Littoral zones are coastal areas where land meets the sea, featuring dynamic ecosystems rich in biodiversity. These regions play a crucial role in protecting shorelines from erosion, supporting marine habitats, and providing resources for fisheries and tourism. Explore the rest of the article to understand how littoral zones impact your environment and community.
Table of Comparison
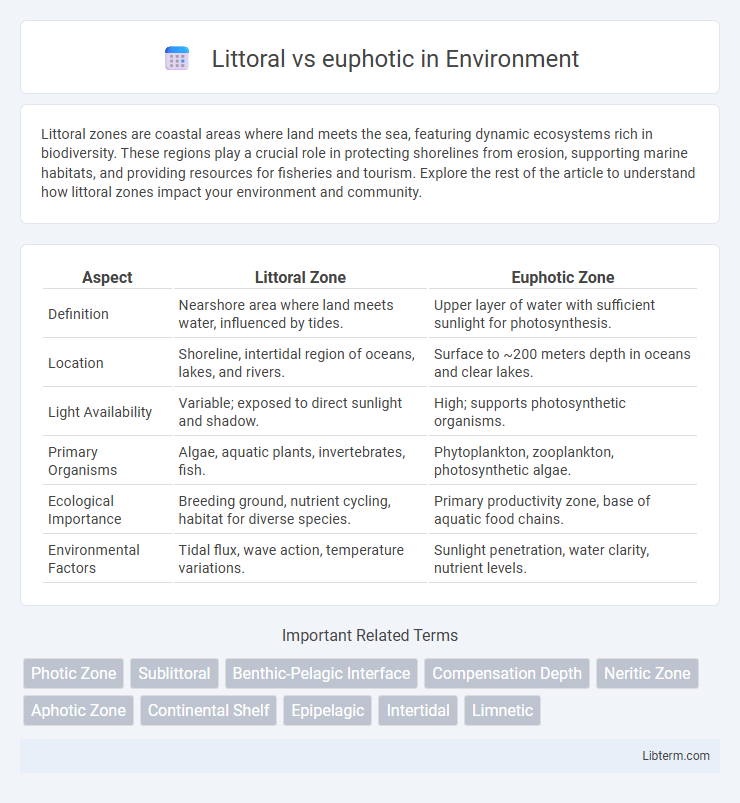
| Aspect | Littoral Zone | Euphotic Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Nearshore area where land meets water, influenced by tides. | Upper layer of water with sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis. |
| Location | Shoreline, intertidal region of oceans, lakes, and rivers. | Surface to ~200 meters depth in oceans and clear lakes. |
| Light Availability | Variable; exposed to direct sunlight and shadow. | High; supports photosynthetic organisms. |
| Primary Organisms | Algae, aquatic plants, invertebrates, fish. | Phytoplankton, zooplankton, photosynthetic algae. |
| Ecological Importance | Breeding ground, nutrient cycling, habitat for diverse species. | Primary productivity zone, base of aquatic food chains. |
| Environmental Factors | Tidal flux, wave action, temperature variations. | Sunlight penetration, water clarity, nutrient levels. |
Introduction to Littoral and Euphotic Zones
The littoral zone refers to the nearshore area of a body of water where sunlight penetrates to the bottom, supporting diverse aquatic plants and animal life. The euphotic zone, extending from the water surface to the depth where light intensity decreases to 1%, is the primary region for photosynthesis and productivity in aquatic ecosystems. Both zones are critical for sustaining marine and freshwater biodiversity through their role in energy capture and habitat provision.
Defining the Littoral Zone
The littoral zone defines the shallow part of a freshwater or marine environment where sunlight reaches the sediment, supporting abundant plant and animal life. This zone extends from the shore to the depth where light penetration diminishes, differentiating it from the euphotic zone, which represents the upper layer of water with sufficient light for photosynthesis. Characterized by rooted vegetation and high biodiversity, the littoral zone is critical for ecosystem productivity and serves as a habitat for numerous aquatic species.
