Restoration ecology focuses on repairing damaged ecosystems to restore their natural functions and biodiversity. This scientific approach involves techniques like reforestation, wetland reconstruction, and invasive species management to revive habitats and enhance ecosystem services. Discover how restoration ecology can transform degraded environments and benefit your local community in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
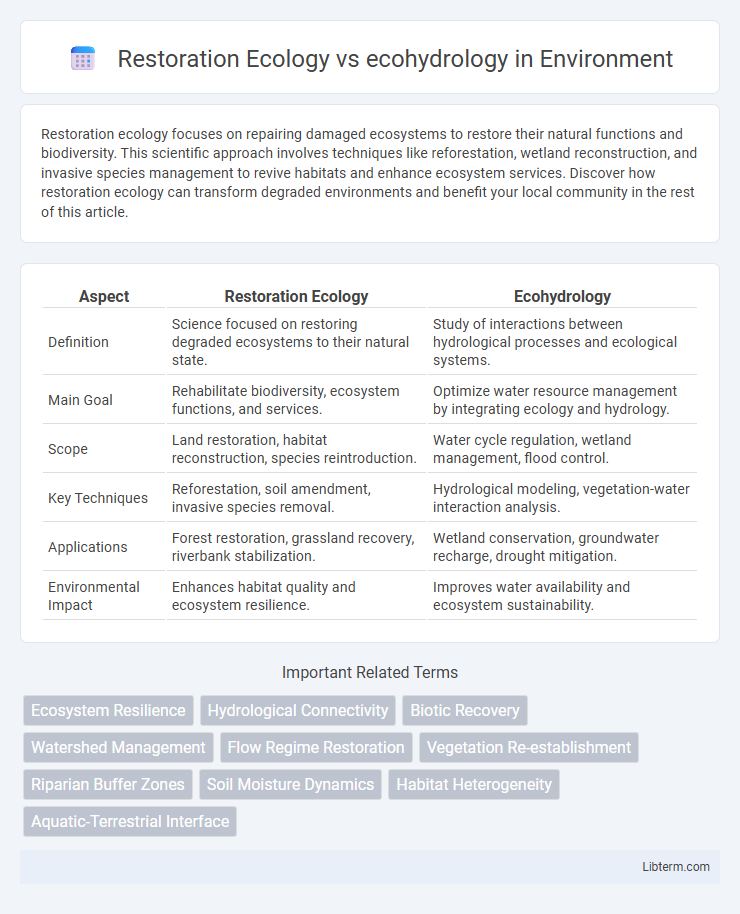
| Aspect | Restoration Ecology | Ecohydrology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Science focused on restoring degraded ecosystems to their natural state. | Study of interactions between hydrological processes and ecological systems. |
| Main Goal | Rehabilitate biodiversity, ecosystem functions, and services. | Optimize water resource management by integrating ecology and hydrology. |
| Scope | Land restoration, habitat reconstruction, species reintroduction. | Water cycle regulation, wetland management, flood control. |
| Key Techniques | Reforestation, soil amendment, invasive species removal. | Hydrological modeling, vegetation-water interaction analysis. |
| Applications | Forest restoration, grassland recovery, riverbank stabilization. | Wetland conservation, groundwater recharge, drought mitigation. |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances habitat quality and ecosystem resilience. | Improves water availability and ecosystem sustainability. |
Introduction to Restoration Ecology and Ecohydrology
Restoration Ecology focuses on the scientific study and practice of renewing degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems by returning them to a stable and sustainable state, emphasizing biodiversity recovery and ecosystem functionality. Ecohydrology integrates ecological and hydrological processes, examining the interactions between water and ecosystems to improve water management and promote ecosystem health. Both fields contribute to environmental sustainability, but Restoration Ecology centers on ecosystem restoration, while Ecohydrology emphasizes water-driven ecological dynamics and conservation.
