Exploring alternative options can unlock new opportunities and enhance your decision-making process. Choosing the right alternative tailored to your needs often leads to better outcomes and increased satisfaction. Discover more insights on how to evaluate and select the best alternatives in the full article.
Table of Comparison
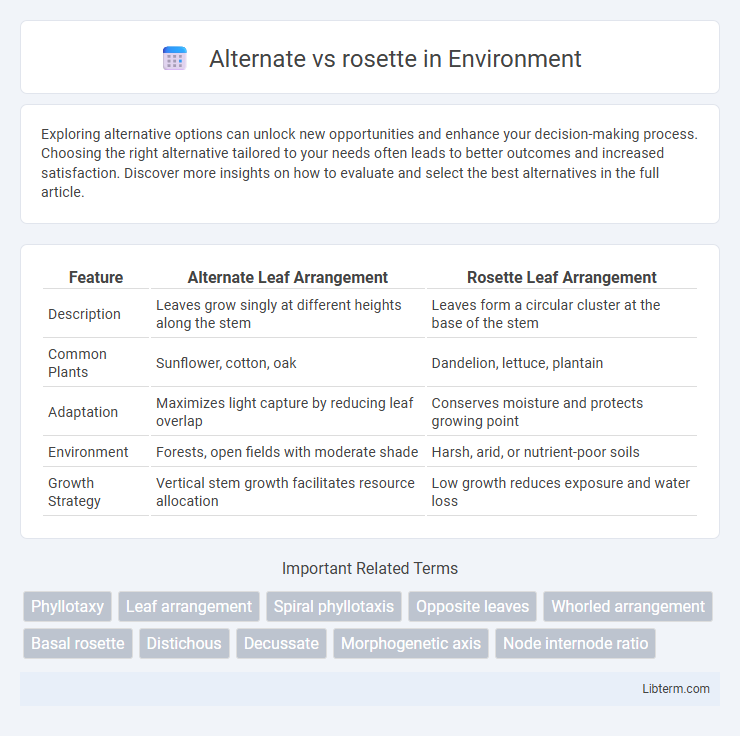
| Feature | Alternate Leaf Arrangement | Rosette Leaf Arrangement |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Leaves grow singly at different heights along the stem | Leaves form a circular cluster at the base of the stem |
| Common Plants | Sunflower, cotton, oak | Dandelion, lettuce, plantain |
| Adaptation | Maximizes light capture by reducing leaf overlap | Conserves moisture and protects growing point |
| Environment | Forests, open fields with moderate shade | Harsh, arid, or nutrient-poor soils |
| Growth Strategy | Vertical stem growth facilitates resource allocation | Low growth reduces exposure and water loss |
Understanding Leaf Arrangements: Alternate vs Rosette
Alternate leaf arrangements feature single leaves spaced at intervals along the stem, optimizing light capture by minimizing overlap and shading. Rosette leaf arrangements consist of leaves clustered at the base of the plant, forming a circular pattern that conserves water and protects meristematic tissue. Understanding these distinct patterns helps in identifying plant species and their adaptive strategies in various environments.
Key Differences Between Alternate and Rosette Patterns
Alternate leaf arrangement features a single leaf per node alternating sides along the stem, optimizing light exposure and air circulation for each leaf. Rosette patterns consist of multiple leaves radiating from a single central point at the base, minimizing stem length and protecting the plant's growth center. Key differences include node spacing, with alternate leaves spaced sequentially, while rosette leaves cluster tightly, affecting overall plant morphology and adaptation strategies.
The Botany Behind Alternate Leaf Arrangement
Alternate leaf arrangement features a single leaf per node, spiraled or staggered along the stem, optimizing light capture and reducing shading compared to rosette patterns where leaves radiate in a circular cluster at the base. Alternate phyllotaxy enhances photosynthetic efficiency by maximizing exposure and airflow, common in species like sunflower and oak. This arrangement contrasts with rosette forms seen in plants like dandelion and lettuce, where leaf proximity limits vertical growth but protects the growing point.
Defining the Rosette Leaf Formation
Rosette leaf formation presents leaves arranged in a circular cluster at the base of the stem, optimizing light capture and minimizing water loss. In contrast, alternate leaf arrangement displays leaves staggered along the stem, enhancing air circulation and reducing shading. Rosette formations are common in plants like dandelions, while alternate leaves are typical in species such as sunflowers.
Evolutionary Advantages of Alternate Leaves
Alternate leaves, arranged singly along the stem, present evolutionary advantages such as improved light capture by minimizing self-shading, enhancing photosynthetic efficiency. This phyllotaxy allows for optimal spacing, promoting better air circulation and reducing fungal infection risk compared to rosette formations. The staggered arrangement in alternate leaves also supports flexible growth in diverse environments, contributing to plant adaptability and survival.
Adaptations Offered by Rosette Formations
Rosette formations in plants offer significant adaptations for survival by minimizing water loss and maximizing nutrient absorption in arid environments. These dense leaf arrangements create a microhabitat that reduces exposure to wind and sunlight, conserving moisture more effectively than alternate leaf patterns. Rosettes also facilitate efficient capture of dew and rainwater, supporting growth in nutrient-poor soils where alternate leaves may be less advantageous.
Examples of Plants with Alternate Leaves
Plants with alternate leaves display a single leaf per node arranged alternately along the stem, enhancing light capture and air flow. Examples include sunflower (Helianthus annuus), oak (Quercus spp.), and cotton (Gossypium spp.), where each leaf emerges at a distinct point on the stem. This contrasts with rosette leaf arrangements, where leaves radiate from a single point at the base, as seen in plants like dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) and lettuce (Lactuca sativa).
Examples of Plants with Rosette Leaves
Plants with rosette leaves include dandelions, African violets, and cabbage, which exhibit leaf arrangements radiating from a central point close to the ground. This leaf pattern enhances light capture efficiency and helps conserve water by reducing exposure. Rosette formations are common in species adapted to harsh environments or low light conditions, highlighting their ecological significance.
How to Identify Alternate and Rosette Structures
Identify alternate leaf arrangement by observing leaves emerging individually at different heights along the stem, typically in a staggered or spiral pattern. Rosette structure features leaves clustered tightly at the base or stem tip, forming a circular or layered arrangement with minimal spacing. Key identification hinges on leaf placement: alternate leaves are spaced out along the stem, while rosettes show leaves densely grouped, often near ground level.
Choosing Between Alternate and Rosette for Garden Design
Choosing between alternate and rosette leaf arrangements significantly impacts garden design by influencing plant spacing and visual texture. Alternate leaf patterns create a balanced, airy appearance, ideal for vertical growth and allowing light penetration, while rosette arrangements form dense, ground-hugging clusters that add lushness and fill lower garden layers. Selecting the appropriate arrangement depends on desired garden aesthetics, plant species compatibility, and maintenance preferences for optimal landscape harmony.
Alternate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com