Climate positive initiatives go beyond reducing greenhouse gas emissions by actively removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, contributing to environmental restoration and sustainability. Businesses and individuals committed to climate positive strategies play a crucial role in mitigating climate change impacts and promoting a healthier planet. Explore the rest of this article to discover how you can support and implement climate positive actions in your life.
Table of Comparison
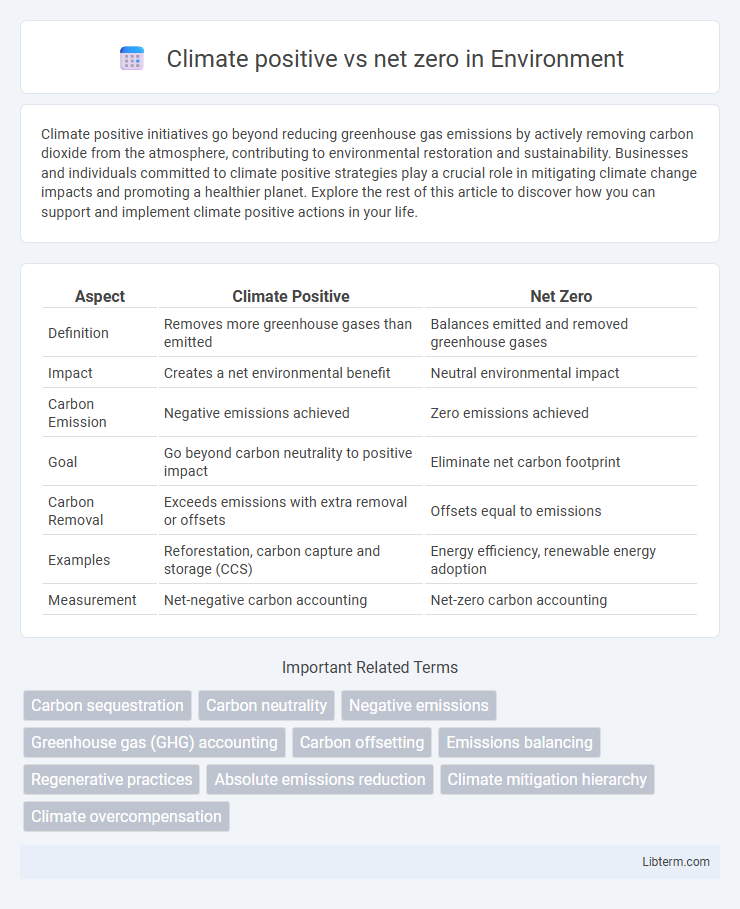
| Aspect | Climate Positive | Net Zero |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removes more greenhouse gases than emitted | Balances emitted and removed greenhouse gases |
| Impact | Creates a net environmental benefit | Neutral environmental impact |
| Carbon Emission | Negative emissions achieved | Zero emissions achieved |
| Goal | Go beyond carbon neutrality to positive impact | Eliminate net carbon footprint |
| Carbon Removal | Exceeds emissions with extra removal or offsets | Offsets equal to emissions |
| Examples | Reforestation, carbon capture and storage (CCS) | Energy efficiency, renewable energy adoption |
| Measurement | Net-negative carbon accounting | Net-zero carbon accounting |
Understanding Climate Positive and Net Zero
Climate positive refers to going beyond net zero by actively removing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than is emitted, creating a positive environmental impact. Net zero focuses on balancing emitted greenhouse gases with an equivalent amount of carbon removal or offsetting, resulting in zero net emissions. Companies aiming for climate positive status implement strategies that not only reduce emissions but also invest in carbon capture, reforestation, and renewable energy projects to generate surplus environmental benefits.
Origins and Evolution of the Concepts
The concept of net zero originated in the early 2000s as a goal to balance carbon emissions with carbon removal, primarily through renewable energy adoption and carbon offsetting. Climate positive emerged later as an evolution of net zero, emphasizing going beyond carbon neutrality by removing additional greenhouse gases to create a net environmental benefit. Both concepts have evolved significantly through international climate agreements, scientific research, and corporate sustainability initiatives, reflecting increasing urgency in addressing climate change.
