Ecodistricts integrate urban development with sustainable practices, creating greenbelts that enhance biodiversity and improve air quality. These greenbelts serve as natural buffers, promoting ecological balance and offering recreational spaces for the community. Discover how your city can benefit by embracing ecodistrict principles in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
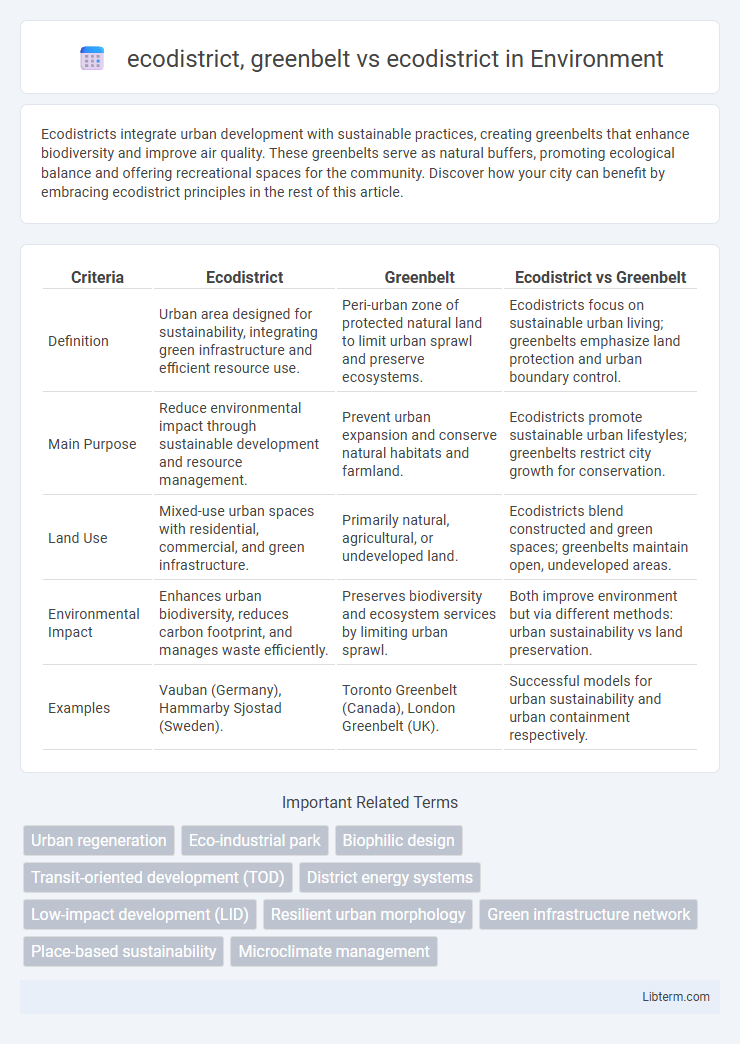
| Criteria | Ecodistrict | Greenbelt | Ecodistrict vs Greenbelt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Urban area designed for sustainability, integrating green infrastructure and efficient resource use. | Peri-urban zone of protected natural land to limit urban sprawl and preserve ecosystems. | Ecodistricts focus on sustainable urban living; greenbelts emphasize land protection and urban boundary control. |
| Main Purpose | Reduce environmental impact through sustainable development and resource management. | Prevent urban expansion and conserve natural habitats and farmland. | Ecodistricts promote sustainable urban lifestyles; greenbelts restrict city growth for conservation. |
| Land Use | Mixed-use urban spaces with residential, commercial, and green infrastructure. | Primarily natural, agricultural, or undeveloped land. | Ecodistricts blend constructed and green spaces; greenbelts maintain open, undeveloped areas. |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances urban biodiversity, reduces carbon footprint, and manages waste efficiently. | Preserves biodiversity and ecosystem services by limiting urban sprawl. | Both improve environment but via different methods: urban sustainability vs land preservation. |
| Examples | Vauban (Germany), Hammarby Sjostad (Sweden). | Toronto Greenbelt (Canada), London Greenbelt (UK). | Successful models for urban sustainability and urban containment respectively. |
Introduction to Ecodistricts
Ecodistricts prioritize sustainable urban development by integrating green infrastructure, energy-efficient buildings, and community-focused design to reduce environmental impact. Unlike traditional greenbelts that primarily serve as protected natural buffers limiting urban sprawl, ecodistricts foster mixed-use, walkable neighborhoods with renewable energy systems and waste reduction strategies. This holistic approach combines social equity, economic viability, and ecological resilience to create healthier, more sustainable urban environments.
