygrometer can significantly improve your control over air quality and climate conditions. Discover more about choosing the right hygrometer and its practical applications in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
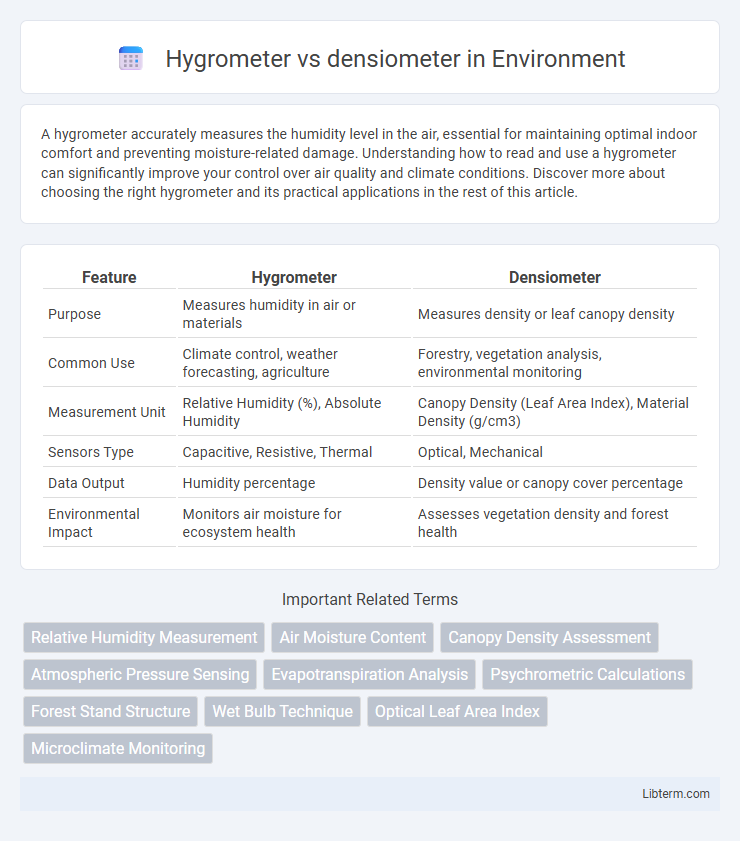
| Feature | Hygrometer | Densiometer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures humidity in air or materials | Measures density or leaf canopy density |
| Common Use | Climate control, weather forecasting, agriculture | Forestry, vegetation analysis, environmental monitoring |
| Measurement Unit | Relative Humidity (%), Absolute Humidity | Canopy Density (Leaf Area Index), Material Density (g/cm3) |
| Sensors Type | Capacitive, Resistive, Thermal | Optical, Mechanical |
| Data Output | Humidity percentage | Density value or canopy cover percentage |
| Environmental Impact | Monitors air moisture for ecosystem health | Assesses vegetation density and forest health |
Introduction to Hygrometers and Densiometers
Hygrometers measure the moisture content or relative humidity in the air, crucial for applications in meteorology, HVAC systems, and agriculture. Densiometers gauge the density or compactness of materials such as soil, wood, or photographic film, playing a vital role in forestry, construction, and material science. Understanding the specific function of each instrument enables precise environmental and material analysis for specialized industries.
What Is a Hygrometer?
A hygrometer is a precise instrument used to measure the moisture content or relative humidity in the air, essential for weather forecasting, HVAC systems, and environmental monitoring. Unlike a densiometer, which quantifies canopy density or light penetration in forestry and agriculture, a hygrometer focuses solely on atmospheric humidity levels. Accurate hygrometer readings help maintain optimal indoor air quality and prevent mold growth by controlling moisture.
What Is a Densiometer?
A densiometer is an instrument used to measure the density or optical properties of surfaces, commonly employed in forestry to assess canopy cover by estimating light transmission through tree leaves. Unlike a hygrometer, which measures humidity levels in the air, a densiometer provides data critical for understanding vegetation density and environmental light conditions. Its precise readings support ecological studies, forest management, and agricultural planning by quantifying canopy density efficiently.
Principle of Operation: Hygrometer vs Densiometer
A hygrometer measures moisture levels in the air by detecting changes in humidity, often using materials like hair or electronic sensors that respond to water vapor concentration. A densiometer quantifies canopy density or leaf area by measuring the amount of light blocked within a defined area, typically using optical sensors to assess vegetation cover. Both instruments rely on physical properties--moisture absorption for hygrometers and light transmission for densiometers--to provide precise environmental data essential for agricultural and meteorological applications.
Key Applications of Hygrometers
Hygrometers are essential instruments for measuring humidity levels, playing a critical role in industries such as meteorology, HVAC, agriculture, and manufacturing where precise moisture control influences product quality and environmental conditions. They are widely used in greenhouses to ensure optimal plant growth, in museums to preserve artifacts by maintaining stable humidity, and in weather stations for accurate atmospheric monitoring. Unlike densiometers, which measure canopy density for vegetation studies and forestry management, hygrometers specifically target air moisture content critical for climate-sensitive processes.
Key Applications of Densiometers
Densiometers are primarily used in forestry and environmental science to measure canopy density and leaf area index, providing critical data for assessing forest health and growth patterns. In contrast to hygrometers that monitor moisture levels, densiometers help quantify sunlight penetration, aiding in habitat evaluation and ecosystem productivity studies. Their key applications include guiding silvicultural decisions and enhancing biodiversity conservation efforts.
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison
Hygrometers provide precise humidity measurements by detecting moisture levels in the air through sensors such as capacitive or resistive elements, ensuring high accuracy in environmental monitoring. Densiometers, designed to measure optical density or vegetation density, rely on light transmission and reflection, which can be influenced by external factors, potentially reducing measurement reliability. In terms of accuracy and reliability, hygrometers generally offer more consistent and dependable results for humidity assessment, while densiometers may require calibration and controlled conditions to maintain measurement precision.
Advantages and Disadvantages
A hygrometer measures humidity levels with high accuracy, essential for climate control and weather monitoring, but it requires regular calibration and can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations. A densiometer quantifies vegetation density or photographic image density, offering precise, rapid assessments important for forestry and imaging applications, though it often demands specialized training and can be limited by environmental conditions or sample variability. Choosing between these instruments depends on the specific measurement needs, balancing precision, ease of use, and the environmental context in which they operate.
How to Choose Between Hygrometer and Densiometer
Choosing between a hygrometer and a densiometer depends on the specific measurement needs: a hygrometer measures atmospheric humidity with precision, essential for climate control and weather monitoring, while a densiometer quantifies foliage density or canopy cover, critical for forestry and ecological studies. Consider the application environment; hygrometers are ideal for indoor air quality, agriculture, and meteorology, whereas densiometers serve best in fieldwork requiring vegetation assessment. Accuracy, portability, and data output formats also influence the optimal instrument choice for environmental analysis.
Conclusion: Which Is Right for Your Needs?
Choosing between a hygrometer and a densiometer depends on your specific measurement requirements. Hygrometers accurately assess moisture levels in air, essential for humidity control in environments like greenhouses or HVAC systems. Densiometers measure canopy density or material opacity, making them ideal for forestry or optical applications, so selecting the right instrument hinges on whether your priority is humidity monitoring or density evaluation.
Hygrometer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com