Aluminum pans are prized for their exceptional heat conductivity and lightweight design, making them an ideal choice for efficient cooking. Their durability and resistance to rust ensure long-lasting performance in your kitchen. Discover the key benefits and tips for choosing the perfect aluminum pan by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
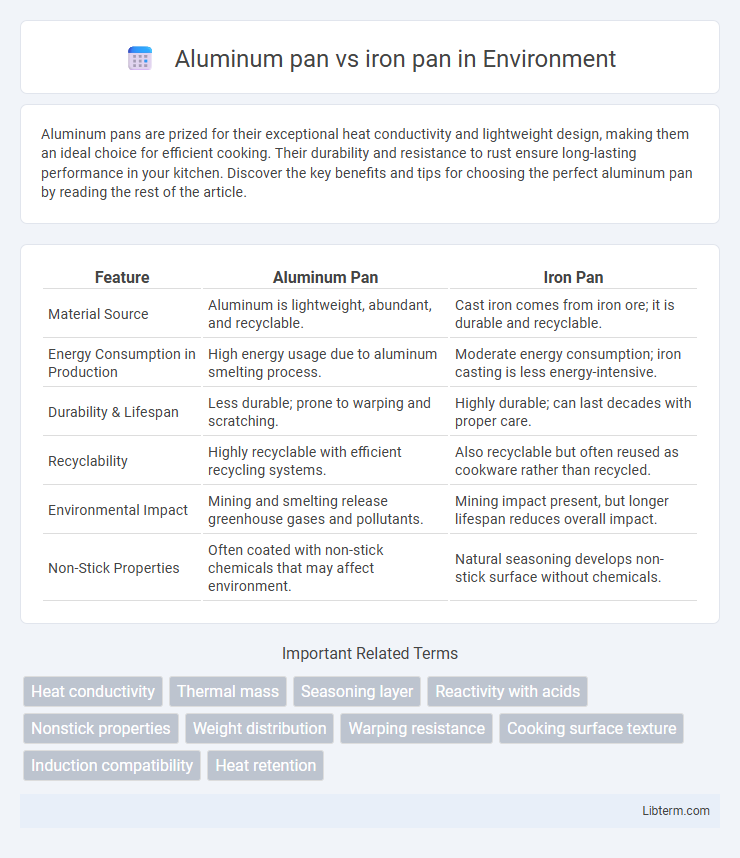
| Feature | Aluminum Pan | Iron Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Aluminum is lightweight, abundant, and recyclable. | Cast iron comes from iron ore; it is durable and recyclable. |
| Energy Consumption in Production | High energy usage due to aluminum smelting process. | Moderate energy consumption; iron casting is less energy-intensive. |
| Durability & Lifespan | Less durable; prone to warping and scratching. | Highly durable; can last decades with proper care. |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable with efficient recycling systems. | Also recyclable but often reused as cookware rather than recycled. |
| Environmental Impact | Mining and smelting release greenhouse gases and pollutants. | Mining impact present, but longer lifespan reduces overall impact. |
| Non-Stick Properties | Often coated with non-stick chemicals that may affect environment. | Natural seasoning develops non-stick surface without chemicals. |
Introduction to Aluminum and Iron Pans
Aluminum pans are lightweight, excellent heat conductors, and resistant to rust, making them ideal for quick and even cooking. Iron pans, including cast iron, offer superior heat retention and durability but require seasoning to maintain a non-stick surface and prevent rusting. Choosing between aluminum and iron depends on cooking needs, with aluminum favored for ease and speed, while iron excels in heat stability and longevity.
Material Composition: Aluminum vs Iron
Aluminum pans are made from lightweight, corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy, providing excellent heat conductivity that ensures even cooking and quick temperature adjustments. In contrast, iron pans, typically cast iron, are heavy and composed of dense iron with high thermal retention, allowing sustained heat and durability but slower response to temperature changes. The distinct material compositions impact factors such as weight, heating performance, and maintenance requirements, making aluminum ideal for everyday use and iron preferred for high-heat searing and long-lasting cookware.
Heat Conductivity and Distribution
Aluminum pans offer superior heat conductivity, allowing them to heat up quickly and distribute heat evenly across the cooking surface, making them ideal for precise temperature control. Iron pans, while slower to heat, retain heat exceptionally well, providing consistent cooking temperatures and excellent heat distribution once fully heated. Choosing between aluminum and iron pans depends on whether rapid heat responsiveness or heat retention is more critical for your cooking needs.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Iron pans exhibit superior durability and longevity due to their dense, sturdy structure that withstands high heat and resists warping or cracking over time. Aluminum pans, while lightweight and efficient at heat conduction, are more prone to dents, scratches, and corrosion, reducing their lifespan notably under frequent use. Seasoned cast iron pans can last for generations, whereas aluminum cookware often requires replacement within a few years when subjected to regular wear and tear.
Weight and Handling Differences
Aluminum pans are significantly lighter than iron pans, making them easier to handle and ideal for quick cooking tasks or frequent stirring. Iron pans, while heavier, provide superior heat retention and stability, which benefits slow cooking and searing. The lightweight nature of aluminum enhances maneuverability, but iron's weight offers greater control during cooking processes.
Cooking Performance and Food Flavor
Aluminum pans heat up quickly and provide even heat distribution, making them ideal for cooking delicate foods that require precise temperature control. Cast iron pans retain heat longer and create a natural non-stick surface, which enhances browning and adds a rich, seared flavor to dishes. The choice between aluminum and cast iron significantly impacts cooking performance and the depth of food flavor, with aluminum offering speed and evenness and iron delivering enhanced taste and texture.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Aluminum pans require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to prevent surface scratches and often benefit from hand washing to maintain their lightweight and non-stick properties. Iron pans demand regular seasoning with oil to develop a natural non-stick layer and should be dried immediately after washing to prevent rust. Both materials need careful maintenance, but iron pans typically require more consistent and thorough upkeep to ensure longevity and performance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Aluminum pans may release trace amounts of aluminum into food, especially when cooking acidic dishes, raising concerns about potential health risks linked to aluminum exposure. Iron pans, particularly cast iron, can contribute to dietary iron intake, which is beneficial for many but could pose risks for individuals with iron overload conditions. Both pans require proper seasoning and maintenance to prevent rust or degradation, impacting food safety and longevity.
Price and Value for Money
Aluminum pans typically offer lower initial costs, making them an affordable choice for budget-conscious buyers, but they may wear out faster, reducing long-term value. Iron pans, while more expensive upfront, provide superior durability and heat retention, offering greater value for money over time through longevity and improved cooking performance. Investing in cast iron or carbon steel pans often results in cost savings and enhanced culinary results, outweighing the higher initial price compared to aluminum options.
Best Uses: Which Pan for Which Cooking Task
Aluminum pans excel at quick, even heat distribution, making them ideal for sauteing vegetables and cooking delicate foods like eggs or fish. Iron pans retain heat longer and provide superior searing for meats and high-heat frying, perfect for tasks like browning steaks or frying chicken. Choosing between aluminum and iron pans depends on cooking requirements: aluminum for rapid, precise temperature control and iron for heavy-duty, high-heat cooking with excellent heat retention.
Aluminum pan Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com