Green manure improves soil fertility by adding organic matter and nutrients through the cultivation of cover crops like clover or legumes. It enhances soil structure, reduces erosion, and supports beneficial microbial activity essential for healthy plant growth. Discover how incorporating green manure into your farming practices can boost productivity and sustainability in the full article.
Table of Comparison
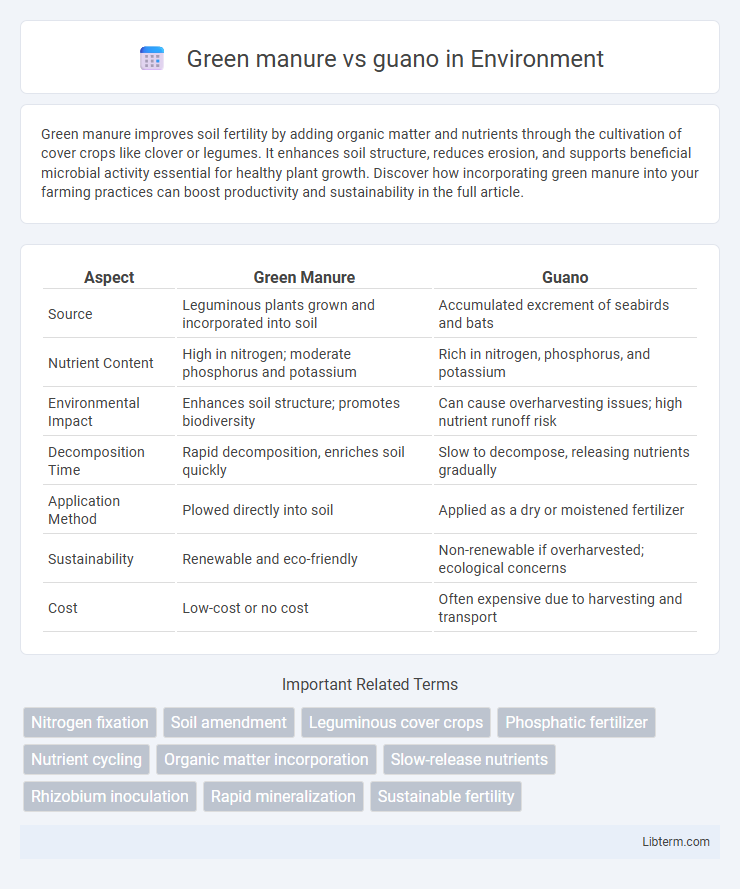
| Aspect | Green Manure | Guano |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Leguminous plants grown and incorporated into soil | Accumulated excrement of seabirds and bats |
| Nutrient Content | High in nitrogen; moderate phosphorus and potassium | Rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances soil structure; promotes biodiversity | Can cause overharvesting issues; high nutrient runoff risk |
| Decomposition Time | Rapid decomposition, enriches soil quickly | Slow to decompose, releasing nutrients gradually |
| Application Method | Plowed directly into soil | Applied as a dry or moistened fertilizer |
| Sustainability | Renewable and eco-friendly | Non-renewable if overharvested; ecological concerns |
| Cost | Low-cost or no cost | Often expensive due to harvesting and transport |
Introduction to Green Manure and Guano
Green manure consists of specific cover crops like legumes and grasses grown to be plowed back into the soil, enhancing organic matter and nitrogen content naturally. Guano is a nutrient-rich fertilizer derived from the accumulated excrement of seabirds and bats, prized for its high concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Both green manure and guano serve critical roles in sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility and promoting plant growth.
What is Green Manure?
Green manure refers to specific plants grown primarily to improve soil health by being plowed back into the soil, enhancing organic matter, nitrogen levels, and microbial activity. Common green manure crops include legumes like clover and vetch, which fix atmospheric nitrogen, boosting soil fertility naturally. Unlike guano, which is animal-derived fertilizer rich in nitrogen and phosphorus from seabird or bat droppings, green manure offers a sustainable, renewable approach to soil nutrient management.
What is Guano?
Guano is a highly effective organic fertilizer composed primarily of the accumulated excrement of seabirds, bats, and seals, rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium essential for plant growth. This natural resource has been used for centuries to enhance soil fertility and boost crop yields due to its concentrated nutrient content. Unlike green manure, which involves growing specific plants to enrich soil, guano provides a ready-to-use, nutrient-dense amendment that decomposes quickly and improves soil microbial activity.
Key Differences Between Green Manure and Guano
Green manure consists of nitrogen-fixing plants grown specifically to improve soil fertility by being plowed back into the ground, promoting organic matter and microbial activity, while guano is a nutrient-rich fertilizer derived from the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats, primarily high in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Green manure provides gradual nutrient release and enhances soil structure and moisture retention, whereas guano offers immediate, concentrated nutrient availability for rapid plant growth. The environmental impact differs as green manure supports sustainable agriculture through soil regeneration, while guano harvesting can threaten wildlife habitats if not managed responsibly.
Nutrient Profiles: Green Manure vs Guano
Green manure enriches soil primarily with nitrogen, organic matter, and improves soil structure through the decomposition of leguminous plants. Guano offers a concentrated source of essential nutrients, including high levels of phosphorus, nitrogen, and potassium, making it a potent natural fertilizer. While green manure enhances long-term soil fertility, guano provides immediate nutrient availability for rapid plant growth.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green manure enhances soil fertility and moisture retention by decomposing organic matter directly into the ground, promoting sustainable agriculture with minimal environmental harm. Guano, rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, provides a potent natural fertilizer but its extraction can disrupt marine and cave ecosystems, leading to habitat degradation and biodiversity loss. While both improve soil quality, green manure has a lower ecological footprint, supporting long-term soil health and reducing pollution risks associated with nutrient runoff.
Application Methods for Green Manure and Guano
Green manure is applied by growing specific cover crops such as legumes or grasses directly in the soil and then plowing them under before planting the main crop, enriching soil organic matter and nitrogen content. Guano, a natural fertilizer derived from accumulated seabird or bat excrement, is typically applied by spreading it evenly on soil surfaces or mixing it into the topsoil for rapid nutrient release, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen. Proper timing in application is crucial; green manure requires incorporation prior to planting, whereas guano can be used as a top dressing or soil amendment during crop growth stages.
Benefits of Using Green Manure
Green manure enhances soil fertility by adding organic matter and improving soil structure, which promotes better water retention and aeration for crops. It naturally fixes nitrogen through leguminous plants, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and supporting sustainable agriculture. Green manure also suppresses weeds, prevents soil erosion, and fosters beneficial microbial activity, boosting overall soil health and crop yield.
Advantages of Guano in Agriculture
Guano provides a rich source of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which significantly enhance soil fertility and crop yields. Its natural origin and high nutrient concentration enable faster nutrient uptake by plants compared to green manure. Guano also promotes beneficial microbial activity in the soil, improving overall soil health and plant growth.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right fertilizer between green manure and guano depends on soil health, nutrient needs, and environmental impact. Green manure, rich in organic matter, improves soil structure and nitrogen fixation, ideal for sustainable farming and long-term soil fertility. Guano, high in phosphorus and nitrogen, offers a potent nutrient boost but requires careful use to avoid soil imbalance and environmental harm.
Green manure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com