Fair Trade Certified products ensure that farmers and workers receive fair wages and work in safe conditions, promoting sustainable farming practices. By choosing these products, you support ethical supply chains that empower communities and protect the environment. Discover more about the impact of Fair Trade Certification and how your choices make a difference in the following article.
Table of Comparison
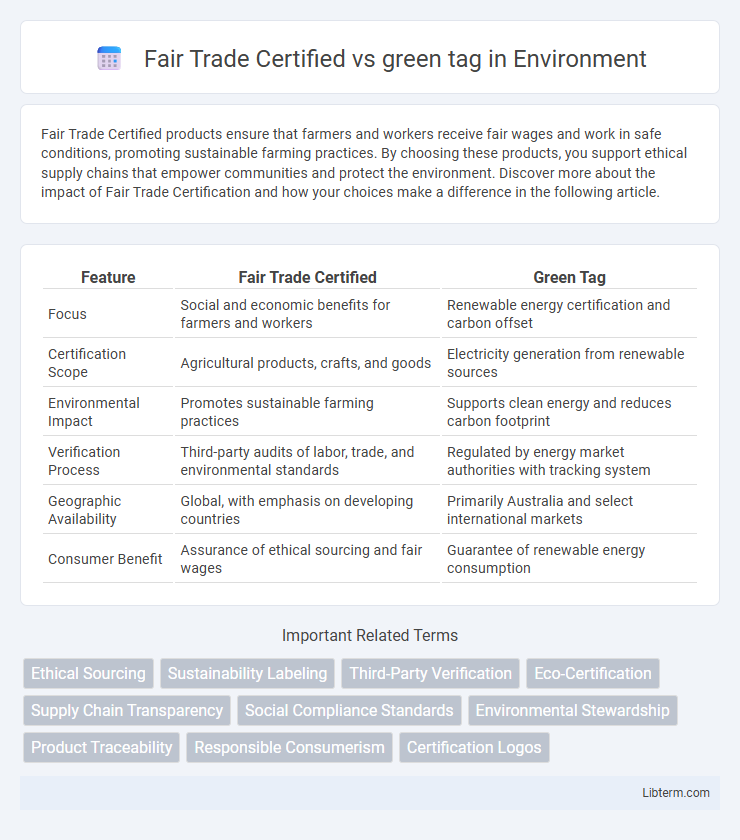
| Feature | Fair Trade Certified | Green Tag |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Social and economic benefits for farmers and workers | Renewable energy certification and carbon offset |
| Certification Scope | Agricultural products, crafts, and goods | Electricity generation from renewable sources |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainable farming practices | Supports clean energy and reduces carbon footprint |
| Verification Process | Third-party audits of labor, trade, and environmental standards | Regulated by energy market authorities with tracking system |
| Geographic Availability | Global, with emphasis on developing countries | Primarily Australia and select international markets |
| Consumer Benefit | Assurance of ethical sourcing and fair wages | Guarantee of renewable energy consumption |
Introduction to Fair Trade Certified and Green Tag
Fair Trade Certified ensures products meet rigorous social, economic, and environmental standards supporting fair wages and sustainable farming practices, primarily benefiting marginalized producers in developing countries. Green Tag focuses on environmental impact by certifying projects and products that contribute to biodiversity conservation and carbon offsetting, emphasizing eco-friendly and sustainable land management. Both certifications promote sustainability but address different priorities: Fair Trade centers on ethical sourcing and community welfare, while Green Tag prioritizes ecological preservation and climate action.
Defining Fair Trade Certification
Fair Trade Certification ensures products meet rigorous social, economic, and environmental standards, promoting equitable trade practices and supporting marginalized producers. The certification verifies compliance with criteria such as fair wages, safe working conditions, and sustainable farming methods. Unlike generic green tags that primarily highlight environmental benefits, Fair Trade Certification emphasizes both human rights and ecological responsibility.
What is a Green Tag?
A Green Tag represents a certification or label indicating a product's compliance with environmentally sustainable practices, emphasizing reduced carbon footprints, renewable energy usage, and eco-friendly materials. Fair Trade Certified focuses primarily on social and economic benefits for workers and producers in developing countries, ensuring fair wages and ethical labor conditions. While Fair Trade Certification targets social justice, Green Tags highlight environmental responsibility and sustainability standards.
Key Principles of Fair Trade Certification
Fair Trade Certification centers on principles such as fair wages, safe working conditions, and environmental sustainability, ensuring producers receive equitable compensation and support for community development. In contrast, Green Tag focuses predominantly on renewable energy verification and carbon offsetting without emphasizing social equity aspects. Fair Trade's holistic approach integrates economic, social, and environmental standards to promote ethical production and long-term development for marginalized farmers and workers.
Core Values Behind Green Tag Programs
Green Tag programs prioritize environmental sustainability, transparency, and community empowerment by certifying products that meet rigorous ecological and social standards. Unlike Fair Trade Certified, which predominantly focuses on fair wages and labor rights for producers, Green Tag certifications emphasize reducing carbon footprints, promoting renewable resources, and protecting biodiversity. Core values behind Green Tag programs include fostering sustainable consumption, incentivizing eco-friendly practices, and supporting climate action initiatives globally.
Certification Processes: Fair Trade vs Green Tag
Fair Trade Certified certification requires rigorous auditing of social, economic, and environmental standards, ensuring ethical sourcing, fair wages, and sustainable farming practices. Green Tag certification primarily focuses on environmental impact, verifying renewable energy usage and carbon offset projects through third-party validation. Both processes involve independent assessments, but Fair Trade emphasizes social equity while Green Tag centers on sustainability metrics and carbon neutrality.
Environmental Impact: Fair Trade Certified vs Green Tag
Fair Trade Certified products prioritize sustainable farming practices, reducing chemical use and promoting biodiversity, which significantly lowers environmental footprints. Green Tag certification emphasizes renewable energy projects and resource efficiency, directly targeting carbon emission reductions and promoting environmental sustainability. Both certifications contribute to eco-friendly goals, but Fair Trade focuses more on agricultural impact while Green Tag centers on energy and carbon management.
Social Benefits Comparison
Fair Trade Certified products ensure fair wages, safe working conditions, and community development projects, directly benefiting marginalized farmers and workers by promoting social equity and economic stability. Green Tag certification primarily emphasizes environmental sustainability, with less focus on social impact metrics or labor rights standards. Consequently, Fair Trade Certified labels provide stronger guarantees for social benefits such as improved healthcare, education access, and empowerment of vulnerable communities compared to Green Tag certifications.
Market Recognition and Consumer Trust
Fair Trade Certified products benefit from widespread market recognition due to rigorous third-party verification, enhancing consumer trust in ethical sourcing and fair labor practices. The Green Tag system, while promoting environmental sustainability, often lacks the same level of consumer awareness and established credibility, limiting its impact on purchasing decisions. Companies leveraging Fair Trade Certification typically experience stronger brand loyalty and positive consumer perceptions compared to those relying solely on Green Tag labels.
Choosing Between Fair Trade Certified and Green Tag
Choosing between Fair Trade Certified and Green Tag depends on your priority for ethical sourcing versus environmental impact. Fair Trade Certified emphasizes social and economic benefits for producers, ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions. Green Tag focuses primarily on environmental sustainability by verifying eco-friendly practices and reduced carbon footprints in products.
Fair Trade Certified Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com