Key Differences Between Climate Positive and Net Zero
Climate positive refers to reducing more greenhouse gas emissions than an organization or individual produces, effectively creating a net environmental benefit, while net zero means balancing emitted gases with equivalent offsets to achieve zero net emissions. Key differences lie in impact scope: net zero aims for neutral carbon output, whereas climate positive strives for surplus reduction beyond neutralization. Climate positive focuses on actively improving the environment, whereas net zero primarily targets carbon neutrality through mitigation and offsetting strategies.
Measuring Carbon Footprint: Approaches and Standards
Measuring carbon footprint involves quantifying greenhouse gas emissions using approaches like the Greenhouse Gas Protocol and ISO 14064 standards, which provide frameworks for accurate inventory and reporting. Climate positive strategies aim to remove or offset more carbon than emitted, requiring rigorous, transparent accounting and verification to ensure net negative emissions beyond net zero targets. Precise measurement and adherence to established methodologies are critical for organizations to demonstrate true climate impact and progress toward sustainability goals.
Benefits of Achieving Climate Positive Status
Achieving climate positive status means removing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than an organization emits, creating a net environmental benefit beyond neutrality. Benefits include enhanced corporate reputation, increased investor confidence, and compliance with emerging global regulations on carbon emissions. This proactive approach drives innovation in sustainable practices and contributes significantly to combating climate change.
Industry Examples: Net Zero vs Climate Positive Practices
Industry leaders like Microsoft and Unilever are pioneering net zero initiatives by reducing carbon emissions through renewable energy adoption and sustainable supply chains. Companies such as Patagonia and Tesla go beyond net zero by implementing climate positive practices, actively removing more carbon from the atmosphere than they emit through reforestation projects and carbon capture technologies. These contrasting approaches highlight how net zero stabilizes emissions, while climate positive strategies drive environmental restoration and promote long-term ecological balance.
Overcoming Challenges in Transitioning Beyond Net Zero
Transitioning beyond net zero to achieve climate positivity requires addressing complex challenges such as enhancing carbon removal technologies, securing sustainable financing, and fostering robust policy frameworks that incentivize negative emissions. Effective strategies include investing in innovative natural and technological carbon sequestration methods and developing transparent measurement and verification systems to ensure accountability. Collaboration between governments, private sectors, and communities plays a crucial role in scaling climate-positive solutions and overcoming regulatory and market barriers.
Policy and Regulatory Impacts on Sustainability Goals
Climate positive initiatives require policies that promote carbon removal beyond net zero emissions, driving innovation in carbon capture technologies and incentivizing sustainable practices. Regulatory frameworks targeting net zero focus on emission reduction targets, carbon pricing mechanisms, and compliance standards to achieve balance between emissions produced and offset. Both approaches influence sustainable development goals by shaping industry behavior, investment strategies, and national commitments under international climate agreements like the Paris Accord.
Tools and Strategies for Climate Leadership
Climate positive initiatives employ carbon removal technologies such as direct air capture and enhanced soil carbon sequestration to go beyond net zero emissions, creating a measurable climate benefit. Net zero strategies focus on balancing emitted greenhouse gases with equivalent carbon offset projects, using tools like carbon accounting software and renewable energy adoption to achieve neutrality. Both approaches leverage innovative climate leadership frameworks, including science-based targets and transparent reporting platforms, to drive accountability and continuous environmental impact reduction.
Future Outlook: Moving from Net Zero to Climate Positive
The future outlook emphasizes transitioning from net zero, which balances emitted and absorbed greenhouse gases, to climate positive strategies that actively reduce atmospheric carbon beyond neutralization. Organizations adopting climate positive goals invest in innovative carbon removal technologies, reforestation projects, and sustainable practices that generate net environmental benefits. This shift accelerates climate action, setting new standards for corporate responsibility and fostering a net-negative global carbon footprint by mid-century.
Climate positive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com