Agrology focuses on the science and technology of soil management and crop production to enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability. It integrates principles of biology, chemistry, and environmental science to optimize land use and support food security. Discover how agrology can transform Your farming practices and contribute to a greener future by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
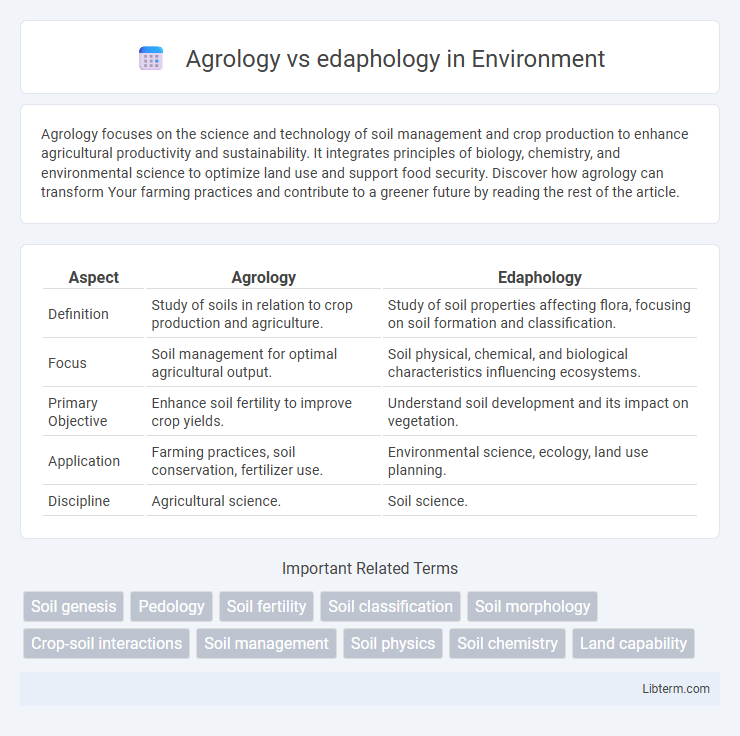
| Aspect | Agrology | Edaphology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of soils in relation to crop production and agriculture. | Study of soil properties affecting flora, focusing on soil formation and classification. |
| Focus | Soil management for optimal agricultural output. | Soil physical, chemical, and biological characteristics influencing ecosystems. |
| Primary Objective | Enhance soil fertility to improve crop yields. | Understand soil development and its impact on vegetation. |
| Application | Farming practices, soil conservation, fertilizer use. | Environmental science, ecology, land use planning. |
| Discipline | Agricultural science. | Soil science. |
Introduction to Agrology and Edaphology
Agrology is the scientific study of soils in relation to crop production, emphasizing soil management practices for agricultural productivity. Edaphology, a branch of soil science, focuses on the influence of soils on living organisms, particularly plants, analyzing soil properties such as texture, structure, and nutrient content. Both fields integrate soil chemistry, biology, and physics to optimize soil use for sustainable agriculture and environmental health.
Defining Agrology: Scope and Focus
Agrology is a branch of soil science emphasizing the application of soil knowledge to agricultural production, focusing on soil management, fertility, and crop growth optimization. It integrates soil chemistry, physics, and biology to improve land use and sustainability in farming practices. Agrology's scope extends to assessing soil health and productivity for food security and environmental stewardship.
Understanding Edaphology: Core Principles
Edaphology, a branch of soil science, concentrates on the influence of soil properties on plant growth and the interactions between soil and living organisms, emphasizing soil's physical, chemical, and biological characteristics. Unlike agrology, which broadly addresses soil management for agricultural productivity, edaphology drills down into soil's role in supporting ecosystems and sustaining plant life. Core principles include studying soil formation, classification, fertility, and the impact of soil on plant nutrition and health, which are critical for sustainable land use and environmental conservation.
Historical Development of Agrology and Edaphology
Agrology and edaphology, both rooted in soil science, have distinct historical developments reflecting their specialized focuses. Agrology emerged as an applied science in the early 20th century, emphasizing soil management for agricultural productivity and integrating plant-soil interactions to enhance crop yields. Edaphology, with origins tracing back to the 19th century, concentrated on the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soils, forming the foundational understanding necessary for later agrological applications.
Key Differences between Agrology and Edaphology
Agrology focuses on the practical application of soil science to agricultural production, emphasizing soil management and fertility for crop growth, while edaphology studies soil as a natural habitat, analyzing its physical, chemical, and biological properties to understand soil formation and behavior in ecosystems. Agrology integrates agronomic principles with soil science to optimize plant nutrition and sustainable farming practices, whereas edaphology provides the foundational knowledge of soil characteristics critical for broader environmental and ecological studies. The key difference lies in agrology's direct orientation towards agricultural productivity versus edaphology's broader scientific investigation of soil environments.
Similarities and Overlapping Areas
Agrology and edaphology both study soil properties and their impact on plant growth, emphasizing soil fertility, nutrient management, and crop productivity. These disciplines overlap in analyzing soil composition, texture, and structure to optimize agricultural practices and ensure sustainable land use. Shared techniques include soil sampling, testing for chemical and physical characteristics, and developing strategies for soil conservation.
Role of Agrology in Modern Agriculture
Agrology plays a crucial role in modern agriculture by integrating soil science, crop production, and environmental management to optimize sustainable farming practices. It involves analyzing soil properties, nutrient availability, and land use patterns to enhance crop yields and prevent land degradation. Agrology supports precision agriculture through data-driven decision-making, leading to efficient resource use and improved agricultural productivity.
Importance of Edaphology in Environmental Science
Edaphology, the study of soil in relation to living organisms, is crucial in environmental science for understanding soil health, nutrient cycling, and ecosystem sustainability. It provides essential insights into soil properties that affect plant growth, water retention, and pollutant degradation, directly influencing environmental quality and land management practices. Compared to agrology's focus on agricultural productivity, edaphology emphasizes the broader ecological role of soils in maintaining environmental balance and supporting biodiversity.
Career Opportunities in Agrology and Edaphology
Career opportunities in agrology primarily encompass roles in agricultural management, crop production, and sustainable farming practices, focusing on optimizing plant growth and soil-plant interactions. Edaphology career paths often involve soil science research, soil fertility analysis, and environmental consultancy, emphasizing soil properties and their impact on ecosystems. Both fields offer prospects in governmental agencies, research institutions, and agribusiness sectors, with agrology leaning more towards applied agricultural production and edaphology towards environmental and soil health management.
Future Trends in Soil Science: Agrology vs Edaphology
Future trends in soil science highlight agrology's focus on sustainable agricultural practices through precision farming and soil health monitoring using advanced sensor technology. Edaphology advances emphasize understanding soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties to enhance ecosystem restoration and combat climate change effects. Integration of big data analytics and machine learning in both fields is driving innovations in soil management and environmental conservation.
Agrology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com