Rotary drilling sampling is a crucial technique used to extract continuous core samples from underground formations, providing accurate data on rock properties and mineral content. This method enhances the precision of geological analysis and supports informed decision-making in exploration and drilling projects. Discover how rotary drilling sampling can improve your project's efficiency and reliability in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
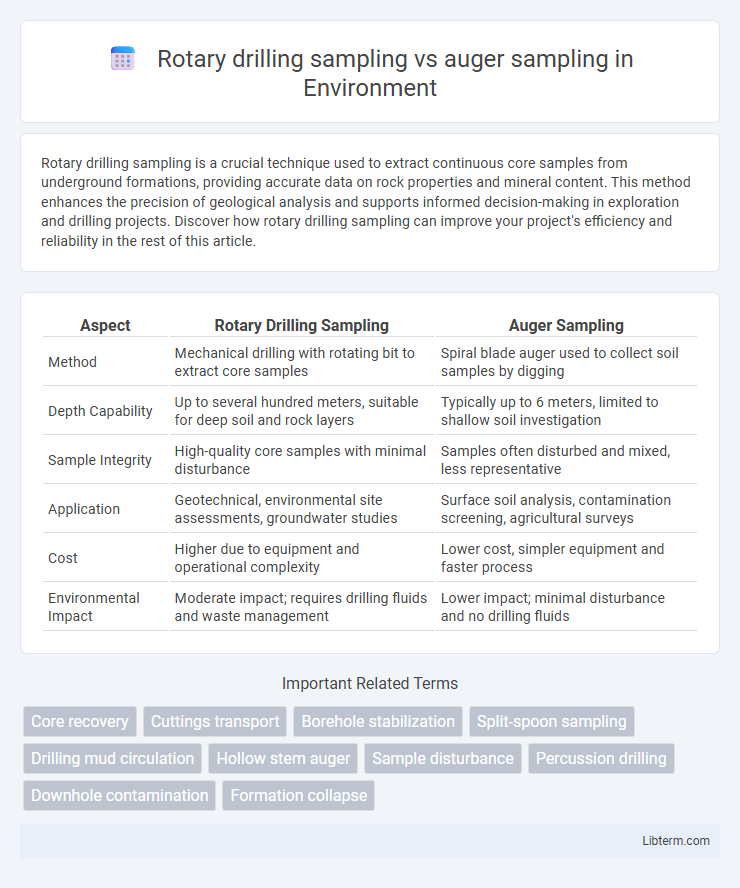
| Aspect | Rotary Drilling Sampling | Auger Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Mechanical drilling with rotating bit to extract core samples | Spiral blade auger used to collect soil samples by digging |
| Depth Capability | Up to several hundred meters, suitable for deep soil and rock layers | Typically up to 6 meters, limited to shallow soil investigation |
| Sample Integrity | High-quality core samples with minimal disturbance | Samples often disturbed and mixed, less representative |
| Application | Geotechnical, environmental site assessments, groundwater studies | Surface soil analysis, contamination screening, agricultural surveys |
| Cost | Higher due to equipment and operational complexity | Lower cost, simpler equipment and faster process |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate impact; requires drilling fluids and waste management | Lower impact; minimal disturbance and no drilling fluids |
Introduction to Rotary Drilling and Auger Sampling
Rotary drilling involves using a rotating drill bit to penetrate rock and soil, allowing retrieval of continuous core samples essential for detailed geological analysis and resource evaluation. Auger sampling employs a helical screw to extract soil or unconsolidated material from near surface layers, offering rapid, cost-effective sampling primarily for environmental and geotechnical investigations. Rotary drilling provides deeper, more precise subsurface data, while auger sampling is favored for shallow, less dense materials due to its operational simplicity and speed.
Overview of Rotary Drilling Sampling
Rotary drilling sampling involves using a rotating drill bit to penetrate deep into the earth, extracting continuous core or cuttings for geological analysis. This method provides detailed, high-quality samples suitable for mineral exploration and geotechnical investigations, often reaching depths unattainable by simpler techniques. Rotary drilling is preferred for its ability to obtain representative subsurface data in complex or hard rock formations.
