Marsh is a well-known global leader in insurance broking and risk management, providing tailored solutions to protect businesses and individuals from potential financial losses. Their expertise spans various industries, offering comprehensive services such as risk assessment, consultancy, and claims advocacy. Explore the rest of this article to understand how Marsh can safeguard your assets and optimize your risk strategy.
Table of Comparison
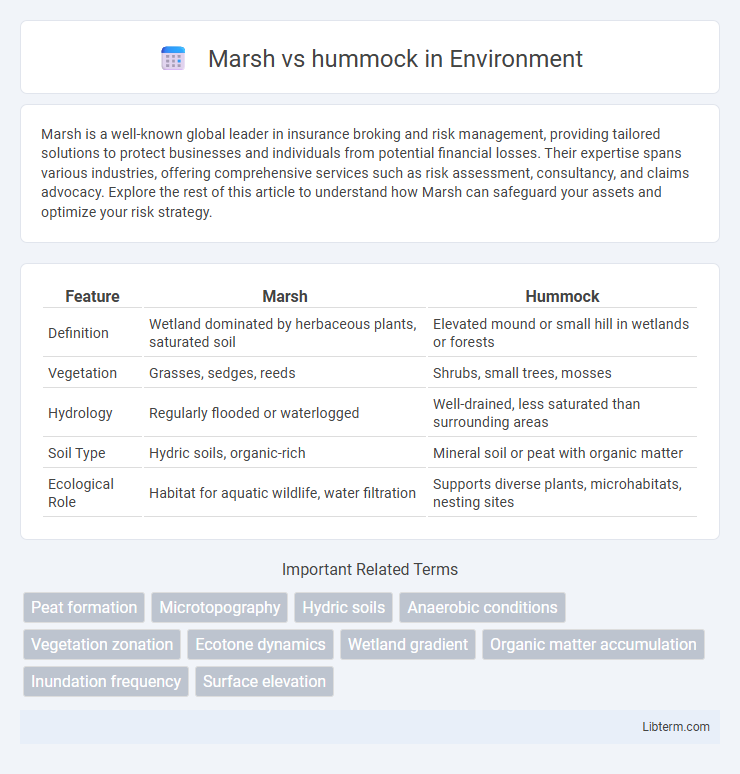
| Feature | Marsh | Hummock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wetland dominated by herbaceous plants, saturated soil | Elevated mound or small hill in wetlands or forests |
| Vegetation | Grasses, sedges, reeds | Shrubs, small trees, mosses |
| Hydrology | Regularly flooded or waterlogged | Well-drained, less saturated than surrounding areas |
| Soil Type | Hydric soils, organic-rich | Mineral soil or peat with organic matter |
| Ecological Role | Habitat for aquatic wildlife, water filtration | Supports diverse plants, microhabitats, nesting sites |
Introduction to Marshes and Hummocks
Marshes are wetland ecosystems characterized by herbaceous plants and saturated soils, typically found in low-lying areas with slow water flow. Hummocks are elevated mounds or ridges, often formed by vegetation or soil accumulation, providing drier microhabitats within marsh landscapes. The contrast between marshes and hummocks creates diverse ecological niches supporting varied plant and animal species.
Defining Marshes: Key Characteristics
Marshes are wetlands dominated by herbaceous plants such as grasses, sedges, and reeds, often found in low-lying areas subject to frequent or permanent flooding. They feature nutrient-rich, waterlogged soils and serve as critical habitats for diverse wildlife, including amphibians, birds, and aquatic invertebrates. Marsh ecosystems play essential roles in water filtration, flood control, and carbon sequestration, distinguishing them from hummocks, which are elevated, dry mounds often formed by vegetation in boggy or marshy environments.
Understanding Hummocks: Unique Features
Hummocks are small, elevated mounds of soil or vegetation that rise distinctly above the surrounding marsh landscape, often formed by peat accumulation or frost heaving. These unique features provide critical microhabitats, supporting diverse plant and animal species not typically found in flatter marsh areas. Their elevation influences water drainage and soil oxygen levels, making hummocks vital for ecological balance and habitat diversity within wetland ecosystems.
Ecological Differences: Marshes vs Hummocks
Marshes are wetland ecosystems characterized by water-saturated soils and dense herbaceous vegetation, providing critical habitats for various aquatic and bird species. Hummocks are elevated mounds often found within marshes or peatlands, created by vegetation growth or soil accumulation, supporting distinct plant communities adapted to drier conditions. These structural differences influence hydrology, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity patterns, resulting in unique ecological niches within the same wetland landscape.
Formation Processes: Marshes Compared to Hummocks
Marshes form primarily through the accumulation of sediments and organic matter in low-lying, water-saturated areas, creating nutrient-rich, waterlogged soils that support dense vegetation like grasses and reeds. Hummocks develop as raised mounds of soil or peat, often resulting from the freeze-thaw cycles in permafrost regions or from decomposed organic material accumulating in clumps, leading to elevated microtopography within wetlands. The key difference lies in marshes' horizontal, expansive sediment build-up versus hummocks' localized vertical elevation caused by soil or peat growth and environmental factors such as frost action.
Biodiversity and Habitat Value
Marshes are wetlands characterized by herbaceous plants that support high biodiversity, providing critical habitats for numerous bird, amphibian, and insect species. Hummocks, elevated mounds within wetlands or marshes, offer distinct microhabitats that increase spatial heterogeneity and species diversity by supporting different plant communities. The combination of marsh and hummock habitats enhances overall ecosystem complexity and resilience, benefiting wildlife diversity and ecological processes.
Hydrological Functions in Marshes and Hummocks
Marshes regulate water flow by absorbing excess rainfall and reducing flooding through their dense vegetation and soil composition, acting as natural sponges. Hummocks, elevated mounds within marsh landscapes, influence hydrological patterns by directing water runoff and creating microhabitats that enhance water retention and soil aeration. Together, marshes and hummocks maintain groundwater recharge, improve water quality, and support diverse aquatic ecosystems through their complementary hydrological functions.
Climate Adaptation and Carbon Sequestration
Marshes play a crucial role in climate adaptation by providing natural flood protection and enhancing resilience against sea-level rise, while hummocks, as elevated microhabitats within wetlands, support biodiversity and help maintain ecosystem stability under changing climatic conditions. Carbon sequestration rates are generally higher in marshes due to their extensive organic soil accumulation and plant biomass, effectively trapping carbon and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, hummocks contribute to carbon storage by supporting distinct vegetation communities that enhance soil carbon pools, although their overall sequestration capacity is typically lower than that of larger marsh areas.
Human Impact and Conservation Challenges
Marshes face significant human impact due to urban expansion, agriculture, and pollution, leading to habitat loss, altered hydrology, and decreased water quality. Hummocks, smaller elevated landforms within wetlands, are similarly threatened by land development and drainage practices that disrupt their natural role in water retention and biodiversity. Conservation challenges for both include balancing human land use with ecosystem preservation, mitigating pollution, and restoring hydrological regimes to support native flora and fauna.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Marshes and Hummocks
Marshes offer rich biodiversity and natural water filtration, making them ideal for conservation and wetland restoration projects. Hummocks provide elevated, stable ground that supports unique plant and animal communities, beneficial in flood-prone areas. Selecting between marshes and hummocks depends on ecological goals, landscape conditions, and specific habitat requirements.
Marsh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com