Core Principles of Restoration Ecology
Restoration ecology centers on reestablishing ecosystem structure, function, and biodiversity through principles such as historical fidelity, ecosystem resilience, and adaptive management. It emphasizes the recovery of native species, soil health, and natural disturbance regimes to restore ecological balance. In contrast, ecohydrology focuses on the interactions between water and ecosystems, applying hydrological processes to support ecosystem restoration and sustainable water management.
Fundamentals of Ecohydrology
Restoration ecology focuses on recovering degraded ecosystems by re-establishing native species and ecological processes, while ecohydrology studies interactions between hydrological and ecological systems to inform sustainable water management. Fundamentals of ecohydrology emphasize the coupling of hydrological cycles with biological components, analyzing water flows, soil moisture, and plant-water relationships to improve ecosystem resilience and restoration outcomes. Integrating ecohydrological principles enhances restoration ecology by optimizing water availability and improving habitat conditions for targeted species and ecosystem functions.
Key Differences Between Restoration Ecology and Ecohydrology
Restoration ecology primarily focuses on repairing damaged ecosystems by reestablishing native species and natural processes to improve biodiversity and habitat function. Ecohydrology emphasizes the interactions between water cycles and ecological processes, analyzing how hydrological factors influence ecosystem health and resilience. Key differences lie in restoration ecology's goal of ecosystem recovery versus ecohydrology's focus on managing water flow to sustain ecosystem functions.
Overlapping Goals and Synergies
Restoration ecology and ecohydrology share overlapping goals centered on rehabilitating degraded ecosystems and enhancing biodiversity through sustainable water management practices. Both disciplines emphasize the restoration of natural hydrological cycles to improve ecosystem resilience, habitat quality, and ecological functions in disturbed landscapes. Synergies between restoration ecology and ecohydrology enable integrated approaches that optimize water availability, soil health, and vegetation recovery, promoting long-term sustainability and climate adaptation.
Methodologies in Restoration Ecology
Restoration ecology employs methodologies such as site assessment, species selection, soil amendment, and ecological monitoring to reestablish native biodiversity and ecosystem functions. Techniques include reforestation, invasive species removal, and hydrological restoration tailored to specific habitat conditions. These approaches integrate adaptive management and long-term data collection to evaluate restoration success and ecosystem resilience.
Techniques and Tools in Ecohydrology
Ecohydrology utilizes techniques such as hydrological modeling, remote sensing, and stable isotope analysis to understand and manage the interactions between water and ecosystems. Tools like Geographic Information Systems (GIS), soil moisture sensors, and ecohydraulic flumes help quantify water flow, vegetation dynamics, and nutrient cycling. These techniques enable targeted restoration practices that enhance ecosystem resilience by optimizing water availability and quality.
Case Studies: Successful Applications
Restoration ecology projects such as the Florida Everglades restoration have demonstrated significant wetland recovery by reestablishing native vegetation and hydrological regimes, improving biodiversity and ecosystem services. Ecohydrology applications in the Loess Plateau, China, successfully combined vegetation restoration with water management to reduce soil erosion and increase groundwater recharge, enhancing agricultural productivity. Both fields highlight the importance of integrating hydrological processes with ecological principles to achieve long-term sustainability in degraded landscapes.
Challenges and Future Trends
Restoration ecology faces challenges such as restoring biodiversity in degraded ecosystems, addressing climate change impacts, and integrating socio-economic factors for sustainable recovery. Ecohydrology contends with understanding complex water-vegetation interactions, predicting hydrological responses to environmental changes, and managing water resources under increasing anthropogenic pressure. Future trends in both fields emphasize the use of advanced remote sensing technologies, ecosystem modeling, and interdisciplinary approaches to enhance resilience and ecosystem services.
Integrating Restoration Ecology and Ecohydrology for Sustainable Ecosystem Management
Restoration ecology emphasizes rehabilitating degraded ecosystems by reinstating native species and natural processes, while ecohydrology investigates water movement and its interactions with biological communities. Integrating these disciplines enhances sustainable ecosystem management by combining hydrological insights with ecological restoration techniques to improve habitat resilience and water quality. This approach supports adaptive management strategies that address both biotic and abiotic factors, leading to long-term ecosystem functionality and stability.
Restoration Ecology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com