Same-species interactions play a crucial role in the survival and social structure of animals, influencing behaviors such as cooperation, competition, and communication. Understanding these interactions helps reveal patterns in mating, territoriality, and group dynamics that are essential for species conservation. Explore the rest of the article to learn how same-species relationships impact ecosystems and what it means for your appreciation of biodiversity.
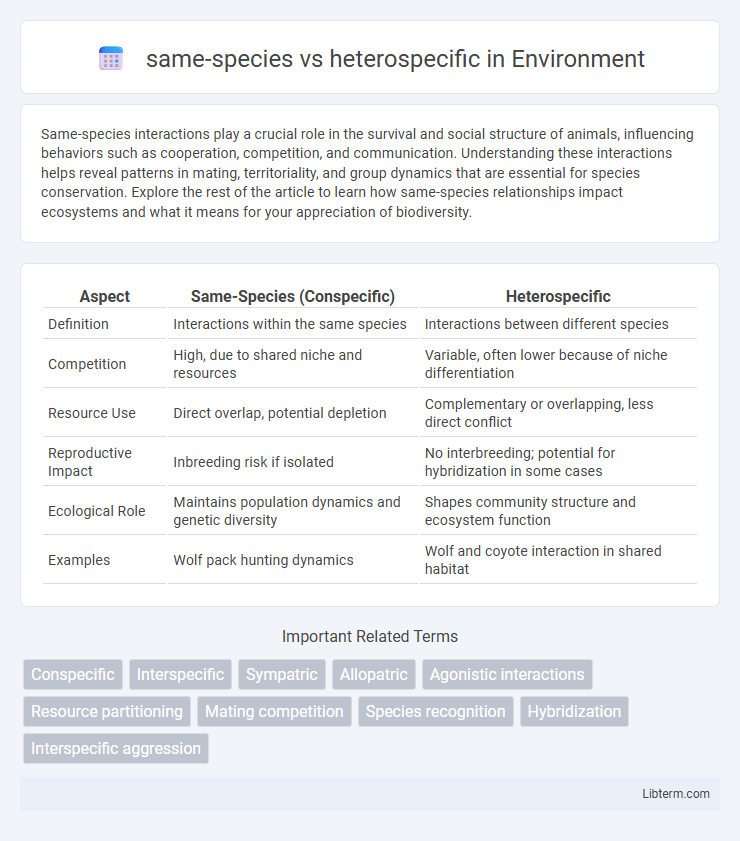
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Same-Species (Conspecific) | Heterospecific |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interactions within the same species | Interactions between different species |
| Competition | High, due to shared niche and resources | Variable, often lower because of niche differentiation |
| Resource Use | Direct overlap, potential depletion | Complementary or overlapping, less direct conflict |
| Reproductive Impact | Inbreeding risk if isolated | No interbreeding; potential for hybridization in some cases |
| Ecological Role | Maintains population dynamics and genetic diversity | Shapes community structure and ecosystem function |
| Examples | Wolf pack hunting dynamics | Wolf and coyote interaction in shared habitat |
Introduction to Same-Species and Heterospecific Interactions
Same-species interactions, also known as conspecific interactions, involve individuals of the same species engaging in behaviors such as cooperation, competition, mating, or communication that influence population dynamics and social structures. Heterospecific interactions occur between different species and include relationships like predation, mutualism, parasitism, and competition that shape ecological communities and biodiversity. Understanding these interactions provides insights into evolutionary strategies, resource allocation, and ecosystem stability.
Defining Same-Species (Conspecific) Relationships
Same-species or conspecific relationships refer to interactions between individuals belonging to the same biological species, characterized by shared genetic makeup and reproductive compatibility. These relationships play a crucial role in social cohesion, breeding, and resource sharing within populations. Understanding conspecific dynamics helps clarify patterns of cooperation, competition, and population structure in ecological and evolutionary studies.
Understanding Heterospecific Interactions
Heterospecific interactions occur between individuals of different species, influencing ecosystem dynamics through competition, predation, or mutualism. Understanding these interactions reveals how species coexist and adapt within shared habitats, shaping biodiversity and community structure. Studies on heterospecific behavior emphasize its role in resource partitioning and ecological balance.
Ecological Significance of Conspecific vs. Heterospecific Dynamics
Conspecific interactions, occurring between individuals of the same species, play a critical role in population regulation, resource competition, and mating systems, directly influencing species survival and reproductive success. Heterospecific dynamics, involving different species, drive community structure, biodiversity maintenance, and ecosystem function by promoting niche differentiation and facilitating mutualistic relationships. The balance between conspecific and heterospecific interactions shapes ecological outcomes such as species coexistence, competitive exclusion, and habitat complexity in diverse environments.
Examples of Same-Species Behavior in Nature
In nature, same-species behavior includes cooperative hunting observed in wolves, which enhances prey capture efficiency and group survival. Another example is the grooming practices among primates like chimpanzees, which strengthen social bonds and reduce stress within the group. Schooling in fish such as sardines exemplifies coordinated movement that improves protection from predators and optimizes foraging success.
Notable Heterospecific Associations in Ecosystems
Notable heterospecific associations in ecosystems, such as mutualistic relationships between cleaner fish and their client fish, enhance biodiversity and ecological stability by promoting species coexistence. In contrast to same-species interactions, heterospecific interactions often involve complementary resource use and reciprocal benefits, exemplified by mycorrhizal fungi partnering with plant roots to improve nutrient uptake. These interspecies connections play a critical role in ecosystem function by facilitating nutrient cycling, pollination, and predator-prey dynamics.
Evolutionary Implications of Species Interactions
Same-species interactions promote genetic cohesion and facilitate the spread of advantageous traits within populations, driving adaptive evolution. Heterospecific interactions, such as competition, predation, and symbiosis, exert selective pressures that shape species diversification and ecological niches. These interspecific dynamics influence coevolutionary pathways, enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem stability through reciprocal evolutionary changes.
Effects on Biodiversity and Community Structure
Interactions among same-species (conspecific) individuals often lead to intensified competition for resources, influencing population density and spatial distribution within ecosystems. In contrast, heterospecific interactions promote niche differentiation and resource partitioning, enhancing species coexistence and increasing overall biodiversity. These dynamics critically shape community structure by balancing competitive exclusion and facilitative relationships, thereby maintaining ecosystem resilience and stability.
Impacts on Resource Competition and Niche Partitioning
Same-species interactions intensify intraspecific competition as individuals vie for identical resources within a shared niche, often leading to resource depletion and population regulation. Heterospecific interactions drive interspecific competition, promoting niche partitioning through resource specialization and spatial or temporal segregation to minimize overlap. These dynamics critically influence community structure, biodiversity maintenance, and ecosystem function by balancing competition pressures and facilitating coexistence.
Future Research Directions in Species Interactions
Future research directions in species interactions emphasize investigating the mechanisms driving same-species (conspecific) and heterospecific interactions to understand their ecological and evolutionary consequences. Advanced genomic and behavioral analysis tools can uncover how intraspecific cooperation and interspecific competition shape community dynamics and biodiversity. Incorporating environmental changes and anthropogenic impacts will enhance predictive models of species coexistence and adaptive strategies.
same-species Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com