Local species play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by supporting biodiversity and ensuring natural processes continue smoothly. Protecting these species helps preserve genetic diversity and enhances resilience against environmental changes. Discover how understanding local species can benefit your environment and why it matters in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
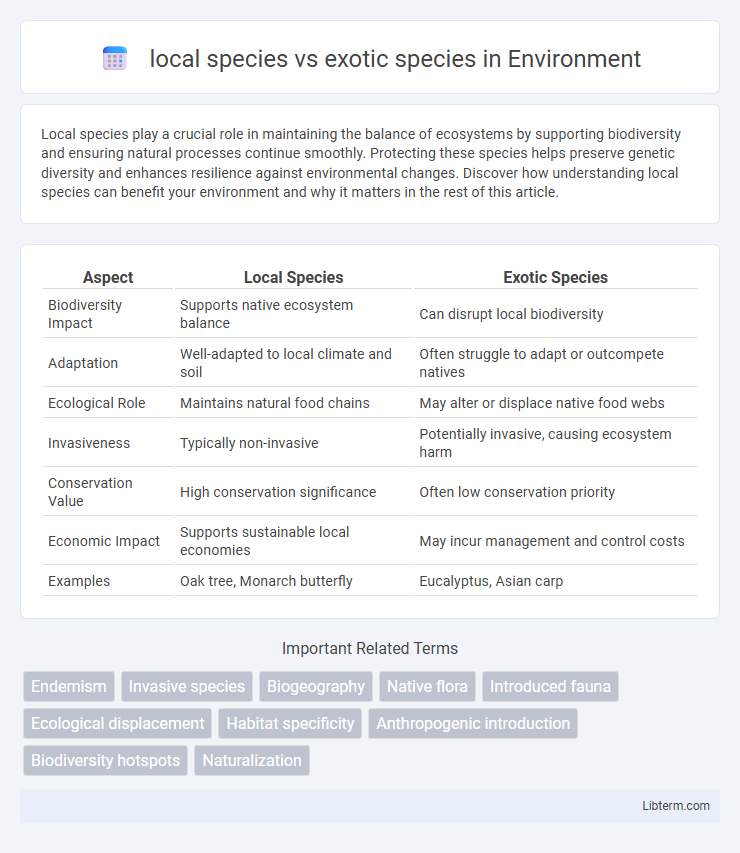
| Aspect | Local Species | Exotic Species |
|---|---|---|
| Biodiversity Impact | Supports native ecosystem balance | Can disrupt local biodiversity |
| Adaptation | Well-adapted to local climate and soil | Often struggle to adapt or outcompete natives |
| Ecological Role | Maintains natural food chains | May alter or displace native food webs |
| Invasiveness | Typically non-invasive | Potentially invasive, causing ecosystem harm |
| Conservation Value | High conservation significance | Often low conservation priority |
| Economic Impact | Supports sustainable local economies | May incur management and control costs |
| Examples | Oak tree, Monarch butterfly | Eucalyptus, Asian carp |
Introduction to Local and Exotic Species
Local species, also known as native species, naturally occur and have evolved within a specific region or ecosystem, playing crucial roles in maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance. Exotic species, introduced intentionally or accidentally from other regions, can disrupt native habitats by competing for resources, altering food chains, and sometimes becoming invasive. Understanding the differences between local and exotic species is essential for effective conservation strategies and ecosystem management.
Defining Local Species
Local species, also known as native species, are organisms that have naturally evolved and adapted to a specific geographic area over thousands of years. These species play integral roles in maintaining ecosystem balance by supporting food webs, nutrient cycles, and habitat stability. Understanding the genetic diversity and ecological functions of local species is essential for conservation efforts and sustainable land management.
What Are Exotic Species?
Exotic species, also known as non-native or invasive species, are plants, animals, or microorganisms introduced intentionally or accidentally into regions outside their natural geographic range. These species can disrupt local ecosystems by outcompeting native species for resources, altering habitat structures, and spreading diseases. Managing exotic species is critical in preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance in affected environments.
Differences Between Local and Exotic Species
Local species, also known as native species, have evolved and adapted to specific ecosystems over long periods, contributing to regional biodiversity and ecological balance. Exotic species are introduced from foreign regions, often lacking natural predators, which can lead to invasive behavior and disrupt native habitats. Differences include their roles in ecosystem stability, reproductive strategies, and impacts on food chains, with local species promoting sustainability and exotic species frequently posing environmental risks.
Ecological Impact of Exotic Species
Exotic species often disrupt local ecosystems by competing with native species for resources, leading to reduced biodiversity and altered habitat structures. Their introduction can result in the decline or extinction of indigenous species through predation, disease transmission, and habitat modification. The ecological imbalance caused by invasive exotic species poses significant challenges for conservation efforts and ecosystem stability.
Benefits of Preserving Local Species
Preserving local species maintains biodiversity, which supports ecosystem stability and resilience against environmental changes. Native species play crucial roles in nutrient cycling, pollination, and habitat formation, ensuring the survival of other organisms dependent on them. Conserving indigenous flora and fauna also supports cultural heritage and promotes sustainable agriculture benefiting local economies.
Challenges Posed by Exotic Species
Exotic species often disrupt local ecosystems by outcompeting native species for resources, leading to biodiversity loss and habitat degradation. Invasive species such as the Burmese python in Florida cause significant ecological imbalances by preying on or displacing indigenous wildlife. Managing these challenges requires robust biosecurity measures and targeted restoration efforts to protect native biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Case Studies: Local vs Exotic Species
Case studies reveal that local species such as the European honeybee (Apis mellifera) maintain balanced ecosystems by supporting native flora and fauna, whereas exotic species like the Argentine ant (Linepithema humile) often disrupt these systems through aggressive competition and habitat alteration. In New Zealand, the introduction of exotic stoats (Mustela erminea) has led to severe declines in native bird populations, highlighting the ecological risks posed by invasive species. Conversely, restoration projects employing native species, such as the reintroduction of the California condor (Gymnogyps californianus), demonstrate significant success in ecosystem recovery and biodiversity enhancement.
Strategies for Managing Exotic Species
Effective strategies for managing exotic species include early detection through regular monitoring and rapid response to prevent their establishment and spread. Biological control methods, such as introducing natural predators or pathogens specific to the invasive species, help reduce their population without harming local ecosystems. Habitat restoration and promoting native species resilience also play crucial roles in mitigating the impact of exotic species.
Promoting Biodiversity Through Native Species
Native species play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem stability by supporting local food webs and enhancing soil health. Promoting biodiversity through native species helps preserve genetic diversity and ensures resilience against environmental changes. Conservation efforts focusing on native flora and fauna foster sustainable habitats that benefit both wildlife and human communities.
local species Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com