A hyetograph visually represents the distribution of rainfall intensity over time, essential for understanding storm patterns and designing effective drainage systems. The mass curve, derived from the hyetograph, illustrates the cumulative rainfall volume, enabling accurate flood forecasting and water resource management. Explore the article to learn how these tools can enhance your hydrological analysis and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
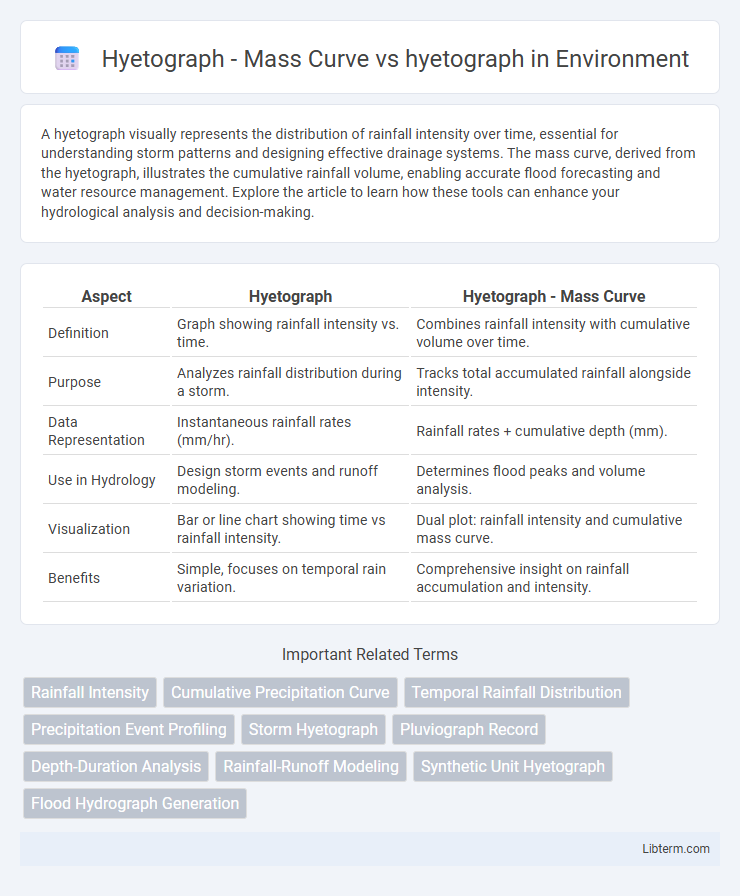
| Aspect | Hyetograph | Hyetograph - Mass Curve |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Graph showing rainfall intensity vs. time. | Combines rainfall intensity with cumulative volume over time. |
| Purpose | Analyzes rainfall distribution during a storm. | Tracks total accumulated rainfall alongside intensity. |
| Data Representation | Instantaneous rainfall rates (mm/hr). | Rainfall rates + cumulative depth (mm). |
| Use in Hydrology | Design storm events and runoff modeling. | Determines flood peaks and volume analysis. |
| Visualization | Bar or line chart showing time vs rainfall intensity. | Dual plot: rainfall intensity and cumulative mass curve. |
| Benefits | Simple, focuses on temporal rain variation. | Comprehensive insight on rainfall accumulation and intensity. |
Introduction to Hyetographs
A hyetograph graphically represents rainfall intensity over time, crucial for hydrological analysis and stormwater management. Compared to the mass curve, which shows cumulative rainfall volume, the hyetograph highlights variations in rainfall intensity and temporal distribution. This distinction enables more accurate flood forecasting and design of drainage systems by capturing the dynamics of rainfall events.
Understanding the Mass Curve
Understanding the mass curve involves analyzing the cumulative rainfall over time, which provides a clearer representation of total precipitation compared to the hyetograph's instantaneous rainfall intensity. The mass curve highlights the accumulation pattern, enabling better assessment of rainfall volume and its temporal distribution essential for hydrological modeling and flood forecasting. Unlike the hyetograph's variable intensity bars, the mass curve's continuous upward trend illustrates the progressive increase in rainfall, facilitating more accurate water resource management and drainage design.
