Sustainability focuses on meeting present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs, emphasizing responsible resource management and environmental stewardship. It integrates economic, social, and ecological dimensions to create long-lasting positive impacts for communities and ecosystems. Discover how sustainability can transform Your lifestyle and business practices by exploring the insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
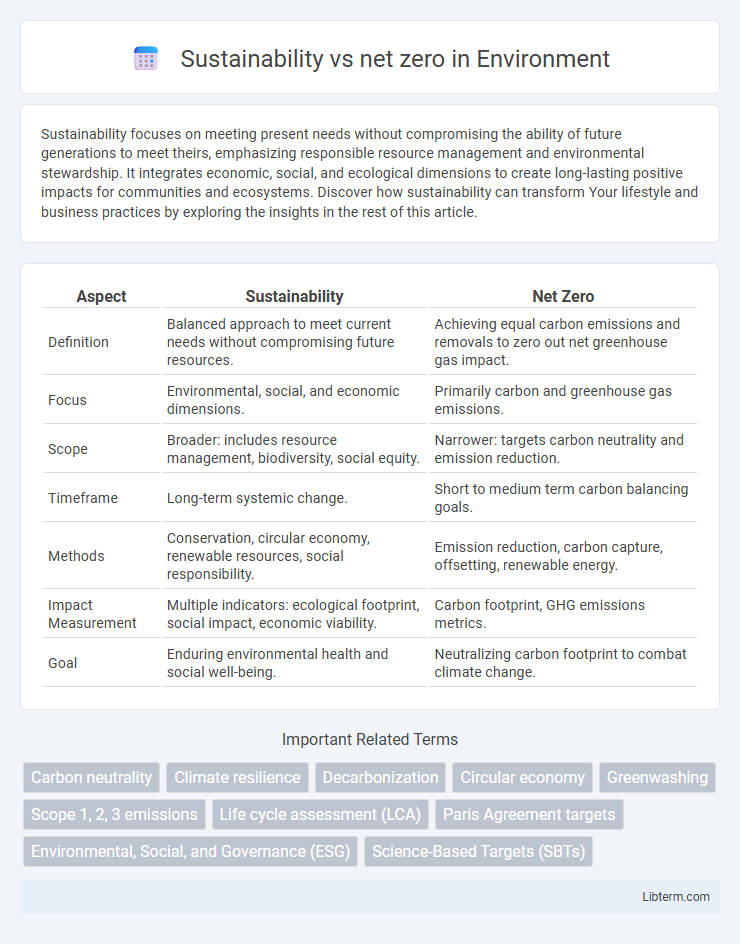
| Aspect | Sustainability | Net Zero |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Balanced approach to meet current needs without compromising future resources. | Achieving equal carbon emissions and removals to zero out net greenhouse gas impact. |
| Focus | Environmental, social, and economic dimensions. | Primarily carbon and greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Scope | Broader: includes resource management, biodiversity, social equity. | Narrower: targets carbon neutrality and emission reduction. |
| Timeframe | Long-term systemic change. | Short to medium term carbon balancing goals. |
| Methods | Conservation, circular economy, renewable resources, social responsibility. | Emission reduction, carbon capture, offsetting, renewable energy. |
| Impact Measurement | Multiple indicators: ecological footprint, social impact, economic viability. | Carbon footprint, GHG emissions metrics. |
| Goal | Enduring environmental health and social well-being. | Neutralizing carbon footprint to combat climate change. |
Understanding Sustainability vs Net Zero: Key Definitions
Sustainability involves meeting present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs, emphasizing environmental, social, and economic balance. Net zero specifically targets reducing greenhouse gas emissions to zero by balancing emitted and removed carbon, focusing primarily on climate change mitigation. Understanding these distinctions helps organizations align strategies with broader sustainability goals while committing to net zero emission targets.
