Ecology examines the relationships between living organisms and their environment, highlighting the delicate balance essential for ecosystem sustainability. Understanding ecological principles helps you recognize the impact of human activities on biodiversity and natural resources. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can contribute to preserving our planet's health.
Table of Comparison
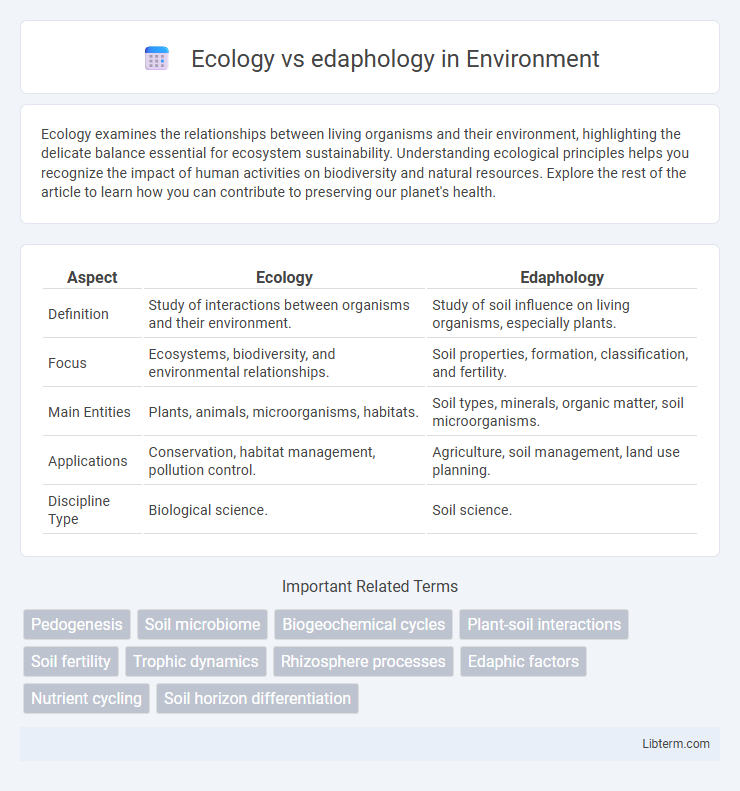
| Aspect | Ecology | Edaphology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of interactions between organisms and their environment. | Study of soil influence on living organisms, especially plants. |
| Focus | Ecosystems, biodiversity, and environmental relationships. | Soil properties, formation, classification, and fertility. |
| Main Entities | Plants, animals, microorganisms, habitats. | Soil types, minerals, organic matter, soil microorganisms. |
| Applications | Conservation, habitat management, pollution control. | Agriculture, soil management, land use planning. |
| Discipline Type | Biological science. | Soil science. |
Introduction to Ecology and Edaphology
Ecology studies the relationships between living organisms and their environments, emphasizing ecosystems, biodiversity, and energy flows. Edaphology focuses specifically on soil properties, formation, and their influence on plant growth and soil management. Understanding both fields is essential for sustainable agriculture and environmental conservation.
Defining Ecology: Scope and Relevance
Ecology examines interactions between organisms and their environments, encompassing biological, chemical, and physical factors influencing ecosystems. Its scope includes studying population dynamics, community structure, and nutrient cycling to understand ecosystem functionality and biodiversity. This discipline is crucial for addressing environmental challenges such as habitat loss, climate change, and sustainable resource management.
Understanding Edaphology: Focus and Importance
Edaphology, a sub-discipline of soil science, concentrates on the study of soil properties and their influence on plant growth and ecosystem health. It examines soil composition, structure, nutrient availability, and microbial activity, providing essential insights for agriculture, forestry, and environmental management. Understanding edaphology is crucial for sustainable land use practices, optimizing crop yields, and mitigating environmental degradation.
Historical Development of Ecology and Edaphology
Ecology emerged as a scientific discipline in the late 19th century through the work of pioneers like Ernst Haeckel, who coined the term to describe the study of organisms and their interactions with the environment. Edaphology developed in parallel, focusing on soil formation, classification, and influence on plant growth, with key contributions from Vasily Dokuchaev in the late 1800s, who established soil science as a distinct field. Both disciplines expanded through the 20th century by integrating biological, chemical, and physical principles to better understand ecosystems and soil-plant relationships.
Key Differences Between Ecology and Edaphology
Ecology studies the interactions between organisms and their environments, focusing on ecosystems, biodiversity, and ecological processes. Edaphology specifically examines soil properties, including soil formation, classification, and influence on plant growth. The key difference lies in ecology's broad environmental scope versus edaphology's specialized focus on soil as a critical factor in terrestrial ecosystems.
Interconnections: How Ecology and Edaphology Overlap
Ecology and edaphology intersect through their mutual focus on soil as a critical component influencing ecosystem dynamics and plant health. Edaphology studies soil properties, composition, and processes, directly affecting ecological factors such as nutrient cycling, habitat quality, and biodiversity. Understanding soil-plant interactions bridges both fields, highlighting their interconnected roles in sustaining environmental balance and ecosystem productivity.
Methods and Approaches in Ecology vs Edaphology
Ecology employs field surveys, remote sensing, and experimental manipulations to study organism interactions within ecosystems, emphasizing population dynamics and energy flow. Edaphology focuses on soil analysis techniques such as soil sampling, laboratory testing for nutrient content, texture, and microbial activity to understand soil properties influencing plant growth. Both fields utilize GIS tools but apply them differently, with ecology mapping habitats and species distributions, while edaphology maps soil types and fertility patterns.
Applications in Environmental Science
Ecology studies interactions between organisms and their environment to inform biodiversity conservation and ecosystem management, while edaphology focuses on soil properties and processes influencing plant growth and soil health. Environmental science applies ecological principles to assess habitat restoration, pollution impacts, and climate change effects, whereas edaphological data guide soil remediation, agriculture sustainability, and land use planning. Integrating ecology and edaphology enhances ecosystem resilience through informed environmental monitoring and resource management strategies.
Current Research Trends in Ecology and Edaphology
Current research trends in ecology emphasize the impact of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystem services, integrating remote sensing and molecular tools for monitoring species interactions and habitat dynamics. In edaphology, investigations focus on soil health assessments, carbon sequestration potential, and the role of microbial communities in nutrient cycling, employing advanced metagenomic and spectroscopic techniques. Both fields increasingly intersect in studies examining soil-plant-atmosphere feedbacks to improve sustainable land management and ecosystem resilience under anthropogenic pressures.
Future Perspectives and Challenges
Future perspectives in ecology emphasize integrating advanced remote sensing and big data analytics to monitor biodiversity and ecosystem dynamics under climate change scenarios. Edaphology faces challenges in developing sustainable soil management practices that enhance soil health and carbon sequestration to mitigate global warming. Both fields increasingly prioritize interdisciplinary approaches to address environmental degradation and promote resilient ecosystems amid rapid anthropogenic pressures.
Ecology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com