Overview of Auger Sampling Techniques
Auger sampling techniques involve using a helical screw blade to extract soil or sediment samples, ideal for shallow subsurface investigations up to 10 meters deep. Compared to rotary drilling, auger sampling is more cost-effective and faster for unconsolidated materials, providing continuous and relatively uncontaminated samples. This method is widely used in environmental assessments, geotechnical studies, and mineral exploration for preliminary site evaluation.
Key Differences Between Rotary Drilling and Auger Sampling
Rotary drilling sampling employs a rotating drill bit to penetrate hard rock formations, producing continuous core samples ideal for detailed geological analysis. Auger sampling, conversely, uses a helical screw to extract soil and unconsolidated materials, providing less precise but faster and cost-effective samples for shallow investigations. The key differences lie in drilling depth capabilities, sample quality, and suitability for varying ground conditions, with rotary drilling suited for deep, solid strata and auger sampling optimized for softer, near-surface sediment layers.
Applications and Suitability of Rotary Drilling
Rotary drilling sampling is ideal for extracting continuous core samples from hard rock formations, making it suitable for mineral exploration, oil and gas drilling, and geological investigations where precise stratigraphic information is essential. It provides high-quality, undisturbed samples critical for detailed petrological and geotechnical analysis, outperforming auger sampling in depth capability and sample integrity. Rotary drilling is preferred in complex subsurface conditions requiring accurate, representative samples for resource evaluation and engineering assessment.
Applications and Suitability of Auger Sampling
Auger sampling is primarily suitable for shallow, unconsolidated soils and deposits, making it ideal for environmental investigations, groundwater monitoring, and preliminary site assessments where soil structure remains largely undisturbed. Unlike rotary drilling, which can penetrate deeper and harder formations for mineral exploration and geotechnical studies, auger sampling offers faster, cost-effective recovery of relatively undisturbed samples in soft materials. Its applications include soil contamination analysis, agricultural soil profiling, and sediment sampling in environmental and construction projects.
Sampling Depth and Recovery Efficiency Comparison
Rotary drilling sampling typically achieves greater sampling depths, often exceeding 500 meters, while auger sampling is limited to shallower depths, generally up to 30 meters. Rotary drilling provides higher recovery efficiency, especially in hard or consolidated formations, with core recovery rates often surpassing 90%, whereas auger sampling recovery efficiency decreases significantly with depth and soil hardness. The choice between rotary drilling and auger sampling hinges on the required sampling depth and the geological conditions impacting the recovery quality.
Sample Quality and Contamination Risks
Rotary drilling sampling provides continuous core samples with better preservation of geological features, offering higher sample quality compared to auger sampling, which often yields disturbed samples due to soil displacement. Rotary drilling reduces contamination risks by minimizing exposure to surface materials and using sealed core barrels, whereas auger sampling is more prone to cross-contamination from soil mixing and surface debris. The superior integrity of rotary drilling samples makes it preferred for detailed mineralogical and geotechnical analysis.
Cost and Time Considerations
Rotary drilling sampling typically incurs higher costs due to the need for specialized drilling rigs and skilled operators, but it provides faster sample retrieval and deeper penetration in varied soil conditions. Auger sampling is more cost-effective and requires less time for shallow, unconsolidated soils, making it ideal for preliminary site investigations. Choosing between the two methods depends on budget constraints, project timeline, and the depth and type of subsurface materials to be analyzed.
Choosing the Right Sampling Method for Your Project
Rotary drilling sampling offers precise core extraction ideal for deep, detailed geological analysis, while auger sampling provides cost-effective, shallow subsurface data suitable for preliminary site assessments. Selecting the right sampling method depends on project depth, budget constraints, and the required resolution of geological information. Understanding the project's technical needs and environmental conditions ensures optimal data quality and operational efficiency.
Rotary drilling sampling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com