Core Principles of Ecodistricts
Ecodistricts prioritize sustainable urban development through core principles such as integrated planning, resource efficiency, and inclusive community engagement. Unlike greenbelts, which primarily serve as natural buffer zones to limit urban sprawl and preserve open space, ecodistricts focus on creating regenerative, energy-efficient neighborhoods that minimize environmental impact. Key elements include localized energy generation, waste reduction, and social equity to foster resilient and livable urban areas.
What is a Greenbelt?
A Greenbelt is a designated area of natural or agricultural land surrounding urban zones to limit urban sprawl and preserve open space. It functions as a protective buffer, promoting biodiversity, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and supporting sustainable land use planning. Unlike an ecodistrict, which integrates sustainable infrastructure and community practices within urban neighborhoods, a Greenbelt emphasizes conservation and environmental protection on a larger, regional scale.
Greenbelt Development: Goals and Strategies
Greenbelt development prioritizes preserving natural landscapes and biodiversity by restricting urban sprawl and promoting sustainable land use. Strategies involve implementing buffer zones around cities to maintain ecological balance, enhance air and water quality, and provide recreational spaces. This approach supports climate resilience and biodiversity conservation while guiding urban growth within designated boundaries.
Ecodistricts vs Greenbelts: Key Differences
Ecodistricts focus on integrating sustainable urban design, energy efficiency, and community resilience within a defined urban area, promoting local resource management and reduced environmental impact. Greenbelts are designated zones of protected open land surrounding cities, aimed at limiting urban sprawl, preserving natural habitats, and maintaining air quality. The key difference lies in ecodistricts being proactive, sustainable urban neighborhoods, whereas greenbelts serve as passive buffers to contain growth and protect ecosystems.
Urban Sustainability: Role of Ecodistricts
Ecodistricts play a pivotal role in urban sustainability by integrating energy-efficient buildings, renewable energy systems, and sustainable transportation within compact, mixed-use neighborhoods designed to minimize environmental impact and enhance quality of life. Unlike greenbelts, which primarily preserve undeveloped land around urban areas to limit sprawl and protect ecosystems, ecodistricts focus on transforming existing urban spaces into high-performance, resource-efficient communities through advanced planning and smart technologies. These sustainable urban clusters optimize water management, waste reduction, and carbon footprint mitigation, positioning ecodistricts as key frameworks for resilient and regenerative city development.
Environmental Impact: Greenbelt vs Ecodistrict
Greenbelts provide extensive carbon sequestration and biodiversity preservation by maintaining large, contiguous natural areas surrounding urban regions, effectively mitigating urban sprawl and reducing heat island effects. Ecodistricts integrate sustainable infrastructure within urban neighborhoods, optimizing energy efficiency, waste management, and local resource cycles to minimize environmental footprints while fostering resilient communities. Compared to greenbelts, ecodistricts address environmental impact through localized solutions that combine green building technologies and smart urban planning, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced ecological connectivity within dense urban settings.
Community Benefits of Each Model
Ecodistricts promote sustainable urban living through integrated infrastructure that supports energy efficiency, local food systems, and social cohesion, enhancing residents' quality of life and fostering community resilience. Greenbelts preserve natural landscapes and ecosystems around urban areas, offering recreational spaces, improving air quality, and mitigating urban sprawl, which benefits public health and biodiversity conservation. While ecodistricts emphasize dense, resource-efficient living environments, greenbelts focus on protecting open spaces, both models contributing uniquely to community well-being and environmental sustainability.
Policy and Planning Considerations
Ecodistricts prioritize integrated, place-based policies that promote sustainability through green infrastructure, renewable energy, and community engagement, while greenbelts primarily focus on preserving natural landscapes and limiting urban sprawl via zoning and land-use regulations. Planning considerations for ecodistricts involve multi-sector collaboration, adaptive governance, and incorporating circular economy principles to enhance resilience and reduce carbon footprints. In contrast, greenbelt policies emphasize maintaining ecological connectivity and agricultural viability, often requiring strict land preservation guidelines and enforcement mechanisms to prevent development encroachment.
Future Trends: Integrating Ecodistricts and Greenbelts
Future trends emphasize the integration of ecodistricts and greenbelts to create sustainable urban ecosystems that enhance biodiversity, improve air quality, and promote resilient community living. Ecodistricts incorporate smart technologies and renewable energy within urban greenbelts, optimizing land use while preserving natural habitats and mitigating urban heat island effects. This synergy supports climate adaptation strategies and fosters social equity by providing accessible green spaces and sustainable infrastructure for future generations.
ecodistrict, greenbelt Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com