Key Differences Between Mass Curve and Hyetograph
A hyetograph represents the variation of rainfall intensity over time, typically plotting rainfall rate against time intervals during a storm event. In contrast, a mass curve is a cumulative representation that shows total rainfall accumulation over time, providing insights into the volume and distribution of rainfall. Key differences include the hyetograph's focus on temporal intensity patterns, while the mass curve emphasizes cumulative depth, making each tool essential for distinct hydrological analyses.
Applications of Hyetographs in Hydrology
Hyetographs graphically represent rainfall intensity over time, enabling precise analysis of storm patterns critical for hydrological modeling. Mass curves accumulate total rainfall volume, facilitating runoff estimation and flood forecasting by correlating rainfall inputs with catchment response. Applications of hyetographs in hydrology include designing urban drainage systems, predicting soil erosion, and optimizing reservoir management to mitigate flood risks effectively.
Applications of Mass Curves in Rainfall Analysis
Mass curves in rainfall analysis offer a graphical representation of cumulative precipitation over time, aiding in identifying rainfall intensity and distribution patterns critical for hydrological modeling. Compared to hyetographs, which depict rainfall intensity at discrete time intervals, mass curves effectively highlight total rainfall accumulation and are essential in flood forecasting, watershed management, and reservoir design. Their application enhances understanding of storm duration, peak rainfall periods, and runoff potential, optimizing water resource planning and disaster mitigation strategies.
Data Requirements for Hyetograph and Mass Curve Construction
Hyetograph and mass curve construction require precise temporal rainfall intensity data and cumulative precipitation totals, respectively, to accurately represent rainfall distribution and volume over time. Hyetographs rely on fine-resolution time series data from rain gauges or radar to capture variations in rainfall intensity for hydrological modeling. Mass curves demand aggregated rainfall data to track cumulative precipitation, essential for assessing watershed response and runoff estimation.
Advantages of Using Hyetographs
Hyetographs provide a detailed representation of rainfall intensity over time, enabling precise analysis of storm patterns and runoff prediction. Using hyetographs allows engineers to design more efficient stormwater management systems by accurately capturing temporal distribution of precipitation. This temporal resolution enhances flood forecasting accuracy and improves the assessment of watershed response compared to mass curves.
Advantages of Using Mass Curves
Mass curves offer distinct advantages over traditional hyetographs by clearly illustrating cumulative rainfall over time, enabling better visualization of total precipitation depth. This cumulative representation aids in flood forecasting and reservoir design by highlighting trends in runoff accumulation and water balance. The straightforward interpretation of mass curves enhances hydrological analysis and decision-making processes compared to the granular intensity-focused view of hyetographs.
Choosing Between Mass Curves and Hyetographs
Mass curves provide a cumulative representation of precipitation over time, ideal for analyzing total rainfall volume and runoff potential in hydrological studies. Hyetographs illustrate rainfall intensity and distribution within specific time intervals, essential for designing drainage systems and flood forecasting. Selecting between mass curves and hyetographs depends on whether the focus is on cumulative rainfall accumulation or temporal intensity variation in a storm event.
Conclusion: Mass Curve vs Hyetograph in Rainfall Studies
Mass curves provide a cumulative representation of rainfall volume over time, enabling the assessment of total precipitation and runoff potential, while hyetographs offer detailed temporal distribution of rainfall intensity. Comparing mass curves with hyetographs allows hydrologists to understand both the magnitude and temporal patterns of rainfall events, essential for effective flood forecasting and water resource management. The integration of mass curve analysis with hyetograph data enhances the precision of rainfall study interpretations and improves stormwater infrastructure design strategies.
Hyetograph - Mass Curve Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com