Afforestation involves planting trees in areas where there were no previous forests, enhancing biodiversity and combating climate change through increased carbon sequestration. This process improves soil quality, reduces erosion, and supports ecosystems vital for wildlife. Explore the benefits and methods of afforestation to understand how your actions can contribute to a greener planet.
Table of Comparison
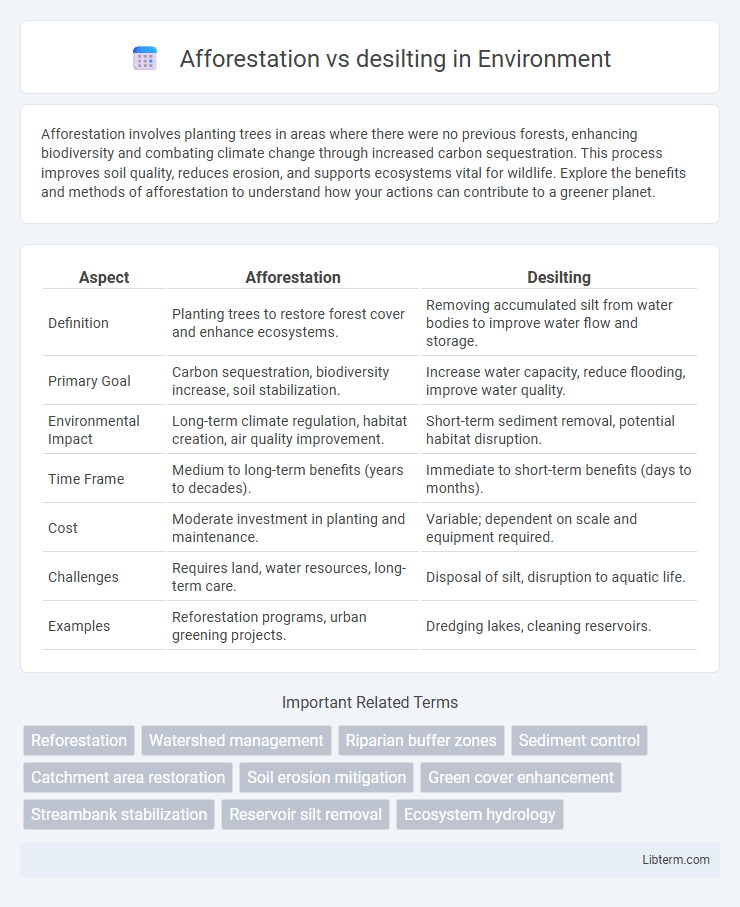
| Aspect | Afforestation | Desilting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planting trees to restore forest cover and enhance ecosystems. | Removing accumulated silt from water bodies to improve water flow and storage. |
| Primary Goal | Carbon sequestration, biodiversity increase, soil stabilization. | Increase water capacity, reduce flooding, improve water quality. |
| Environmental Impact | Long-term climate regulation, habitat creation, air quality improvement. | Short-term sediment removal, potential habitat disruption. |
| Time Frame | Medium to long-term benefits (years to decades). | Immediate to short-term benefits (days to months). |
| Cost | Moderate investment in planting and maintenance. | Variable; dependent on scale and equipment required. |
| Challenges | Requires land, water resources, long-term care. | Disposal of silt, disruption to aquatic life. |
| Examples | Reforestation programs, urban greening projects. | Dredging lakes, cleaning reservoirs. |
Introduction to Afforestation and Desilting
Afforestation involves planting trees on barren or deforested land to restore ecological balance, enhance biodiversity, and sequester carbon dioxide. Desilting is the process of removing accumulated silt and sediments from water bodies such as lakes and reservoirs to increase water storage capacity and improve water quality. Both techniques play vital roles in environmental management, contributing to sustainable water resources and ecosystem restoration.
Definition and Core Concepts
Afforestation refers to the process of planting trees in barren or deforested areas to restore ecosystems, improve carbon sequestration, and enhance biodiversity. Desilting involves the removal of accumulated silt and sediment from water bodies such as reservoirs, rivers, or canals to improve water flow, storage capacity, and prevent flooding. Both practices are essential for environmental management but target different issues: afforestation focuses on vegetation restoration and soil conservation, while desilting emphasizes water resource maintenance and flood control.
Environmental Benefits of Afforestation
Afforestation significantly enhances air quality by increasing carbon sequestration, reducing greenhouse gases, and mitigating climate change effects. It promotes biodiversity by creating new habitats for diverse flora and fauna, contributing to ecosystem stability and resilience. Unlike desilting, which primarily improves water flow and reduces flood risks, afforestation offers long-term environmental benefits such as soil erosion control and improved groundwater recharge.
Ecological Impact of Desilting
Desilting enhances aquatic ecosystems by restoring water flow, improving oxygen levels, and reducing harmful sediment accumulation that can suffocate fish and plant life. This process supports biodiversity by preventing the degradation of wetlands and maintaining habitat quality for aquatic and riparian species. Effective desilting also mitigates nutrient overloads that cause algal blooms, thereby promoting healthier and more balanced freshwater environments.
Carbon Sequestration: Trees vs Water Bodies
Afforestation significantly enhances carbon sequestration by absorbing atmospheric CO2 through photosynthesis and storing it in biomass and soil, making it a critical strategy for mitigating climate change. Water bodies, maintained through desilting, support carbon sequestration indirectly by preserving aquatic ecosystems that capture carbon in sediments and support vegetation growth. Comparing both, afforestation provides a more direct and substantial carbon sink, while desilting sustains the carbon storage capacity of aquatic environments, emphasizing the complementary role of terrestrial and aquatic systems in carbon management.
Soil Health: Effects of Afforestation and Desilting
Afforestation enhances soil health by increasing organic matter and promoting microbial activity, which improves soil structure and nutrient cycling. Desilting removes sediment buildup from water bodies, preventing nutrient overload and restoring soil permeability and aeration in adjacent lands. Together, these practices mitigate soil degradation, support fertility, and maintain sustainable land productivity.
Flood Control and Water Management
Afforestation enhances flood control by increasing soil absorption and reducing surface runoff, which stabilizes water flow and minimizes flood risks. Desilting improves water management by clearing sediment from water bodies, increasing storage capacity and ensuring efficient water flow during peak rainfall. Combining afforestation with regular desilting optimizes flood mitigation and sustains water resources in catchment areas.
Biodiversity Enhancement: Forests vs Aquatic Systems
Afforestation significantly enhances biodiversity by creating habitats for diverse terrestrial species, promoting ecological stability and increasing carbon sequestration. Desilting improves aquatic systems by restoring water flow, reducing sedimentation, and enhancing habitats for fish and invertebrates, thus supporting freshwater biodiversity. While afforestation expands biodiversity on land, desilting primarily rejuvenates aquatic ecosystems, both playing crucial roles in ecosystem health and species diversity.
Cost-Effectiveness and Practical Challenges
Afforestation offers a cost-effective, long-term solution for soil stabilization and watershed management by enhancing biodiversity and reducing erosion naturally. In contrast, desilting requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs, often proving less sustainable due to the recurrent need to remove sediment accumulation. Practical challenges for afforestation include land availability and growth time, while desilting struggles with equipment costs and the disposal of dredged materials.
Integrated Approaches for Sustainable Land and Water Management
Afforestation enhances soil stability and increases groundwater recharge, complementing desilting efforts that restore reservoir capacity and improve water quality. Integrated approaches combining afforestation with desilting optimize land productivity and water availability by reducing erosion and enhancing sediment control. Sustainable land and water management rely on this synergy to maintain ecosystem health and support agricultural resilience.
Afforestation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com