Understanding the Euphotic Zone
The euphotic zone, also known as the sunlight zone, extends from the water surface down to approximately 200 meters where sufficient sunlight penetrates to facilitate photosynthesis, supporting primary producers like phytoplankton. In contrast, the littoral zone refers to the nearshore area where sunlight reaches the bottom, allowing for the growth of aquatic plants and benthic organisms, but it is much shallower compared to the euphotic zone. Understanding the euphotic zone is crucial for studying marine ecosystems, as it represents the main region of energy production and biological activity in open water environments.
Key Differences Between Littoral and Euphotic Zones
The littoral zone is the shallow water area near the shore where sunlight penetrates to the bottom, supporting abundant plant and animal life, while the euphotic zone extends deeper and encompasses the upper layer of ocean water with sufficient light for photosynthesis but lacks a solid substrate. The key difference lies in their depth and substrate presence: the littoral zone is a nearshore, benthic environment with sunlight reaching the seabed, whereas the euphotic zone is an open-water column zone defined by light availability for phytoplankton growth. Biodiversity in the littoral zone is often higher due to the interaction of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, contrasting with the euphotic zone's emphasis on planktonic organisms and free-floating life forms.
Ecological Importance of the Littoral Zone
The littoral zone, located along the shoreline where sunlight penetrates to the sediment, supports diverse aquatic plants and animals, fostering high biodiversity crucial for ecosystem stability. This zone serves as a primary habitat for fish spawning, invertebrates, and algae, facilitating nutrient cycling and energy flow. Compared to the deeper euphotic zone, the littoral zone's access to sunlight and substrate complexity enhances its role as a critical nursery and feeding ground in freshwater and marine ecosystems.
Ecological Significance of the Euphotic Zone
The euphotic zone, characterized by sufficient sunlight penetration, supports photosynthesis, fueling primary production and sustaining diverse aquatic food webs. Unlike the littoral zone, which is limited to nearshore areas, the euphotic zone extends vertically to depths of up to 200 meters in clear waters, critically influencing oxygen generation and carbon cycling. This zone's ecological significance is paramount in regulating aquatic ecosystems' productivity and global biogeochemical processes.
Light Penetration: Littoral vs Euphotic Zone
Light penetration in the littoral zone varies significantly due to its proximity to shore and often shallower depths, allowing sunlight to reach the seabed and support benthic plant life. In contrast, the euphotic zone extends deeper into open water, with sufficient light penetration primarily for photosynthesis but typically without full illumination of the ocean floor. Understanding differences in light availability between these zones is crucial for assessing aquatic ecosystems' productivity and biodiversity.
Biological Diversity in Littoral vs Euphotic Zones
The littoral zone, characterized by shallow waters and abundant sunlight, supports higher biological diversity due to the presence of diverse substrates, aquatic plants, and ample nutrients fostering various invertebrates, fish, and algae. In contrast, the euphotic zone, extending deeper with enough light for photosynthesis, hosts planktonic communities, phytoplankton, and nekton, but generally exhibits less habitat complexity and species variety compared to the structurally rich littoral zone. This spatial variation in light penetration, substrate type, and nutrient availability fundamentally influences the composition and abundance of organisms in each zone.
Human Impact on Littoral and Euphotic Zones
Human activities significantly impact the littoral zone through coastal development, pollution runoff, and habitat destruction, which disturb biodiversity and disrupt ecological balance. In the euphotic zone, pollutants like oil spills and nutrient loading cause algal blooms and oxygen depletion, threatening marine life dependent on sunlight for photosynthesis. Overfishing and climate change further exacerbate stress on both zones, reducing resilience and altering ecosystem dynamics.
Summary: Littoral vs Euphotic Zone Comparison
The littoral zone refers to the nearshore area where sunlight penetrates to the bottom, supporting diverse aquatic plants and animals, whereas the euphotic zone denotes the upper layer of a water body with sufficient light for photosynthesis, extending deeper than the littoral zone but without contact to the substrate. Both zones are critical for aquatic ecosystems, with the littoral zone emphasizing benthic interactions and the euphotic zone focusing on primary productivity. Understanding their differences aids in ecological studies, fisheries management, and conservation of aquatic habitats.
Littoral Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com