The Evolution of Environmental Strategies
Sustainability has evolved from broad eco-friendly practices to targeted net zero goals emphasizing carbon neutrality by reducing greenhouse gas emissions to zero through balancing emissions with removals. Companies increasingly adopt circular economy principles and renewable energy solutions as foundational elements of sustainability strategies, shifting towards measurable net zero commitments. This evolution reflects a strategic progression from general environmental responsibility to precise, science-based targets aimed at mitigating climate change impacts.
Core Principles of Sustainability
The core principles of sustainability encompass environmental protection, social equity, and economic viability, creating a balanced approach to meet present needs without compromising future generations. Sustainability aims for long-term resilience by integrating resource conservation, reducing pollution, and promoting social well-being across communities. Net zero prioritizes carbon neutrality by balancing emitted greenhouse gases with removal or offset efforts but is a component within the broader sustainability framework.
What Does Net Zero Really Mean?
Net zero refers to achieving a balance between the greenhouse gases emitted and those removed from the atmosphere, effectively resulting in no net increase in carbon emissions. It involves reducing emissions through energy efficiency, renewable energy, and carbon offset projects like reforestation or carbon capture. Sustainability encompasses a broader scope, including environmental health, social equity, and economic viability, whereas net zero specifically targets carbon neutrality as a key component of climate action.
Comparing Goals: Sustainability and Net Zero
Sustainability aims to balance environmental, social, and economic factors to ensure long-term ecosystem health and human well-being, while net zero specifically targets reducing greenhouse gas emissions to zero by balancing emitted and absorbed carbon. Sustainability encompasses broader objectives including resource conservation, social equity, and economic viability, whereas net zero focuses primarily on climate mitigation through carbon neutrality. Achieving net zero is often viewed as a critical milestone within the broader sustainability framework to address global climate change impacts effectively.
Practical Approaches for Achieving Sustainability
Practical approaches for achieving sustainability emphasize resource efficiency, waste minimization, and renewable energy adoption to reduce environmental impact. Organizations implement circular economy models and sustainable supply chain management to promote long-term ecological balance. Incorporating life cycle assessment tools and stakeholder collaboration ensures measurable progress toward sustainability goals beyond just net zero emissions.
Practical Approaches for Achieving Net Zero
Practical approaches for achieving net zero focus on reducing carbon emissions through energy efficiency upgrades, adoption of renewable energy sources, and investment in carbon capture technologies. Organizations implement science-based targets aligned with the Paris Agreement to measure progress and ensure accountability. Integrating circular economy principles and promoting sustainable supply chains further supports long-term net zero goals while balancing environmental and economic demands.
Challenges in Reaching Sustainability and Net Zero Targets
Achieving sustainability and net zero targets faces challenges such as insufficient renewable energy infrastructure, high transition costs, and inconsistent regulatory frameworks. Corporate and governmental commitment often varies, hindering coordinated efforts and long-term planning. Data gaps and measurement inconsistencies further complicate tracking progress and verifying emissions reductions.
Measuring Success: Metrics for Both Strategies
Sustainability success is measured through comprehensive metrics such as carbon footprint reduction, resource efficiency, waste minimization, and social impact indicators like community engagement and labor practices. Net zero strategies primarily focus on quantifiable greenhouse gas (GHG) emission metrics, including carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) reductions verified by scientific methodologies like the Greenhouse Gas Protocol. Both strategies require robust data tracking, third-party verification, and continual improvement benchmarks to ensure accountability and transparent progress toward environmental goals.
Future Trends: Integrating Sustainability and Net Zero Initiatives
Future trends indicate a growing integration of sustainability and net zero initiatives as businesses increasingly adopt comprehensive environmental strategies. Advances in renewable energy, carbon capture technology, and circular economy practices drive the transition toward holistic sustainability models that align with net zero targets. Enhanced regulatory frameworks and stakeholder demands further accelerate the convergence of sustainability efforts with ambitious net zero commitments.
Sustainability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com