Riparian zones are critical ecological areas along rivers and streams that support diverse plant and animal life. Proper management of these areas helps prevent erosion, improve water quality, and maintain habitat connectivity. Discover how protecting your local riparian zones can benefit the environment and community in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
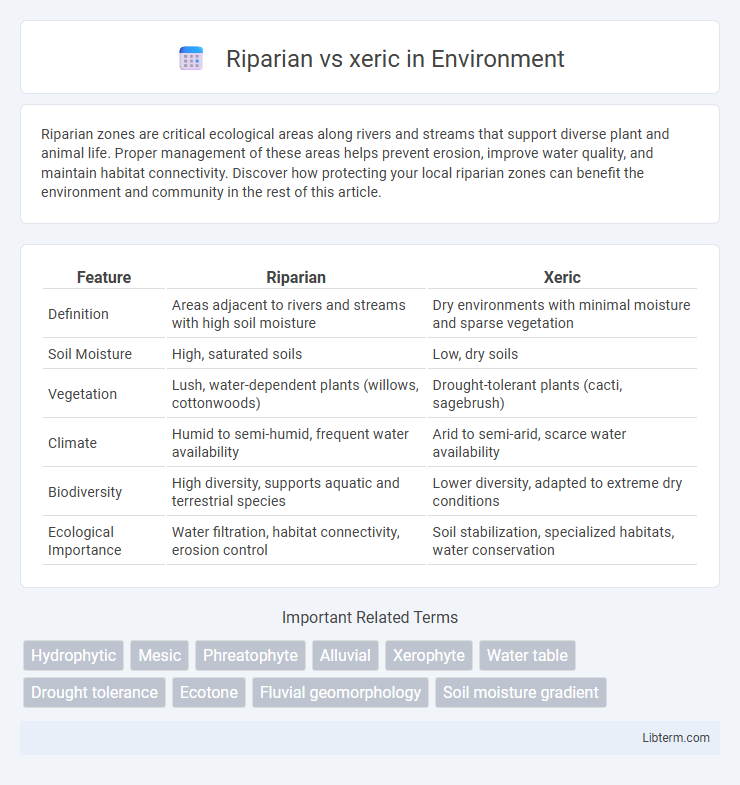
| Feature | Riparian | Xeric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Areas adjacent to rivers and streams with high soil moisture | Dry environments with minimal moisture and sparse vegetation |
| Soil Moisture | High, saturated soils | Low, dry soils |
| Vegetation | Lush, water-dependent plants (willows, cottonwoods) | Drought-tolerant plants (cacti, sagebrush) |
| Climate | Humid to semi-humid, frequent water availability | Arid to semi-arid, scarce water availability |
| Biodiversity | High diversity, supports aquatic and terrestrial species | Lower diversity, adapted to extreme dry conditions |
| Ecological Importance | Water filtration, habitat connectivity, erosion control | Soil stabilization, specialized habitats, water conservation |
Understanding Riparian and Xeric Ecosystems
Riparian ecosystems are characterized by their proximity to water bodies, supporting lush vegetation and diverse wildlife adapted to moist, fertile soils. Xeric ecosystems thrive in arid conditions with sparse precipitation, featuring drought-resistant plants like cacti and shrubs adapted to nutrient-poor soils. Understanding the distinct hydrology, soil composition, and flora of these ecosystems is crucial for effective environmental management and conservation efforts.
Key Differences Between Riparian and Xeric Habitats
Riparian habitats are characterized by their proximity to water sources, supporting lush vegetation and high biodiversity due to consistent moisture availability. Xeric habitats, in contrast, are defined by arid conditions with sparse vegetation adapted to water scarcity and extreme temperature fluctuations. Key differences between riparian and xeric environments include soil moisture levels, plant species diversity, and ecosystem productivity.
Climate and Water Availability
Riparian environments thrive in areas with abundant water availability, typically along riverbanks and floodplains where the climate supports consistent moisture levels. Xeric habitats, in contrast, are characterized by arid or semi-arid climates with limited water resources, resulting in drought-tolerant vegetation adapted to sporadic precipitation. These contrasting climate and water conditions directly influence the biodiversity and soil moisture gradients within riparian and xeric ecosystems.
Soil Composition and Nutrient Levels
Riparian soils typically exhibit higher organic matter content and moisture retention due to proximity to water sources, fostering enriched nutrient levels such as nitrogen and phosphorus essential for lush vegetation. Xeric soils are characterized by low organic material, coarse texture, and limited water retention, resulting in reduced nutrient availability and often higher mineral concentrations like calcium and magnesium. These contrasting soil compositions directly influence plant communities, with riparian zones supporting nutrient-demanding species while xeric environments favor drought-tolerant flora adapted to nutrient-poor conditions.
Plant Adaptations in Riparian vs. Xeric Zones
Plants in riparian zones exhibit adaptations such as broad leaves, extensive root systems for water absorption, and tolerance to periodic flooding, thriving in moist, nutrient-rich soils. Xeric zone plants have evolved drought-resistant features like thick cuticles, reduced leaf surface area, deep or widespread roots, and CAM photosynthesis to minimize water loss in arid conditions. These contrasting adaptations enable vegetation to optimize survival and growth in either water-abundant riparian environments or water-scarce xeric landscapes.
Wildlife Diversity and Habitats
Riparian habitats, characterized by abundant water availability, support high wildlife diversity, including amphibians, birds, and aquatic mammals, due to lush vegetation and stable microclimates. Xeric environments, defined by arid conditions and sparse vegetation, host specialized wildlife adapted to extreme temperatures and limited water, such as reptiles, small mammals, and drought-resistant plants. The contrast between riparian and xeric ecosystems highlights the influence of water availability on habitat complexity and species richness.
Ecological Functions and Benefits
Riparian ecosystems provide critical ecological functions such as water filtration, habitat connectivity, and flood mitigation, supporting diverse plant and animal species. Xeric environments excel in water conservation, soil stabilization, and resilience to drought, fostering specialized flora and fauna adapted to arid conditions. Together, riparian and xeric habitats contribute to landscape biodiversity, hydrological balance, and climate regulation.
Human Impacts on Riparian and Xeric Areas
Human impacts on riparian areas include water pollution, altered hydrology due to damming and water extraction, and habitat fragmentation, which degrade biodiversity and ecosystem services. Xeric environments face challenges like overgrazing, land development, and groundwater depletion, leading to soil erosion and loss of native plant species. Both ecosystems suffer from invasive species introduction and climate change effects, intensifying stress on their natural resilience.
Conservation Challenges and Strategies
Riparian ecosystems face conservation challenges such as water pollution, habitat fragmentation, and invasive species, requiring strategies like buffer zone restoration, controlled water management, and native vegetation replanting to maintain biodiversity. Xeric environments struggle with soil degradation, limited water availability, and increased wildfire risk, necessitating approaches including drought-resistant plant cultivation, erosion control techniques, and fire management protocols. Both ecosystems benefit from integrated land-use planning and community engagement to ensure sustainable conservation outcomes.
Choosing Between Riparian and Xeric Landscaping
Choosing between riparian and xeric landscaping hinges on understanding water availability and native plant adaptability; riparian landscapes thrive in moist, well-watered environments with species like willows and cottonwoods, while xeric landscapes are designed for arid conditions using drought-tolerant plants such as succulents and sagebrush. Riparian landscapes support biodiversity by preserving natural waterways and reducing erosion, making them ideal for properties near rivers or wetlands. Xeric landscaping conserves water and lowers maintenance costs, suitable for drought-prone regions seeking sustainable and energy-efficient garden solutions.
Riparian Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com